An interdisciplinary approach integrates methods and insights from multiple academic fields to address complex problems more effectively. This strategy fosters innovation and comprehensive understanding by bridging gaps between traditional disciplines. Discover how adopting an interdisciplinary framework can transform your research and practice by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
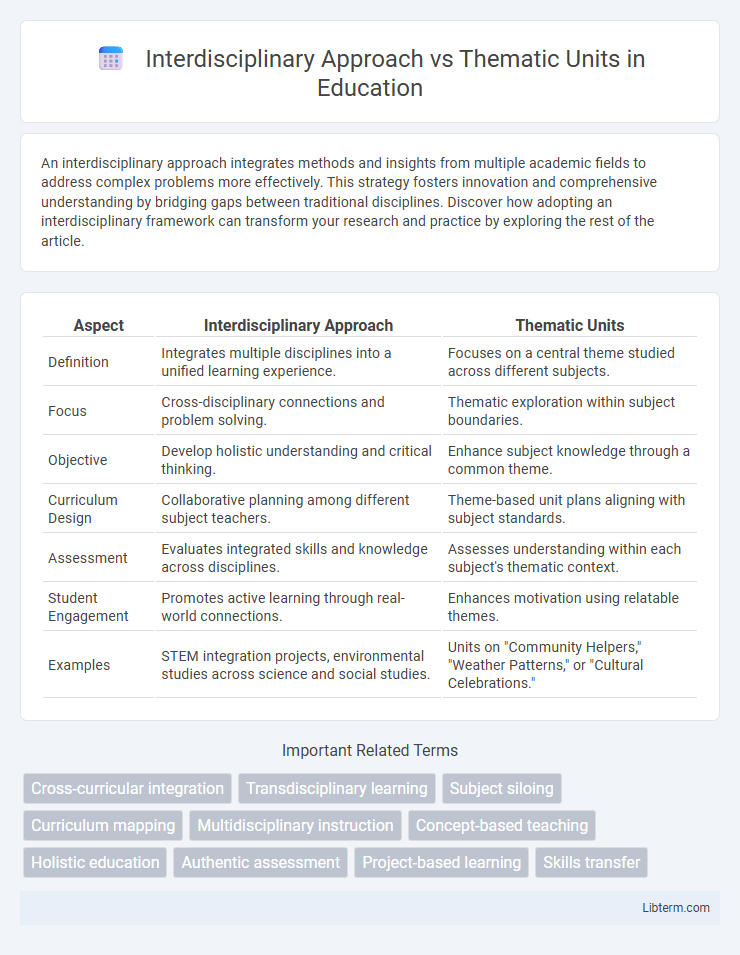
| Aspect | Interdisciplinary Approach | Thematic Units |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrates multiple disciplines into a unified learning experience. | Focuses on a central theme studied across different subjects. |
| Focus | Cross-disciplinary connections and problem solving. | Thematic exploration within subject boundaries. |
| Objective | Develop holistic understanding and critical thinking. | Enhance subject knowledge through a common theme. |
| Curriculum Design | Collaborative planning among different subject teachers. | Theme-based unit plans aligning with subject standards. |
| Assessment | Evaluates integrated skills and knowledge across disciplines. | Assesses understanding within each subject's thematic context. |
| Student Engagement | Promotes active learning through real-world connections. | Enhances motivation using relatable themes. |
| Examples | STEM integration projects, environmental studies across science and social studies. | Units on "Community Helpers," "Weather Patterns," or "Cultural Celebrations." |
Understanding Interdisciplinary Approach: Definition and Purpose
The interdisciplinary approach integrates knowledge and methods from different disciplines to address complex problems and enhance critical thinking skills. Its purpose is to create connections across subject areas, fostering deeper understanding and real-world application. This approach contrasts with thematic units, which organize learning around a central theme but may not require the same level of cross-disciplinary integration.
Thematic Units Explained: Key Concepts and Structures
Thematic units integrate various subjects around a central theme, promoting deeper understanding through connected concepts and real-world applications. Key structures of thematic units include clearly defined objectives, cohesive content strands, and interdisciplinary activities that foster critical thinking and student engagement. This approach enhances curriculum coherence by aligning learning goals across disciplines, enabling students to make meaningful connections between knowledge areas.
Core Differences: Interdisciplinary vs Thematic Units
Interdisciplinary approach integrates multiple subject areas to create a cohesive learning experience that emphasizes connections and real-world applications, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Thematic units organize curriculum around central themes, focusing primarily on content within each subject while linking concepts through a common topic. Core differences lie in the interdisciplinary approach's emphasis on synthesizing knowledge across disciplines versus thematic units' focus on subject-specific content framed within a thematic context.
Benefits of Interdisciplinary Teaching Methods
Interdisciplinary teaching methods enhance critical thinking by integrating knowledge across multiple subjects, promoting deeper understanding and real-world application. This approach fosters collaboration skills and creativity by encouraging students to connect concepts from diverse disciplines, enriching their learning experience. Enhanced engagement and retention result from contextualized learning, making education more meaningful and effective compared to isolated thematic units.
Advantages of Thematic Units in Curriculum Design
Thematic units in curriculum design promote holistic learning by integrating multiple subject areas around a central theme, fostering deeper understanding and retention. This approach enhances student engagement by connecting lessons to real-world contexts and diverse perspectives, supporting critical thinking and creativity. Thematic units also facilitate differentiated instruction, allowing educators to tailor content to varied learning styles and abilities within a cohesive framework.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
The interdisciplinary approach often faces challenges related to integrating diverse subject knowledge and coordinating collaboration among teachers with different expertise, which can lead to inconsistencies in curriculum delivery. Thematic units may be limited by a lack of depth in individual subjects and difficulties in aligning themes with standardized academic standards. Both approaches require careful planning and resource investment to overcome barriers in assessment and ensuring comprehensive coverage of essential skills.
Impact on Student Engagement and Learning Outcomes
Interdisciplinary approach enhances student engagement by integrating multiple subjects, promoting critical thinking, and real-world problem-solving, which leads to deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. Thematic units focus learning around a central theme, fostering contextual connections and relevance, but may limit the breadth of skill application compared to interdisciplinary methods. Research indicates that interdisciplinary strategies produce higher academic achievement and motivation, especially in complex, multifaceted topics.
Implementing Effective Interdisciplinary Strategies
Implementing effective interdisciplinary strategies requires seamless integration of diverse subject areas to enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Educators must design collaborative lesson plans that connect core concepts across disciplines while maintaining clear learning objectives and assessment criteria. Emphasizing real-world applications fosters deeper understanding and student engagement, distinguishing interdisciplinary approaches from thematic units focused primarily on organizing content around a single theme.
Best Practices for Thematic Unit Integration
Effective thematic unit integration involves aligning curriculum content across subjects to create cohesive, meaningful learning experiences that reflect real-world contexts. Best practices emphasize collaborative planning among educators to ensure consistency in vocabulary, concepts, and skills, enhancing student engagement and retention. Utilizing interdisciplinary connections strategically within thematic units promotes critical thinking and deeper understanding by linking themes to diverse disciplines.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right teaching approach depends on curriculum goals, student needs, and subject integration levels. The interdisciplinary approach fosters connections across disciplines, enhancing critical thinking and real-world problem solving, while thematic units provide in-depth exploration of specific topics within a structured framework. Educators should evaluate resources, assessment methods, and collaboration opportunities to determine which method maximizes engagement and learning outcomes.
Interdisciplinary Approach Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com