Flipped Classroom transforms traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online, allowing students to learn at their own pace outside the classroom. This approach fosters active learning and maximizes in-class time for hands-on activities, discussions, and personalized support. Discover how flipping your classroom can enhance engagement and improve learning outcomes in the full article.
Table of Comparison
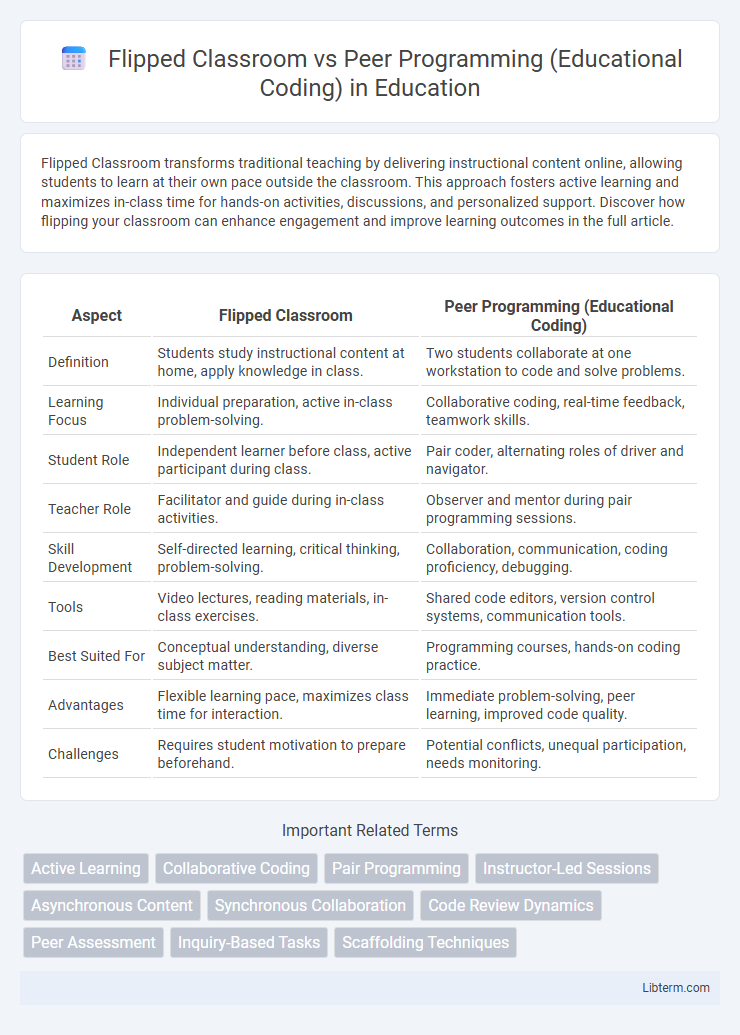
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Peer Programming (Educational Coding) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students study instructional content at home, apply knowledge in class. | Two students collaborate at one workstation to code and solve problems. |
| Learning Focus | Individual preparation, active in-class problem-solving. | Collaborative coding, real-time feedback, teamwork skills. |
| Student Role | Independent learner before class, active participant during class. | Pair coder, alternating roles of driver and navigator. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and guide during in-class activities. | Observer and mentor during pair programming sessions. |
| Skill Development | Self-directed learning, critical thinking, problem-solving. | Collaboration, communication, coding proficiency, debugging. |
| Tools | Video lectures, reading materials, in-class exercises. | Shared code editors, version control systems, communication tools. |
| Best Suited For | Conceptual understanding, diverse subject matter. | Programming courses, hands-on coding practice. |
| Advantages | Flexible learning pace, maximizes class time for interaction. | Immediate problem-solving, peer learning, improved code quality. |
| Challenges | Requires student motivation to prepare beforehand. | Potential conflicts, unequal participation, needs monitoring. |
Introduction to Flipped Classroom and Peer Programming
Flipped Classroom reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class, allowing in-person sessions to focus on interactive coding activities and problem-solving. Peer Programming emphasizes collaborative learning through two students jointly writing and reviewing code, fostering real-time feedback and deeper understanding. Both methods enhance coding education by promoting active engagement and practical experience over passive lecture consumption.
Core Principles of Flipped Classroom
The flipped classroom model centers on pre-class content delivery through videos and readings, enabling students to engage actively in problem-solving and collaboration during in-person sessions. This approach prioritizes student-centered learning by shifting direct instruction outside the classroom, fostering deeper understanding and application of coding concepts. In contrast to peer programming, which emphasizes real-time code collaboration, the flipped classroom focuses on maximizing classroom interaction and personalized feedback.
Key Elements of Peer Programming in Coding Education
Peer programming in coding education emphasizes real-time collaboration, where two students alternate roles as driver and navigator to enhance problem-solving skills and code quality. Essential elements include continuous communication, immediate feedback, and shared responsibility for coding tasks, fostering teamwork and active learning. This approach boosts comprehension and retention by enabling learners to articulate their thought processes and tackle coding challenges collectively.
Benefits of Flipped Classroom for Coding Students
Flipped Classroom enhances coding students' learning by providing flexible access to instructional videos and materials, allowing learners to study concepts at their own pace before practical sessions. This approach increases active engagement during coding labs and promotes deeper understanding through hands-on problem-solving and collaborative discussions. The model supports differentiated learning styles and improves retention, leading to higher coding proficiency and confidence among students.
Advantages of Peer Programming in Learning Coding
Peer programming enhances coding education by fostering real-time collaboration, which improves problem-solving skills and code quality through continuous feedback. It cultivates communication and teamwork abilities, essential for professional software development environments. This method also accelerates learning by allowing students to learn from each other's perspectives and debugging techniques.
Challenges Faced in Flipped Classroom Models
Flipped Classroom models often face challenges such as students' varying levels of self-motivation and time management, leading to inconsistent engagement with pre-class materials. Technical issues and lack of access to reliable internet or devices can hinder students' ability to prepare effectively for in-class coding activities. Furthermore, educators may struggle with balancing the design of meaningful pre-class content and interactive, collaborative coding sessions to maximize learning outcomes.
Common Obstacles in Peer Programming Approaches
Common obstacles in peer programming approaches include coordination challenges where mismatched skill levels create imbalances, hindering effective collaboration. Communication barriers often arise, leading to misunderstandings and reduced code quality. Time management issues also affect productivity as synchronized schedules are difficult to maintain, impacting the overall learning experience.
Comparing Student Engagement: Flipped vs Peer Programming
Flipped Classroom enhances student engagement by allowing learners to absorb coding concepts independently before class, promoting active participation during in-person sessions where they apply knowledge through problem-solving. Peer Programming increases engagement through collaboration, requiring students to communicate, share ideas, and troubleshoot code in real time, fostering deeper understanding and immediate feedback. Studies show Peer Programming often results in higher sustained engagement due to constant interaction, while Flipped Classroom supports individual accountability and prepares students for collaborative tasks.
Impact on Coding Skill Development: A Comparative Analysis
Flipped Classroom enhances coding skills by allowing students to engage with instructional content independently, fostering a deeper understanding through self-paced learning and in-class problem-solving. Peer Programming promotes collaborative coding, improving debugging abilities, code quality, and communication skills by pairing learners to write and review code together. Comparative analysis shows Peer Programming offers stronger gains in teamwork and real-time coding proficiency, while Flipped Classroom excels in conceptual knowledge retention and individual coding autonomy.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right approach between Flipped Classroom and Peer Programming in educational coding depends on factors such as student learning styles, class size, and available technology resources. Flipped Classroom is ideal for self-motivated learners who benefit from pre-class content review, while Peer Programming promotes collaboration and immediate feedback in coding tasks. Educators should evaluate curriculum goals, student engagement levels, and assessment methods to determine the most effective teaching strategy for their coding courses.
Flipped Classroom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com