The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) redefines federal education policy by emphasizing state and local control over K-12 education while maintaining accountability for student outcomes. It focuses on improving equity, closing achievement gaps, and ensuring all students have access to high-quality education. Explore the rest of the article to understand how ESSA impacts your child's academic experience and educational opportunities.
Table of Comparison
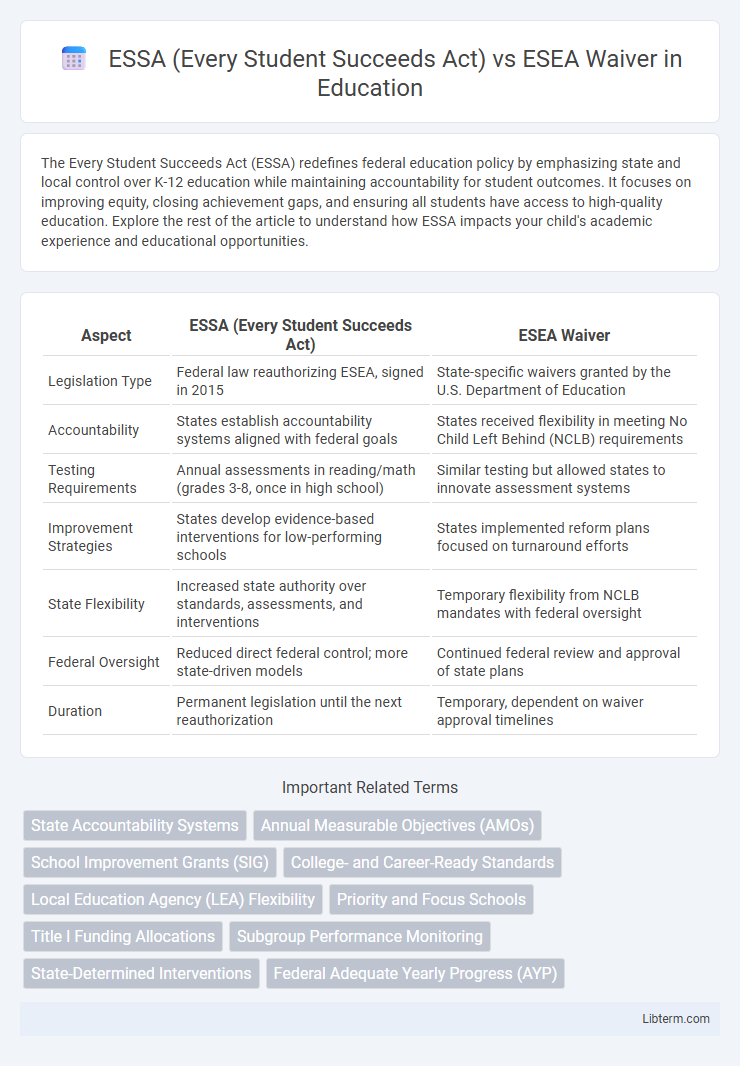
| Aspect | ESSA (Every Student Succeeds Act) | ESEA Waiver |
|---|---|---|
| Legislation Type | Federal law reauthorizing ESEA, signed in 2015 | State-specific waivers granted by the U.S. Department of Education |
| Accountability | States establish accountability systems aligned with federal goals | States received flexibility in meeting No Child Left Behind (NCLB) requirements |
| Testing Requirements | Annual assessments in reading/math (grades 3-8, once in high school) | Similar testing but allowed states to innovate assessment systems |
| Improvement Strategies | States develop evidence-based interventions for low-performing schools | States implemented reform plans focused on turnaround efforts |
| State Flexibility | Increased state authority over standards, assessments, and interventions | Temporary flexibility from NCLB mandates with federal oversight |
| Federal Oversight | Reduced direct federal control; more state-driven models | Continued federal review and approval of state plans |
| Duration | Permanent legislation until the next reauthorization | Temporary, dependent on waiver approval timelines |
Overview: ESSA and ESEA Waiver Explained
ESSA (Every Student Succeeds Act) replaced the No Child Left Behind Act, providing states with greater flexibility in setting education standards and accountability while maintaining federal oversight to ensure equity. The ESEA Waiver, granted to states under the No Child Left Behind Act, allowed temporary relief from strict federal mandates by approving state-designed plans aimed at improving student outcomes and accountability systems. ESSA codifies many waiver principles into law, emphasizing state control, evidence-based interventions, and a balanced approach to school improvement.
Historical Context: From NCLB to ESSA and Waivers
The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) replaced the No Child Left Behind Act (NCLB) in 2015, marking a significant shift toward increased state control over education policy and accountability. Prior to ESSA, the U.S. Department of Education issued ESEA waivers from 2012 to 2016, allowing states flexibility to bypass NCLB's rigid requirements. These waivers served as an interim solution, maintaining federal oversight while enabling states to implement more tailored strategies for improving student outcomes before ESSA's comprehensive reforms took effect.
Key Objectives: What ESSA and ESEA Waivers Aim to Achieve
ESSA (Every Student Succeeds Act) aims to provide states with greater flexibility in designing their accountability systems while ensuring high academic standards and closing achievement gaps among diverse student groups. ESEA Waivers, granted under the previous No Child Left Behind Act, enabled states to bypass specific federal requirements to implement tailored improvement strategies focused on turning around low-performing schools. Both policies prioritize improving educational outcomes, increasing equity, and enhancing school accountability, but ESSA formalizes these goals with more state control and reduced federal mandates.
Accountability Systems: Comparing Requirements
The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) mandates states to implement comprehensive accountability systems measuring academic achievement, graduation rates, and English language proficiency, with greater flexibility in setting goals compared to the ESEA Waiver requirements. Unlike the ESEA Waiver, which required states to identify and intervene in the bottom 5% of schools along with specific subgroups, ESSA emphasizes a broader set of indicators, including school climate and student engagement, to ensure a well-rounded evaluation of school performance. States under ESSA have more autonomy to design accountability frameworks that reflect local priorities while maintaining federal oversight to ensure equity and transparency.
State Flexibility: ESSA vs ESEA Waiver Provisions
ESSA grants states greater flexibility by allowing them to design their own accountability systems and set tailored performance targets aligned with federal standards, unlike ESEA waivers which imposed stricter federal conditions and limited state discretion. Under ESSA, states control school identification criteria and intervention strategies, promoting localized solutions and innovation in education reform. This shift enhances state autonomy in addressing unique educational challenges while maintaining federal oversight through required transparency and equity measures.
Assessment and Testing Approaches
ESSA (Every Student Succeeds Act) emphasizes state-designed assessment systems that include annual testing in reading and math for grades 3-8 and once in high school, allowing states flexibility to incorporate multiple measures beyond standardized tests. In contrast, the ESEA Waiver permitted states to modify testing requirements temporarily, often incorporating growth models and alternate assessments to reduce the focus on single-year proficiency scores. ESSA's approach prioritizes accountability through transparent reporting and balanced assessment strategies, while the ESEA Waiver allowed for experimental assessment frameworks during its waiver period.
Funding and Resource Allocation Differences
The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) provides states greater flexibility in funding allocation while maintaining Title I funding requirements to target low-income schools, ensuring more equitable resource distribution. ESEA waivers, granted during the No Child Left Behind (NCLB) era, allowed states temporary relief from certain federal mandates but often maintained funding formulas without significant changes to resource allocation strategies. ESSA emphasizes strategic use of federal funds to support school improvement and innovation, contrasting with the more rigid and waiver-dependent funding approaches under ESEA waivers.
Impact on Schools and Districts
The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) provides states with greater flexibility compared to the ESEA Waiver by allowing them to design tailored accountability systems and set their own performance targets, which directly impacts schools and districts by promoting localized control over educational priorities. Unlike the ESEA Waiver, which mandated specific reforms and triggered federal oversight for underperforming schools, ESSA reduces federal intervention, empowering districts to innovate in improving student outcomes while maintaining compliance with federal standards. This shift influences resource allocation, school improvement strategies, and accountability measures, fostering a more collaborative environment for educational growth at the district and school levels.
Stakeholder Engagement: Policy and Practice
ESSA mandates comprehensive stakeholder engagement, requiring states to involve educators, parents, and community members in policy development and decision-making processes, enhancing transparency and collaboration. ESEA Waivers allowed states more flexibility but often lacked structured requirements for meaningful stakeholder input, leading to varied levels of engagement. The shift from ESEA Waivers to ESSA emphasizes sustained and equitable participation to improve educational outcomes and accountability systems.
Future Implications for Education Reform
The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) replaces the ESEA Waiver by granting states more flexibility in setting educational standards and accountability systems, which is expected to foster innovation in teaching methods and resource allocation. ESSA's emphasis on local control and tailored interventions aims to address diverse student needs more effectively, potentially narrowing achievement gaps over time. Future education reform under ESSA is likely to prioritize equity and inclusion while encouraging states to develop data-driven strategies for continuous improvement.
ESSA (Every Student Succeeds Act) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com