Project-Based Learning immerses students in real-world challenges, enhancing critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. This hands-on approach connects theory to practice, making education more engaging and meaningful for Your development. Explore how Project-Based Learning can transform Your educational experience in the full article.
Table of Comparison
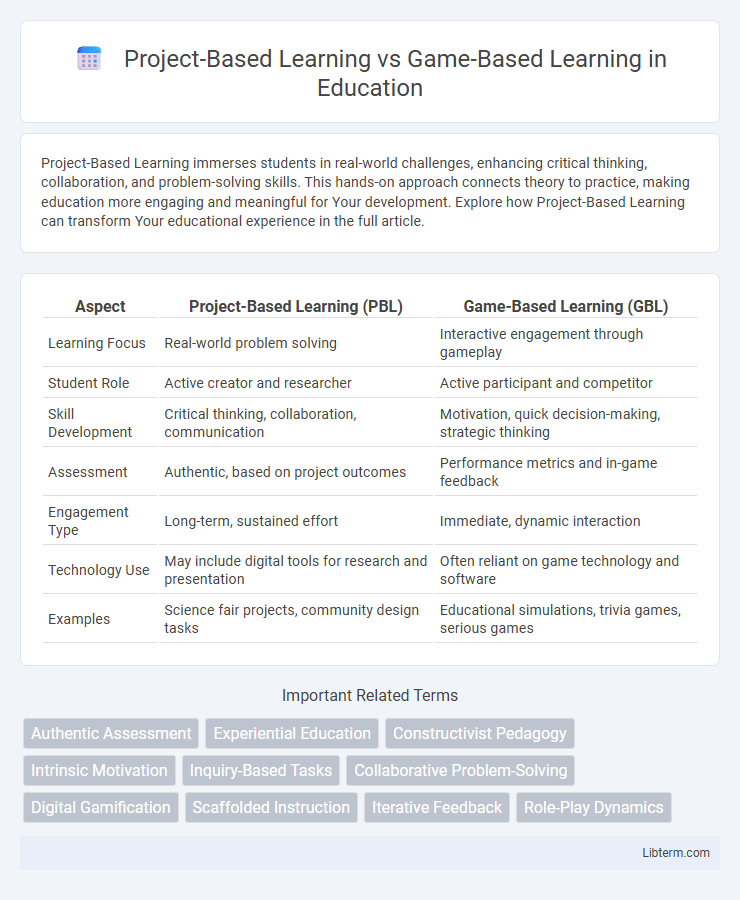
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Game-Based Learning (GBL) |
|---|---|---|
| Learning Focus | Real-world problem solving | Interactive engagement through gameplay |
| Student Role | Active creator and researcher | Active participant and competitor |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, collaboration, communication | Motivation, quick decision-making, strategic thinking |
| Assessment | Authentic, based on project outcomes | Performance metrics and in-game feedback |
| Engagement Type | Long-term, sustained effort | Immediate, dynamic interaction |
| Technology Use | May include digital tools for research and presentation | Often reliant on game technology and software |
| Examples | Science fair projects, community design tasks | Educational simulations, trivia games, serious games |
Introduction to Project-Based Learning and Game-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) engages students in gaining knowledge through active exploration of real-world challenges and problems, promoting critical thinking, collaboration, and practical application of skills. Game-Based Learning (GBL) incorporates game elements and mechanics to enhance motivation, engagement, and retention by transforming educational content into interactive, goal-oriented experiences. Both methodologies prioritize student-centered learning but differ in approach: PBL emphasizes hands-on projects and problem-solving, while GBL leverages play and competition to reinforce concepts.
Core Principles of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) centers on student-driven inquiry, real-world problem-solving, and collaboration to deepen understanding and develop critical thinking skills. Core principles include sustained inquiry, authentic tasks, student autonomy, and reflective assessment, all aimed at fostering meaningful learning experiences. PBL contrasts with Game-Based Learning by emphasizing extended projects and tangible outcomes rather than interactive play for engagement and skill acquisition.
Key Features of Game-Based Learning
Game-Based Learning centers on interactive, engaging environments where learners acquire knowledge through gameplay mechanics and challenges tailored to educational goals. Key features include immediate feedback, adaptive difficulty levels, and immersive storytelling, which enhance motivation and retention by fostering active problem-solving and critical thinking skills. This approach leverages rewards, competition, and collaboration to create a dynamic learning experience that supports skill development and knowledge application in real-world contexts.
Differences in Learning Objectives
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes developing critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving skills by engaging students in complex, multifaceted projects over extended periods. Game-Based Learning (GBL) focuses on motivation, immediate feedback, and skill mastery through interactive gameplay designed to reinforce specific content and learning objectives. While PBL aims at deep understanding and application of knowledge across disciplines, GBL centers on engagement and incremental skill improvement within a controlled learning environment.
Student Engagement and Motivation Comparison
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances student engagement by promoting critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving, leading to intrinsic motivation through meaningful tasks. Game-Based Learning (GBL) increases motivation by incorporating elements like competition, rewards, and immediate feedback that stimulate dopamine release and active participation. Research indicates that PBL fosters deeper cognitive engagement, while GBL excels in sustaining short-term motivation and excitement.
Assessment Methods in Both Approaches
Project-Based Learning employs authentic assessment methods such as portfolio reviews, presentations, and rubric-based evaluations to measure students' problem-solving, collaboration, and critical thinking skills throughout the project lifecycle. Game-Based Learning often utilizes formative assessments embedded within the game mechanics, including scoring systems, levels completed, and real-time feedback, enabling continuous performance tracking and skill mastery. Both approaches emphasize competency-based assessment but differ in format; Project-Based Learning prioritizes comprehensive deliverables while Game-Based Learning relies on interactive, immediate data-driven evaluations.
Real-World Applications and Examples
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes real-world applications by engaging students in complex projects such as designing sustainable urban gardens or developing community health campaigns, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Game-Based Learning (GBL) integrates real-world scenarios within interactive simulations like virtual stock market trading or historical battle reenactments, promoting strategic decision-making and experiential understanding. Both methods effectively connect theoretical knowledge to practical outcomes, enhancing learner motivation and skill transferability to authentic contexts.
Challenges and Limitations
Project-Based Learning faces challenges such as time-intensive planning, assessment difficulties, and uneven student engagement, which can hinder consistent learning outcomes. Game-Based Learning often encounters limitations like high development costs, accessibility issues, and potential distraction from educational goals due to overly competitive elements. Both approaches require careful integration of instructional design to overcome these barriers and maximize educational effectiveness.
Integrating Both Approaches in Curriculum
Integrating Project-Based Learning (PBL) and Game-Based Learning (GBL) in curriculum enhances student engagement by combining hands-on real-world problem solving with interactive, gamified experiences. This approach leverages PBL's emphasis on collaboration and critical thinking alongside GBL's motivational elements such as rewards and challenges, fostering deeper knowledge retention. Schools adopting this blended methodology report improved creativity, decision-making skills, and overall learner motivation across diverse subjects.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Method for Your Classroom
Selecting between Project-Based Learning (PBL) and Game-Based Learning (GBL) depends on your classroom goals, student engagement levels, and curriculum requirements. PBL excels in fostering critical thinking and real-world problem-solving skills through extended exploration, while GBL enhances motivation and immediate feedback through interactive gameplay. Integrating both methods strategically can maximize learning outcomes by combining deep understanding with active participation.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com