Cognitive strategies enhance your ability to process information, solve problems, and make decisions effectively. Techniques such as chunking, rehearsal, and elaboration improve memory retention and learning efficiency. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical cognitive strategies that can boost your mental performance.
Table of Comparison
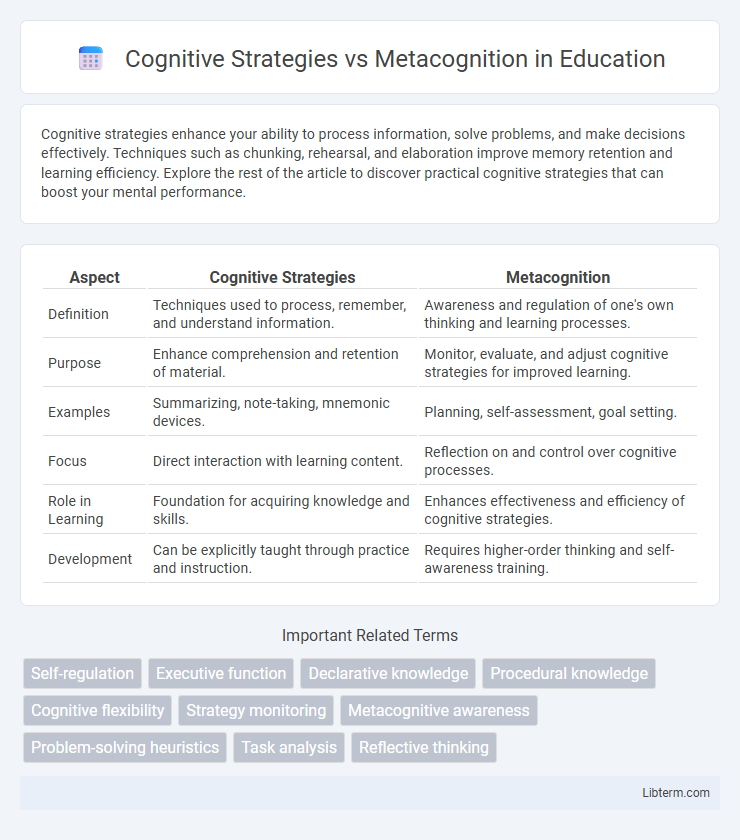
| Aspect | Cognitive Strategies | Metacognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Techniques used to process, remember, and understand information. | Awareness and regulation of one's own thinking and learning processes. |
| Purpose | Enhance comprehension and retention of material. | Monitor, evaluate, and adjust cognitive strategies for improved learning. |
| Examples | Summarizing, note-taking, mnemonic devices. | Planning, self-assessment, goal setting. |
| Focus | Direct interaction with learning content. | Reflection on and control over cognitive processes. |
| Role in Learning | Foundation for acquiring knowledge and skills. | Enhances effectiveness and efficiency of cognitive strategies. |
| Development | Can be explicitly taught through practice and instruction. | Requires higher-order thinking and self-awareness training. |
Understanding Cognitive Strategies
Cognitive strategies are specific mental processes used to acquire, organize, and retain information, such as rehearsal, elaboration, and summarization. These strategies enhance learning efficiency by actively engaging with material to improve comprehension and memory retention. Understanding cognitive strategies is crucial for developing effective study habits and improving problem-solving skills across various academic disciplines.
Defining Metacognition
Metacognition refers to the awareness and regulation of one's own cognitive processes, encompassing planning, monitoring, and evaluating learning activities to enhance comprehension and problem-solving. Unlike cognitive strategies, which are specific techniques used to process information, metacognition involves a higher-order thinking skill that guides and controls these cognitive strategies. This self-regulatory framework enables learners to adjust their methods based on ongoing assessment of understanding and task demands.
Key Differences Between Cognitive Strategies and Metacognition
Cognitive strategies involve specific mental processes like rehearsal, elaboration, and organization used to enhance learning and problem-solving. Metacognition refers to the awareness and regulation of one's own cognitive processes, including planning, monitoring, and evaluating understanding and performance. The key difference lies in cognitive strategies being direct actions applied to learning tasks, while metacognition encompasses the higher-order thinking about those strategies and overall cognitive control.
The Role of Cognitive Strategies in Learning
Cognitive strategies are deliberate methods employed by learners to process, encode, and retrieve information, significantly enhancing comprehension and retention. These strategies include summarization, elaboration, and organization, which actively engage cognitive resources to improve learning outcomes. Effective use of cognitive strategies facilitates deeper understanding and problem-solving skills, serving as foundational tools for academic success.
The Importance of Metacognition for Self-Regulation
Metacognition plays a crucial role in self-regulation by enabling individuals to monitor, evaluate, and adjust their cognitive processes during learning. Unlike cognitive strategies that involve specific techniques for information processing, metacognition encompasses awareness and control over one's thinking, promoting effective goal-setting and problem-solving. This heightened self-awareness facilitates adaptive behaviors and improves academic performance by guiding learners to refine strategies based on ongoing self-assessment.
Practical Examples of Cognitive Strategies
Cognitive strategies include techniques such as summarizing information, creating mind maps, and using mnemonic devices to enhance memory and understanding. For example, highlighting key points in a textbook or organizing notes into charts helps improve information retention and problem-solving skills. These practical applications of cognitive strategies support effective learning by directly engaging with the material.
How Metacognitive Skills Enhance Problem-Solving
Metacognitive skills, including self-monitoring, goal-setting, and evaluating progress, significantly enhance problem-solving by enabling individuals to plan, regulate, and adjust their cognitive strategies effectively. These skills foster awareness of one's thought processes, allowing for the identification of errors and the adaptation of approaches to complex tasks. Research in educational psychology demonstrates that metacognition improves critical thinking, leading to more efficient and successful problem resolution compared to relying solely on basic cognitive strategies.
Integrating Cognitive Strategies and Metacognition in Education
Integrating cognitive strategies and metacognition in education enhances students' learning efficiency by promoting active knowledge processing and self-regulation skills. Cognitive strategies like summarization, elaboration, and organization improve information encoding, while metacognitive practices such as goal-setting, monitoring, and evaluating learning foster deeper understanding and adaptability. Research indicates that combining these approaches leads to improved academic performance, critical thinking, and lifelong learning capabilities.
Benefits of Teaching Metacognitive Awareness
Teaching metacognitive awareness enhances learners' ability to regulate their cognitive processes, leading to improved problem-solving and critical thinking skills. Unlike cognitive strategies that focus on specific task-related techniques, metacognition fosters self-reflection, planning, and monitoring of one's learning, resulting in greater academic independence and adaptability. Empirical studies show that students trained in metacognitive skills achieve higher retention rates and transfer knowledge more effectively across disciplines.
Developing Effective Cognitive and Metacognitive Habits
Developing effective cognitive and metacognitive habits enhances learning by improving information processing and self-regulation. Cognitive strategies involve techniques like summarization, elaboration, and organization to deepen understanding, while metacognitive strategies focus on planning, monitoring, and evaluating one's own learning process. Mastery of both allows learners to adapt strategies dynamically, leading to greater academic success and lifelong learning skills.
Cognitive Strategies Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com