Ungrading challenges traditional assessment by removing numerical or letter grades to focus on deeper learning and critical thinking. This approach emphasizes feedback and personal growth, fostering intrinsic motivation rather than external rewards. Explore the rest of the article to discover how ungrading can transform your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
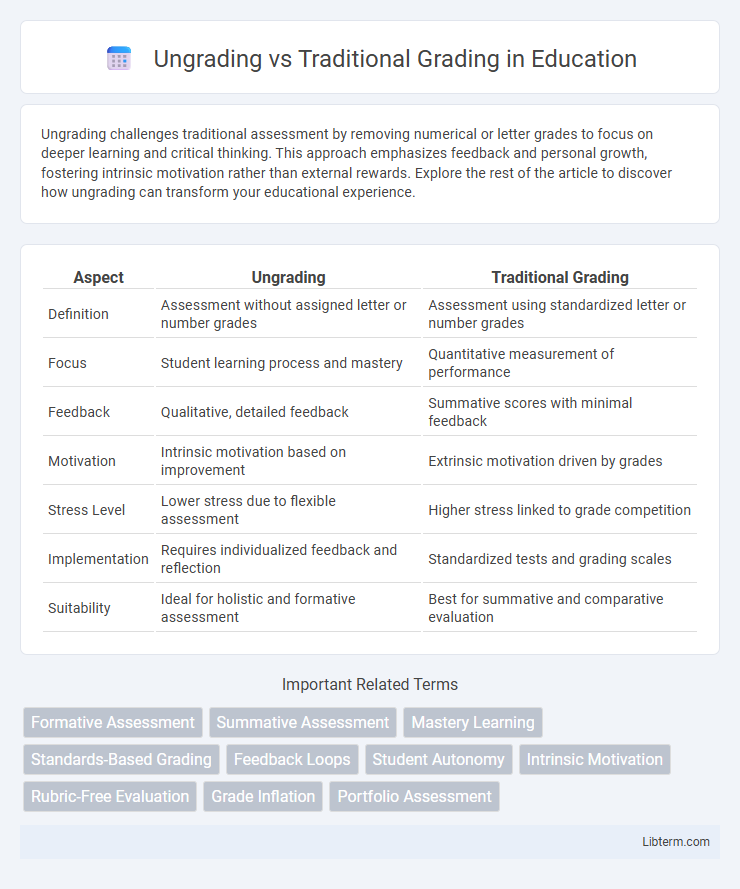
| Aspect | Ungrading | Traditional Grading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessment without assigned letter or number grades | Assessment using standardized letter or number grades |
| Focus | Student learning process and mastery | Quantitative measurement of performance |
| Feedback | Qualitative, detailed feedback | Summative scores with minimal feedback |
| Motivation | Intrinsic motivation based on improvement | Extrinsic motivation driven by grades |
| Stress Level | Lower stress due to flexible assessment | Higher stress linked to grade competition |
| Implementation | Requires individualized feedback and reflection | Standardized tests and grading scales |
| Suitability | Ideal for holistic and formative assessment | Best for summative and comparative evaluation |
Understanding Ungrading: A Modern Approach
Ungrading emphasizes ongoing feedback and self-assessment rather than relying on numerical or letter grades, promoting deeper learning and intrinsic motivation. This approach fosters a growth mindset by encouraging students to focus on mastery and improvement instead of comparison or performance anxiety. Educators implementing ungrading observe increased engagement and critical thinking as students take active roles in their learning progress.
What Is Traditional Grading?
Traditional grading is a standardized evaluation system that assigns letter grades or numerical scores based on student performance, often emphasizing exams, quizzes, and homework completion. This method relies on summative assessments to measure knowledge retention and compares student achievement against preset benchmarks or class averages. Critics argue that traditional grading may prioritize rote memorization and competition over deep learning and skill development.
Key Differences Between Ungrading and Traditional Grading
Ungrading emphasizes qualitative feedback over numerical scores, fostering intrinsic motivation and deeper learning, while traditional grading relies on quantitative assessments that often prioritize performance over understanding. In ungrading, students engage in self-assessment and reflection, encouraging ownership of their learning process, whereas traditional grading typically uses standardized tests and assignments graded by instructors. This shift from summative evaluation to formative feedback in ungrading supports personalized learning trajectories, contrasting with the fixed, comparative nature of traditional grading systems.
Benefits of Ungrading for Student Learning
Ungrading fosters intrinsic motivation by encouraging students to focus on mastering content rather than earning grades, leading to deeper engagement and improved critical thinking skills. It reduces anxiety and stress associated with high-stakes assessments, creating a supportive learning environment that promotes creativity and risk-taking. By emphasizing formative feedback over numeric scores, ungrading enhances personalized learning and helps students develop self-assessment abilities essential for lifelong learning.
Drawbacks and Criticisms of Ungrading
Ungrading faces criticism for potentially reducing student motivation due to the absence of clear performance benchmarks, which can make it difficult for learners to gauge their progress. Traditional grading's quantifiable feedback provides structured evaluation, while ungrading's subjective assessments may lead to inconsistencies and perceived unfairness. Critics also highlight challenges in standardizing ungrading practices across diverse educational settings, impacting scalability and comparability of student achievement.
Advantages and Limitations of Traditional Grading
Traditional grading provides a standardized method for assessing student performance, enabling easy comparison across different educators and institutions. Its limitations include fostering competition rather than collaboration, often inducing anxiety in students, and failing to capture individual learning growth or critical thinking skills effectively. Despite its widespread use, traditional grading can overlook the nuances of student understanding and does not always encourage deeper engagement with the material.
Impact on Student Motivation and Engagement
Ungrading enhances student motivation and engagement by fostering intrinsic interest and reducing anxiety associated with traditional point-based assessments. Research indicates that students in ungrading environments demonstrate higher levels of creativity, risk-taking, and ownership over their learning process. In contrast, traditional grading often leads to extrinsic motivation, where students focus primarily on earning grades rather than mastering content, potentially undermining long-term engagement.
Teacher Perspectives on Assessment Methods
Teachers favor ungrading for its emphasis on formative feedback, which fosters deeper learning and reduces student anxiety compared to traditional grading. Traditional grading often pressures educators to assign scores quickly, limiting opportunities for personalized feedback and holistic student evaluation. Many educators report that ungrading enhances student motivation and engagement by prioritizing mastery over numeric or letter grades.
Implementing Ungrading in the Classroom
Implementing ungrading in the classroom involves shifting focus from numeric scores to detailed qualitative feedback that promotes student growth and self-reflection. Teachers facilitate student-led assessments, encouraging goal-setting and ongoing dialogue rather than relying solely on summative evaluations. This approach fosters intrinsic motivation and deeper learning by prioritizing mastery and personalized progress over comparative ranking.
Which Assessment Method Suits Your Educational Goals?
Ungrading emphasizes qualitative feedback and student self-assessment, fostering deeper learning and intrinsic motivation, while traditional grading relies on quantitative scores that provide standardized benchmarks for academic performance. Choose ungrading if your educational goals prioritize critical thinking, creativity, and student engagement over numerical metrics. Opt for traditional grading when your objectives include consistent evaluation, accountability, and measurable achievement outcomes.
Ungrading Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com