Collaborative work fosters creativity and enhances problem-solving by combining diverse perspectives and skills. Effective collaboration tools streamline communication, ensuring your team stays aligned and productive. Discover how embracing collaboration can transform your projects and boost success in the full article.
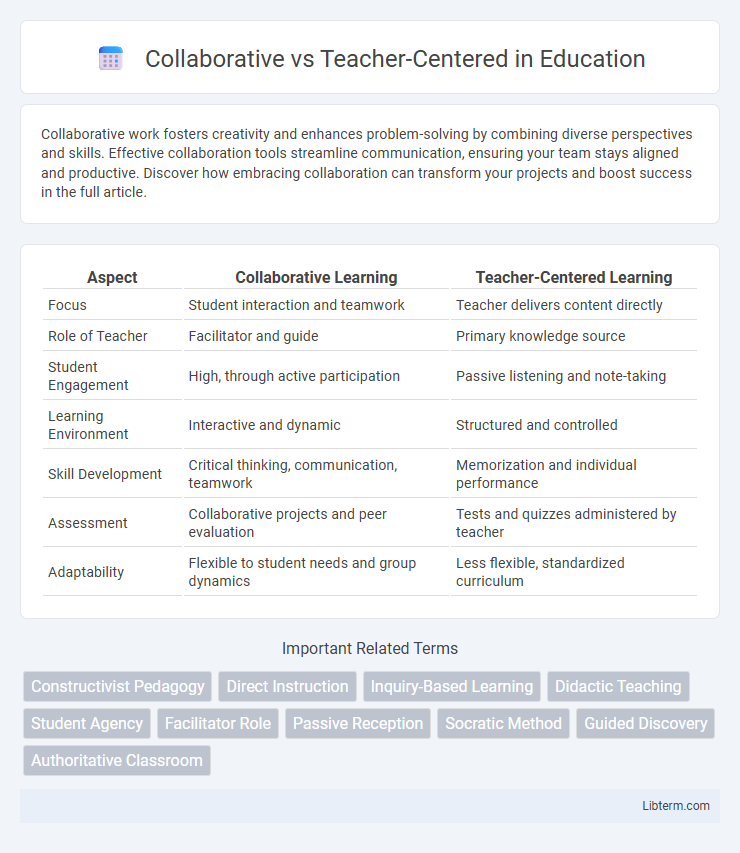
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Collaborative Learning | Teacher-Centered Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Student interaction and teamwork | Teacher delivers content directly |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide | Primary knowledge source |
| Student Engagement | High, through active participation | Passive listening and note-taking |
| Learning Environment | Interactive and dynamic | Structured and controlled |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, communication, teamwork | Memorization and individual performance |
| Assessment | Collaborative projects and peer evaluation | Tests and quizzes administered by teacher |
| Adaptability | Flexible to student needs and group dynamics | Less flexible, standardized curriculum |
Introduction to Collaborative and Teacher-Centered Approaches
Collaborative approaches emphasize student interaction, shared responsibility, and active participation, fostering critical thinking and communication skills. Teacher-centered approaches prioritize direct instruction, where the teacher controls content delivery and classroom management to ensure structured learning. Both methods shape educational experiences, with collaborative learning promoting engagement and teacher-centered learning focusing on efficient content mastery.
Defining Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning is an instructional approach where students actively work together in small groups to solve problems, complete tasks, or create projects, promoting shared responsibility and diverse perspectives. In contrast to teacher-centered methods, collaborative learning shifts the focus from the instructor delivering content to students engaging in peer interaction and critical thinking. This approach enhances communication skills, fosters deeper understanding, and supports social and cognitive development through meaningful collaboration.
Understanding Teacher-Centered Instruction
Teacher-centered instruction emphasizes a structured classroom environment where the teacher directs learning through lectures, demonstrations, and controlled discussions, ensuring clear content delivery and consistent assessment. This approach prioritizes accurate knowledge transmission, teacher authority, and efficient management of time and resources, often resulting in increased student compliance and discipline. While it may limit student autonomy, teacher-centered methods are effective in environments requiring standardized curriculum adherence and clear accountability measures.
Key Differences Between Collaborative and Teacher-Centered Methods
Collaborative methods emphasize student interaction, peer learning, and shared responsibility for knowledge construction, while teacher-centered approaches prioritize direct instruction and authoritative control by the educator. Collaborative learning fosters critical thinking and communication skills through group tasks, whereas teacher-centered methods focus on content delivery and individual student accountability. Assessment in collaborative settings often includes group evaluations and formative feedback, contrasting with the summative, exam-based assessments common in teacher-centered environments.
Benefits of Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning enhances critical thinking, communication, and teamwork skills by encouraging students to engage actively with peers in problem-solving tasks. This method fosters deeper understanding and retention of material as learners share diverse perspectives and co-construct knowledge. Collaborative environments promote increased motivation and greater student autonomy compared to traditional teacher-centered instruction.
Advantages of Teacher-Centered Approaches
Teacher-centered approaches provide structured learning environments that prioritize clear guidance and consistent instruction, ensuring that essential content is efficiently covered. This method supports classroom management by establishing authority and minimizing distractions, which can enhance student focus and discipline. Moreover, teacher-centered instruction allows for standardized assessment and streamlined curriculum delivery, facilitating measurable academic outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Collaborative learning often faces challenges such as uneven participation, time constraints, and potential conflicts among group members that can hinder the learning process. Teacher-centered approaches may limit student engagement, reduce opportunities for critical thinking, and create a passive learning environment where students rely heavily on the instructor for information. Balancing these limitations is essential for effective education strategies that aim to maximize student interaction and knowledge retention.
Situations Best Suited for Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning thrives in situations that require critical thinking, problem-solving, and diverse perspectives, such as group projects, discussions, and case studies. It is particularly effective in fostering communication skills and deeper understanding through peer interaction in both classroom and virtual environments. Collaborative approaches best suit settings where active participation and shared responsibility enhance engagement and knowledge retention.
Scenarios Where Teacher-Centered Instruction Excels
Teacher-centered instruction excels in scenarios requiring clear, structured delivery of foundational knowledge, such as large lecture halls or standardized test preparation. It ensures efficient coverage of curriculum content and maintains classroom control, especially in situations where time constraints or large student numbers limit individualized interaction. This approach is effective for subjects demanding precise information dissemination, including mathematics, science, and language grammar rules.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach for Effective Learning
Selecting the right instructional approach depends on the learning objectives and student needs, with collaborative methods fostering critical thinking and social skills, while teacher-centered approaches provide structured knowledge delivery. Effective learning often emerges from blending both strategies, leveraging collaboration for engagement and teacher guidance for clarity. Tailoring the approach to the specific educational context maximizes retention and skill development.
Collaborative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com