Phonological awareness is the ability to recognize and manipulate sounds in spoken language, including syllables, rhymes, and individual phonemes. Mastering this skill is essential for developing strong reading and spelling abilities in early learners. Explore the rest of the article to understand how phonological awareness can enhance your child's literacy journey.
Table of Comparison
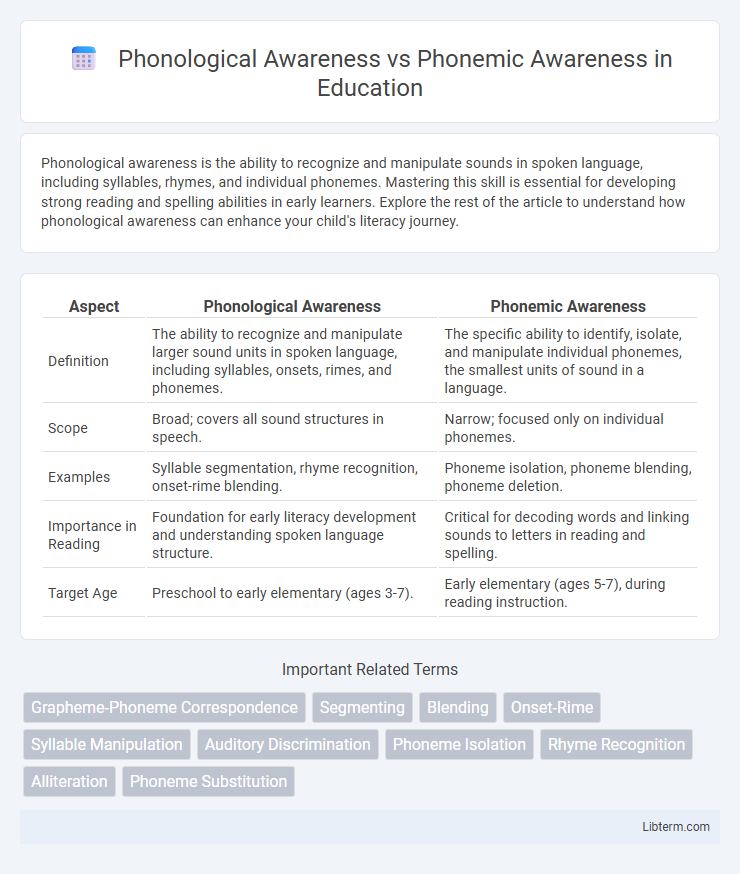
| Aspect | Phonological Awareness | Phonemic Awareness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The ability to recognize and manipulate larger sound units in spoken language, including syllables, onsets, rimes, and phonemes. | The specific ability to identify, isolate, and manipulate individual phonemes, the smallest units of sound in a language. |
| Scope | Broad; covers all sound structures in speech. | Narrow; focused only on individual phonemes. |
| Examples | Syllable segmentation, rhyme recognition, onset-rime blending. | Phoneme isolation, phoneme blending, phoneme deletion. |
| Importance in Reading | Foundation for early literacy development and understanding spoken language structure. | Critical for decoding words and linking sounds to letters in reading and spelling. |
| Target Age | Preschool to early elementary (ages 3-7). | Early elementary (ages 5-7), during reading instruction. |
Introduction to Phonological and Phonemic Awareness
Phonological awareness encompasses the broad skill of recognizing and manipulating sounds in spoken language, including syllables, rhymes, and onsets. Phonemic awareness, a subset of phonological awareness, specifically involves the ability to identify and manipulate individual phonemes, the smallest units of sound. Early literacy development depends heavily on both phonological and phonemic awareness for successful reading and spelling acquisition.
Defining Phonological Awareness
Phonological awareness is the broad skill of recognizing and manipulating sound structures in spoken language, including words, syllables, onsets, rimes, and phonemes. It encompasses various levels of sound units, such as identifying rhymes, counting syllables, and isolating individual phonemes. Phonemic awareness, a subset of phonological awareness, specifically involves the ability to focus on and manipulate individual phonemes, the smallest units of sound in a language.
What Is Phonemic Awareness?
Phonemic awareness is the ability to recognize and manipulate individual sounds, or phonemes, within spoken words, serving as a foundational skill for effective reading and spelling. It differs from phonological awareness, which encompasses broader sound recognition such as syllables and rhymes, while phonemic awareness specifically targets the smallest units of sound. Mastery of phonemic awareness enhances decoding skills and supports early literacy development by enabling children to segment, blend, and manipulate sounds.
Key Differences: Phonological vs Phonemic Awareness
Phonological awareness encompasses recognizing and manipulating larger sound units in language, such as syllables, onsets, rimes, and phonemes, while phonemic awareness specifically focuses on the ability to identify and manipulate individual phonemes, the smallest units of sound. The key difference lies in phonological awareness involving broader auditory skills, including rhyming and syllable segmentation, whereas phonemic awareness targets precise phoneme-level skills crucial for decoding and spelling. Effective reading instruction often develops phonological awareness first, progressing to targeted phonemic awareness to support early literacy development.
Why Phonological Awareness Matters in Early Literacy
Phonological awareness encompasses the recognition of sound structures in spoken language, including words, syllables, and rhymes, crucial for developing reading skills. Phonemic awareness, a subset of phonological awareness, specifically targets the ability to identify and manipulate individual phonemes, the smallest sound units. Early literacy success depends heavily on phonological awareness because it lays the foundation for decoding skills, vocabulary acquisition, and spelling proficiency, essential components of fluent reading and effective communication.
The Role of Phonemic Awareness in Reading Development
Phonemic awareness, a subset of phonological awareness, involves the ability to identify and manipulate individual sounds (phonemes) in words, which is crucial for decoding and word recognition skills in reading development. Strong phonemic awareness predicts better reading outcomes by enabling learners to sound out words and understand the alphabetic principle effectively. Teaching strategies that emphasize phoneme segmentation, blending, and manipulation significantly enhance early literacy skills and support successful reading acquisition.
Signs of Difficulty in Phonological or Phonemic Awareness
Difficulty recognizing rhyming words, clapping out syllables, or identifying initial sounds are common signs of phonological awareness challenges. Struggles with isolating, blending, or segmenting individual phonemes indicate phonemic awareness deficits. Early identification of these signs is critical for targeted interventions to support reading development.
Classroom Activities to Strengthen Phonological Awareness
Phonological awareness encompasses the ability to recognize and manipulate larger sound units in language such as words, syllables, and onsets and rimes, while phonemic awareness specifically targets the smallest sound units, phonemes. Effective classroom activities to strengthen phonological awareness include clapping syllables in words, segmenting and blending onsets and rimes, and playing rhyming games that encourage sound recognition in varied contexts. Incorporating multisensory techniques such as using visual aids, manipulatives, and movement can enhance students' ability to hear and manipulate oral language sounds before progressing to phonemic-level tasks.
Effective Strategies for Teaching Phonemic Awareness
Phonemic awareness, a subset of phonological awareness, involves recognizing and manipulating individual sounds (phonemes) in words, crucial for early reading skills. Effective strategies for teaching phonemic awareness include explicit instruction through activities like segmenting, blending, and phoneme substitution to enhance sound recognition and manipulation. Incorporating multisensory approaches such as using visual aids, manipulatives, and interactive games can significantly improve students' phonemic awareness and subsequent decoding abilities.
Conclusion: Integrating Both Skills for Literacy Success
Phonological awareness and phonemic awareness are both critical components of early literacy, with phonological awareness encompassing a broad range of sound recognition skills and phonemic awareness focusing specifically on the manipulation of individual phonemes. Integrating both skills in literacy instruction enhances decoding, spelling, and reading comprehension, leading to more effective reading development. Research consistently shows that a combined approach supports stronger word recognition and phonological processing abilities, essential for reading fluency and academic achievement.
Phonological Awareness Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com