Formal curriculum outlines a structured educational plan designed by institutions to ensure consistent learning outcomes across various subjects and grade levels. It typically includes predefined objectives, content, assessments, and instructional strategies tailored to meet academic standards. Explore the rest of the article to understand how a formal curriculum can effectively shape Your educational journey.
Table of Comparison
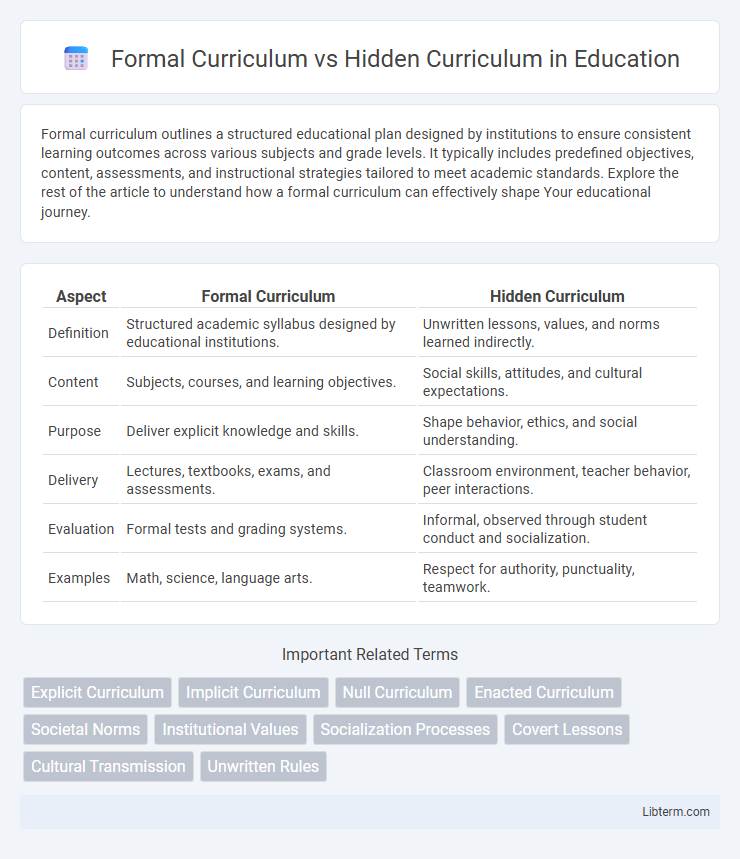
| Aspect | Formal Curriculum | Hidden Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured academic syllabus designed by educational institutions. | Unwritten lessons, values, and norms learned indirectly. |
| Content | Subjects, courses, and learning objectives. | Social skills, attitudes, and cultural expectations. |
| Purpose | Deliver explicit knowledge and skills. | Shape behavior, ethics, and social understanding. |
| Delivery | Lectures, textbooks, exams, and assessments. | Classroom environment, teacher behavior, peer interactions. |
| Evaluation | Formal tests and grading systems. | Informal, observed through student conduct and socialization. |
| Examples | Math, science, language arts. | Respect for authority, punctuality, teamwork. |
Introduction to Formal and Hidden Curriculum
Formal curriculum consists of the structured educational content and lessons intentionally designed by schools, including syllabi, textbooks, and standardized assessments. Hidden curriculum refers to the implicit lessons, values, and social norms conveyed through classroom interactions, school culture, and institutional practices beyond the official syllabus. Understanding both formal and hidden curricula is essential for comprehending how education shapes students' knowledge and social development.
Defining Formal Curriculum
The formal curriculum refers to the structured and officially documented educational content deliberately designed by educational authorities, outlining specific learning objectives, lesson plans, and assessment criteria. It encompasses subjects, syllabi, and instructional materials systematically organized to achieve measurable academic outcomes. This explicit curriculum contrasts with the hidden curriculum, which involves the implicit social and cultural lessons students learn through the educational environment.
Understanding Hidden Curriculum
The hidden curriculum refers to the unwritten, unofficial lessons, values, and perspectives that students learn in school alongside the formal curriculum. This includes social norms, attitudes, and behaviors that are conveyed through the school culture, teacher interactions, and peer relationships. Understanding the hidden curriculum is essential for educators to address implicit biases and foster an inclusive learning environment.
Key Differences Between Formal and Hidden Curriculum
Formal curriculum consists of structured, intentional educational objectives, lesson plans, and assessment methods designed by educational authorities to deliver specific academic knowledge and skills. Hidden curriculum refers to the implicit lessons, values, norms, and social expectations transmitted informally through school culture, peer interactions, and teacher attitudes, often influencing student behavior and social development. Key differences include explicit versus implicit content, planned versus unplanned delivery, and academic versus social-emotional learning outcomes.
Role of Teachers in Both Curricula
Teachers play a pivotal role in the formal curriculum by delivering structured content, assessing student comprehension, and ensuring alignment with academic standards and learning objectives. In the hidden curriculum, educators influence social norms, values, and behaviors by modeling attitudes, enforcing implicit rules, and shaping classroom culture. Effective teachers navigate both curricula to foster not only cognitive skills but also social-emotional development and ethical understanding.
Impact on Student Learning and Development
Formal curriculum provides structured academic content and clear learning objectives essential for mastering core skills and knowledge. Hidden curriculum influences socialization, values, and behavior through implicit lessons conveyed by school culture, teacher attitudes, and peer interactions. Both curricula collectively shape student learning outcomes, critical thinking abilities, and socio-emotional development, highlighting the importance of integrating awareness of hidden curriculum impacts in educational planning.
Examples of Formal Curriculum
The formal curriculum includes structured, explicitly outlined educational content such as textbooks, lesson plans, standardized tests, and official syllabi designed by educational authorities. Examples include mathematics courses defining operations and formulas, history classes covering specific time periods and events, and science curricula stipulating laboratory experiments and scientific principles. These elements provide clear learning objectives and measurable outcomes that guide both teaching and assessment in formal education settings.
Examples of Hidden Curriculum
Examples of hidden curriculum include social norms taught through classroom interactions, such as respect for authority, cooperation among peers, and adherence to punctuality. Schools implicitly convey values like competitiveness and conformity through disciplinary methods and reward systems. These lessons, though not part of the formal syllabus, significantly shape students' social behaviors and attitudes.
Addressing Hidden Curriculum in Educational Settings
Addressing the hidden curriculum in educational settings requires intentional strategies that uncover implicit values, norms, and social expectations students learn alongside formal content. Educators can implement reflective practices, promote inclusivity, and create open dialogues to make unconscious biases and cultural assumptions explicit. Understanding and managing the hidden curriculum enhances equity and supports holistic student development beyond the academic syllabus.
Conclusion: Balancing Formal and Hidden Curriculum
Balancing formal and hidden curriculum is essential for comprehensive education that addresses both explicit learning objectives and the implicit social and cultural lessons students absorb. Effective integration enhances critical thinking, ethical understanding, and social skills alongside academic knowledge. Educators must consciously design environments that recognize and align both curricula to foster well-rounded development.
Formal Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com