Summative assessments provide a comprehensive evaluation of student learning by measuring their knowledge and skills at the end of an instructional period. These evaluations help educators identify strengths and areas needing improvement to refine teaching strategies. Discover how summative assessments can enhance your educational outcomes by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
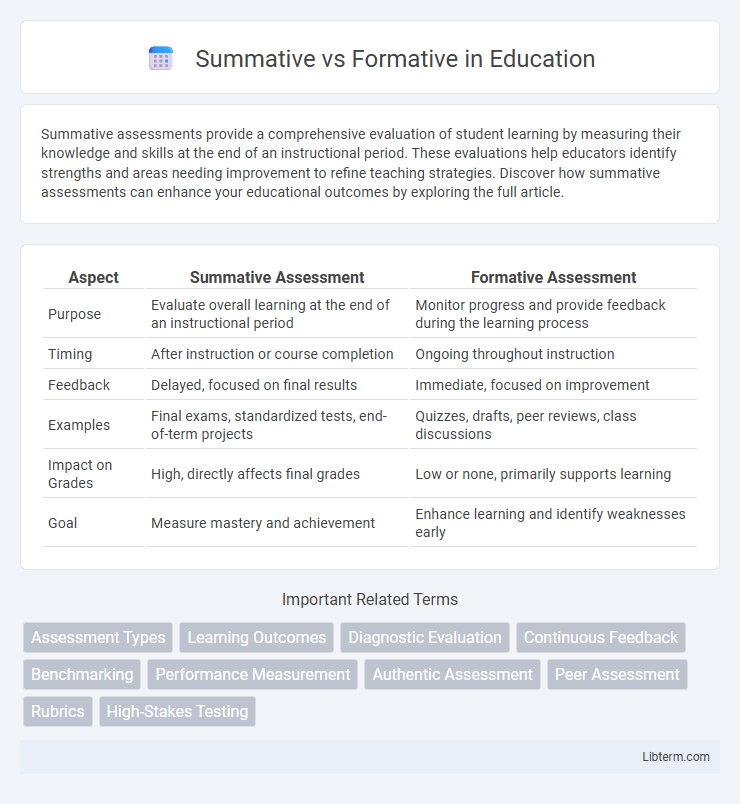
| Aspect | Summative Assessment | Formative Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate overall learning at the end of an instructional period | Monitor progress and provide feedback during the learning process |
| Timing | After instruction or course completion | Ongoing throughout instruction |
| Feedback | Delayed, focused on final results | Immediate, focused on improvement |
| Examples | Final exams, standardized tests, end-of-term projects | Quizzes, drafts, peer reviews, class discussions |
| Impact on Grades | High, directly affects final grades | Low or none, primarily supports learning |
| Goal | Measure mastery and achievement | Enhance learning and identify weaknesses early |
Introduction to Summative and Formative Assessment
Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period by measuring knowledge through exams, final projects, or standardized tests, providing a summary of achievement against learning objectives. Formative assessment, conducted during the learning process, includes quizzes, observations, and feedback sessions aimed at identifying strengths and areas for improvement to guide instruction. Both assessment types are essential for comprehensive educational evaluation, balancing outcome measurement with ongoing learning support.
Defining Summative Assessment
Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period by comparing it against a standard or benchmark, often through final exams, standardized tests, or end-of-term projects. This type of assessment provides a conclusive measure of student achievement and mastery of the curriculum. Summative assessments are critical for determining final grades, informing curriculum effectiveness, and guiding educational policy decisions.
Defining Formative Assessment
Formative assessment is an ongoing process used by educators to monitor student learning and provide continuous feedback, helping to identify strengths and areas for improvement before final evaluations. It includes activities such as quizzes, observations, and peer reviews that inform instructional adjustments. Unlike summative assessment, which measures cumulative achievement at the end of a period, formative assessment emphasizes learning development and progress throughout the instructional process.
Key Differences Between Summative and Formative
Summative assessments evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional period, providing a final measure of achievement through exams, final projects, or standardized tests. Formative assessments occur during the learning process, offering ongoing feedback that helps identify strengths and areas for improvement through quizzes, observations, or class discussions. The key difference lies in summative assessments being evaluative and grading-focused, whereas formative assessments are diagnostic and aimed at guiding instruction and enhancing learning outcomes.
Purposes and Goals of Each Assessment Type
Summative assessment aims to evaluate student learning by measuring mastery of content at the end of an instructional period, providing a comprehensive overview of achievement for grading and accountability purposes. Formative assessment focuses on monitoring student progress during the learning process, enabling timely feedback and instructional adjustments to support skill development and conceptual understanding. The goal of formative assessment is to enhance future learning, while summative assessment seeks to validate learning outcomes.
Examples of Summative Assessments
Summative assessments include final exams, standardized tests, end-of-unit projects, and cumulative essays that evaluate student learning at the conclusion of an instructional period. These assessments provide quantifiable data used for assigning grades and measuring overall achievement against learning objectives. Examples such as the SAT, AP exams, and final term papers highlight their role in summarizing knowledge rather than guiding ongoing instruction.
Examples of Formative Assessments
Formative assessments include quizzes, classroom discussions, and peer reviews that provide ongoing feedback to students and instructors. Examples such as exit tickets, observation checklists, and draft submissions help identify learning gaps and guide instructional adjustments in real-time. These methods promote active learning and continuous improvement before final evaluations like summative exams.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Summative Assessment
Summative assessment offers clear benefits by providing a comprehensive evaluation of student learning at the end of an instructional period, allowing educators to measure achievement against standards and make data-driven decisions. However, its drawbacks include limited feedback for ongoing improvement and a tendency to emphasize high-stakes testing, which may increase student stress and reduce opportunities for formative learning. This assessment type is valuable for accountability but often lacks the flexibility needed to support continuous student development.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Formative Assessment
Formative assessment enhances learning by providing ongoing feedback, enabling students to identify strengths and weaknesses and adjust their efforts accordingly, which fosters deeper understanding and skills development. Its benefits include promoting student engagement and personalized instruction, but drawbacks involve the significant time investment required from educators and potential inconsistencies in grading. Despite challenges, formative assessment supports continuous improvement, making it a valuable tool for adaptive learning environments.
Choosing the Right Assessment for Learning Objectives
Summative assessments measure overall student learning outcomes at the end of an instructional period, making them ideal for evaluating mastery of course content and assigning final grades. Formative assessments provide ongoing feedback during the learning process, helping educators identify knowledge gaps and adjust teaching strategies to improve student understanding. Selecting the right assessment aligns with specific learning objectives: use summative assessments for comprehensive evaluation and formative assessments to support continuous skill development.
Summative Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com