Interdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge and methods from different fields to solve complex problems more effectively. This fusion fosters innovation and offers comprehensive insights that single-discipline perspectives might miss. Explore the rest of the article to see how interdisciplinary strategies can transform Your work and thinking.
Table of Comparison
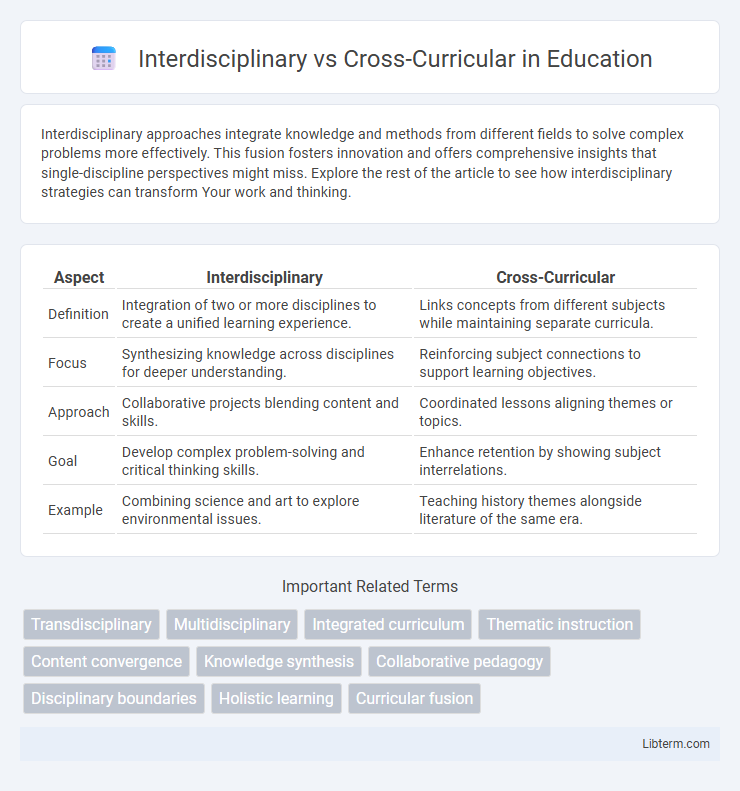
| Aspect | Interdisciplinary | Cross-Curricular |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of two or more disciplines to create a unified learning experience. | Links concepts from different subjects while maintaining separate curricula. |
| Focus | Synthesizing knowledge across disciplines for deeper understanding. | Reinforcing subject connections to support learning objectives. |
| Approach | Collaborative projects blending content and skills. | Coordinated lessons aligning themes or topics. |
| Goal | Develop complex problem-solving and critical thinking skills. | Enhance retention by showing subject interrelations. |
| Example | Combining science and art to explore environmental issues. | Teaching history themes alongside literature of the same era. |
Defining Interdisciplinary Approaches
Interdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge and methods from multiple disciplines to create a synthesized understanding of complex topics, fostering collaboration and innovation. Unlike cross-curricular methods that link subjects around a common theme, interdisciplinary strategies dissolve traditional boundaries to develop new frameworks and solutions. This approach enhances critical thinking by encouraging students to analyze problems through diverse academic lenses and develop comprehensive problem-solving skills.
Understanding Cross-Curricular Teaching
Cross-curricular teaching integrates content and skills across different subject areas, fostering connections that enhance student understanding and application of knowledge in real-world contexts. It emphasizes collaborative planning and instruction, enabling students to make meaningful links between disciplines rather than learning each subject in isolation. This approach supports holistic development by encouraging critical thinking, problem-solving, and the transfer of skills across multiple domains.
Key Differences Between Interdisciplinary and Cross-Curricular Methods
Interdisciplinary methods integrate concepts and skills from multiple disciplines to address complex problems, fostering a holistic understanding beyond traditional subject boundaries. Cross-curricular approaches coordinate content from different subjects, maintaining distinct disciplinary frameworks while enhancing connections and relevance for students. The key difference lies in interdisciplinarity's synthesis of knowledge versus cross-curricular's alignment and simultaneous teaching across disciplines.
Educational Benefits of Interdisciplinary Learning
Interdisciplinary learning integrates multiple subject areas to create a cohesive educational experience, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging students to make connections across disciplines. It fosters deeper understanding and retention of knowledge through real-world applications and collaborative projects that mirror complex, multifaceted challenges. This approach promotes creativity, adaptability, and the ability to synthesize diverse perspectives, preparing students for dynamic careers and lifelong learning.
Advantages of Cross-Curricular Integration
Cross-curricular integration enhances student engagement by connecting concepts across multiple subjects, fostering deeper understanding and real-world application. It promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging learners to view challenges through diverse disciplinary lenses. This approach also supports curriculum coherence, improving retention and making learning more relevant and meaningful.
Curriculum Planning: Interdisciplinary vs Cross-Curricular
Interdisciplinary curriculum planning integrates concepts and skills from multiple disciplines to create cohesive learning experiences that mirror real-world applications. Cross-curricular planning connects content from different subjects, emphasizing the reinforcement of knowledge through thematic links without fully merging the disciplines. Effective curriculum design balances interdisciplinary depth with cross-curricular breadth to enhance student engagement and comprehension.
Assessment Strategies for Both Approaches
Assessment strategies in interdisciplinary approaches emphasize integrated evaluations that measure students' ability to synthesize knowledge across multiple disciplines, often through project-based assessments and thematic portfolios. Cross-curricular assessment focuses on evaluating specific skills and content mastery within individual subjects while highlighting connections between them, using targeted quizzes, standardized tests, and rubrics that reflect interdisciplinary skills. Both approaches benefit from formative assessments that encourage critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of concepts beyond traditional subject boundaries.
Teacher Collaboration in Integrated Learning
Teacher collaboration in interdisciplinary learning involves blending subjects to create unified lessons, fostering deeper connections and critical thinking by integrating knowledge from multiple disciplines. Cross-curricular collaboration, however, aligns distinct subject areas around common themes or skills while maintaining disciplinary boundaries, enhancing student engagement through relevant, real-world applications. Effective integrated learning depends on teachers co-planning, sharing expertise, and coordinating assessment strategies to enrich curriculum coherence and student outcomes.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementation
Interdisciplinary and cross-curricular approaches face challenges such as aligning diverse subject standards, managing collaborative planning time, and addressing varying teacher expertise. Solutions include establishing clear communication channels, providing professional development focused on integrated lesson design, and utilizing shared assessment frameworks to ensure coherence. Effective implementation hinges on administrative support, flexible scheduling, and leveraging technology to facilitate resource sharing and ongoing collaboration among educators.
Choosing the Right Approach for Student Success
Interdisciplinary learning integrates multiple subjects to solve complex problems, fostering critical thinking and real-world application, while cross-curricular approaches link related content across disciplines to reinforce core skills and concepts. Selecting the appropriate method depends on educational goals: interdisciplinary frameworks suit projects requiring deep synthesis, whereas cross-curricular strategies enhance understanding through thematic connections. Educators should align their choice with curriculum standards, student needs, and assessment criteria to maximize engagement and academic achievement.
Interdisciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com