Direct instruction is a structured teaching method that involves clear, explicit teaching of specific skills or concepts through step-by-step demonstrations and guided practice. This approach emphasizes teacher-led activities to ensure students master foundational knowledge efficiently and confidently. Discover how integrating direct instruction can transform your teaching strategies by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
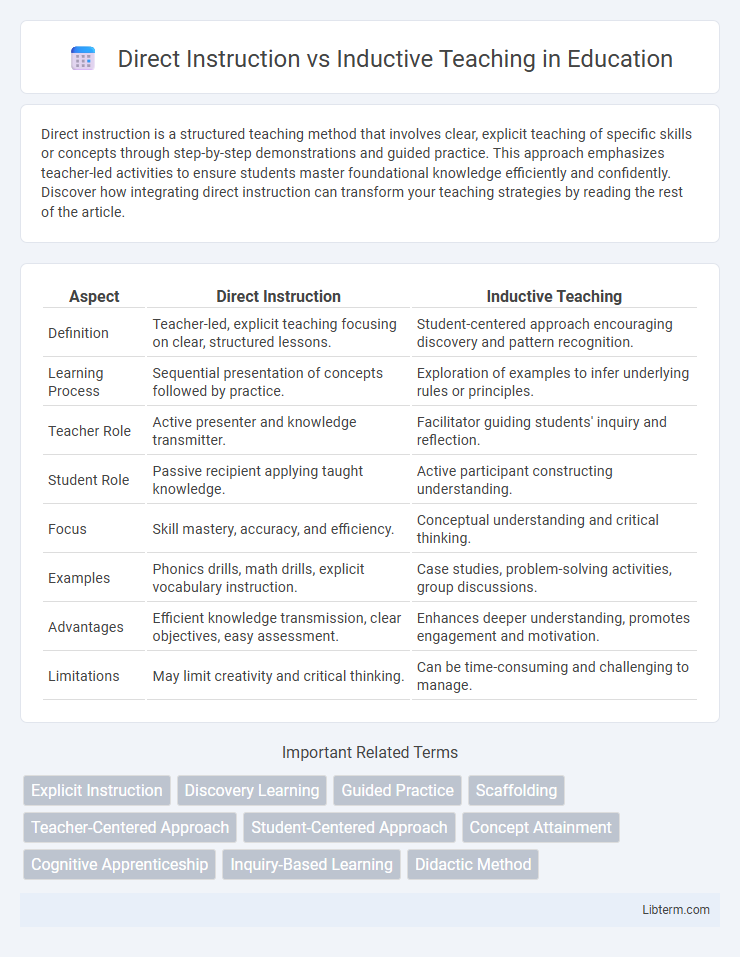
| Aspect | Direct Instruction | Inductive Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teacher-led, explicit teaching focusing on clear, structured lessons. | Student-centered approach encouraging discovery and pattern recognition. |
| Learning Process | Sequential presentation of concepts followed by practice. | Exploration of examples to infer underlying rules or principles. |
| Teacher Role | Active presenter and knowledge transmitter. | Facilitator guiding students' inquiry and reflection. |
| Student Role | Passive recipient applying taught knowledge. | Active participant constructing understanding. |
| Focus | Skill mastery, accuracy, and efficiency. | Conceptual understanding and critical thinking. |
| Examples | Phonics drills, math drills, explicit vocabulary instruction. | Case studies, problem-solving activities, group discussions. |
| Advantages | Efficient knowledge transmission, clear objectives, easy assessment. | Enhances deeper understanding, promotes engagement and motivation. |
| Limitations | May limit creativity and critical thinking. | Can be time-consuming and challenging to manage. |
Understanding Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction emphasizes a highly structured, teacher-led approach that delivers clear, explicit teaching of concepts and skills, often through step-by-step guidance and immediate feedback. It is designed to maximize efficiency in learning by reducing ambiguity, ensuring students understand the material before moving on. Research indicates that Direct Instruction improves student outcomes significantly in foundational areas such as reading, math, and science by fostering precise comprehension and mastery of content.
Exploring Inductive Teaching
Inductive teaching emphasizes student-centered learning by encouraging learners to observe patterns, formulate hypotheses, and derive general principles through active exploration and problem-solving. This approach fosters critical thinking, deeper understanding, and long-term retention by engaging students in discovering concepts rather than passively receiving information. Research highlights that inductive strategies enhance motivation and adaptability, especially in complex or open-ended subjects, making them effective for developing higher-order cognitive skills.
Key Principles of Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction emphasizes clear, explicit teaching with structured lessons and scripted materials to ensure consistent delivery of content. It relies on frequent assessment and immediate corrective feedback to reinforce learning and maintain student engagement. The key principles involve systematic skill-building, precise teacher modeling, and guided practice before independent application.
Core Features of Inductive Teaching
Inductive teaching emphasizes student-centered learning by encouraging exploration, pattern recognition, and hypothesis formation to derive principles independently. Core features include presenting specific examples before general concepts, promoting active engagement, and fostering critical thinking to build deeper understanding. This approach contrasts with direct instruction's explicit teaching of rules and procedures, aiming to develop learners' analytical and problem-solving skills through discovery.
Advantages of Direct Instruction
Direct Instruction offers clear, structured lessons that enhance student comprehension and retention by providing explicit guidance. It reduces cognitive load, allowing learners to focus on mastering specific skills or knowledge efficiently. This method is particularly advantageous for novices or students requiring additional support, as it ensures consistent, measurable outcomes through systematic instruction.
Benefits of Inductive Approaches
Inductive teaching promotes deeper conceptual understanding by encouraging students to discover patterns and principles through exploration and inquiry. This method enhances critical thinking skills and fosters learner autonomy, resulting in improved long-term retention of knowledge. Research indicates that inductive approaches lead to greater engagement and motivation compared to traditional direct instruction.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Direct Instruction faces challenges such as limited opportunities for student creativity and critical thinking due to its highly structured format, often leading to reduced engagement. Inductive Teaching encounters limitations in inconsistent knowledge acquisition, as students may develop misconceptions without guided support, and it demands significant teacher expertise and time for effective implementation. Both methods require careful adaptation to student needs to balance clarity with active learning.
Comparing Classroom Applications
Direct Instruction emphasizes structured, teacher-led lessons with clear objectives and step-by-step guidance, fostering efficient skill acquisition and minimizing misconceptions. Inductive Teaching relies on student discovery and pattern recognition, encouraging critical thinking and deeper conceptual understanding through exploration and inquiry-based activities. Classroom applications of Direct Instruction suit beginners needing foundational knowledge, while Inductive Teaching excels in advanced settings promoting analytical skills and learner autonomy.
Choosing the Right Approach for Learners
Direct Instruction offers structured guidance and clear objectives, ideal for learners needing explicit support and foundational skill acquisition. Inductive Teaching fosters critical thinking and problem-solving through discovery, benefiting learners who thrive in exploratory and interactive environments. Selecting the right approach depends on learner preferences, content complexity, and desired educational outcomes.
Blending Direct and Inductive Strategies
Blending direct instruction with inductive teaching strategies creates a dynamic learning environment that balances explicit guidance and discovery-based learning. This hybrid approach leverages the clarity and structure of direct instruction while fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills through inductive reasoning. Research shows that combining these methods enhances student engagement, promotes deeper understanding, and improves knowledge retention across diverse subjects.
Direct Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com