Conversation analysis examines the structure and patterns of spoken interactions to uncover how meaning is created and shared between participants. It focuses on elements such as turn-taking, pauses, and conversational repairs to reveal underlying social norms and communication strategies. Discover how understanding these dynamics can enhance your communication skills by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
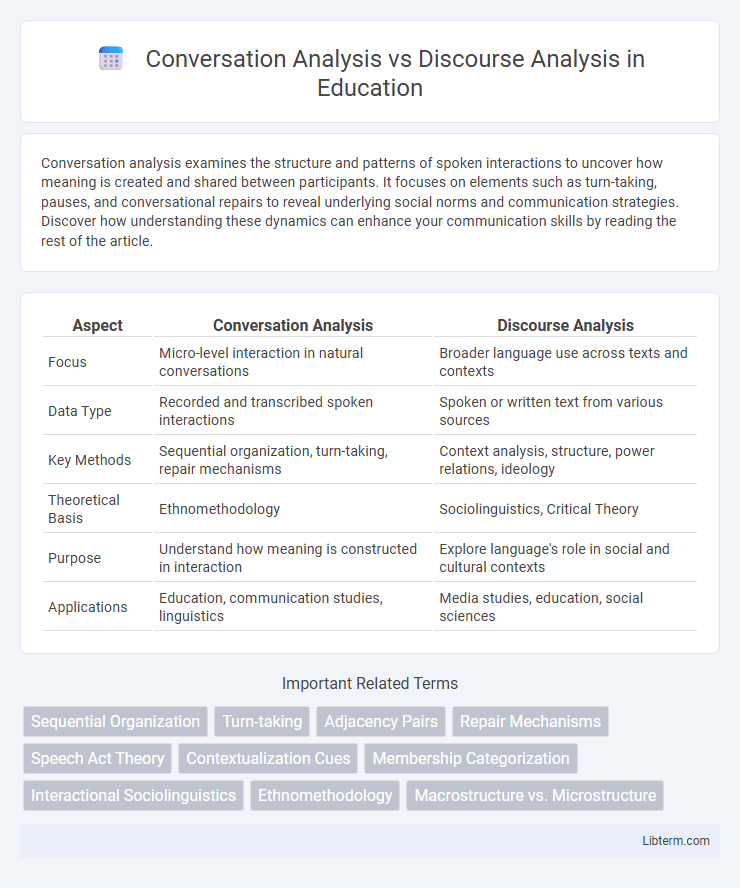
| Aspect | Conversation Analysis | Discourse Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Micro-level interaction in natural conversations | Broader language use across texts and contexts |
| Data Type | Recorded and transcribed spoken interactions | Spoken or written text from various sources |
| Key Methods | Sequential organization, turn-taking, repair mechanisms | Context analysis, structure, power relations, ideology |
| Theoretical Basis | Ethnomethodology | Sociolinguistics, Critical Theory |
| Purpose | Understand how meaning is constructed in interaction | Explore language's role in social and cultural contexts |
| Applications | Education, communication studies, linguistics | Media studies, education, social sciences |
Introduction to Conversation Analysis and Discourse Analysis
Conversation Analysis (CA) systematically studies the structures and patterns of spoken interaction, emphasizing turn-taking, repair mechanisms, and the sequential organization of talk in natural settings. Discourse Analysis (DA) examines language use beyond sentence boundaries, focusing on social context, power relations, and meaning construction across various communication forms. Both methods offer valuable insights into communicative processes, with CA prioritizing micro-level interactional details and DA addressing broader sociolinguistic aspects.
Defining Conversation Analysis
Conversation Analysis (CA) is the systematic study of the structure and patterns of interaction in spoken communication, focusing on the turn-by-turn organization of talk. It examines how participants produce and interpret conversational actions, such as turn-taking, repairs, and sequence organization, to create meaning in social interactions. Unlike Discourse Analysis, which often explores broader social and textual contexts, CA prioritizes the micro-level mechanisms shaping everyday conversation.
Defining Discourse Analysis
Discourse Analysis examines language use across texts and social contexts, focusing on how power, identity, and ideology shape communication. It studies larger units like conversations, written texts, and social interactions to understand meaning construction and social effects. This approach contrasts with Conversation Analysis, which analyzes the detailed structure and organization of spoken interaction at a micro-level.
Historical Background and Evolution
Conversation Analysis (CA) originated in the 1960s through the work of sociologists Harvey Sacks, Emanuel Schegloff, and Gail Jefferson, focused on the detailed study of naturally occurring talk-in-interaction. Discourse Analysis (DA) emerged earlier in the 1950s and 1960s within linguistics and anthropology, emphasizing broader social and cultural contexts of language use beyond turn-by-turn interactions. Over time, both fields evolved with CA concentrating on micro-level structures of conversation and DA expanding to include diverse modes of communication and critical social theory.
Theoretical Foundations: Key Principles
Conversation Analysis (CA) centers on the micro-level study of talk-in-interaction, emphasizing turn-taking, repair mechanisms, and sequence organization within natural conversational settings. Discourse Analysis (DA) explores language use across broader social and cultural contexts, focusing on power dynamics, ideology, and the construction of social identities through texts and spoken communication. CA is rooted in ethnomethodology and pragmatics, while DA incorporates critical theory and sociolinguistics as key theoretical foundations.
Core Methodologies and Techniques
Conversation Analysis (CA) employs detailed transcription techniques such as Jeffersonian notation to capture turn-taking, repair mechanisms, and sequential organization in spoken interactions, emphasizing micro-level structural patterns. Discourse Analysis (DA) utilizes thematic coding, narrative analysis, and critical frameworks to explore language use within social contexts, focusing on macro-level structures, power dynamics, and meaning construction. Both methodologies prioritize context but differ as CA provides fine-grained analysis of conversational mechanics while DA interprets broader social and cultural discourses.
Focus of Study: Micro vs. Macro Perspectives
Conversation Analysis (CA) examines the micro-level details of spoken interactions, focusing on turn-taking, pauses, and repair mechanisms within conversations. Discourse Analysis (DA) explores macro-level structures, analyzing broader social and cultural contexts that shape language use across texts and communicative events. CA's micro perspective emphasizes the mechanics of interaction, while DA's macro perspective addresses the influence of power, ideology, and social norms on discourse.
Applications in Linguistics and Beyond
Conversation Analysis (CA) primarily examines the structure and patterns of spoken interaction, making it essential for research in sociolinguistics, communication studies, and artificial intelligence, especially in developing natural language processing systems and improving human-computer dialogues. Discourse Analysis (DA) investigates broader language use across texts and contexts, influencing fields such as media studies, education, political communication, and critical theory by revealing power dynamics, identity construction, and social norms. Both methods enrich linguistic research and interdisciplinary applications by providing insights into language function, interaction, and social meaning.
Similarities and Overlapping Areas
Conversation Analysis (CA) and Discourse Analysis (DA) both investigate spoken language in social contexts, emphasizing how participants produce and interpret meaning during interaction. Both fields analyze turn-taking, repair mechanisms, and sequential organization, highlighting the structured nature of everyday communication. Overlapping areas include studying institutional talk, narrative construction, and the role of context in shaping language use, with CA offering micro-analytic detail and DA providing broader interpretive frameworks.
Key Differences and Comparative Insights
Conversation Analysis (CA) focuses on the micro-level structure of spoken interaction, analyzing turn-taking, repair mechanisms, and sequential organization within everyday conversations. Discourse Analysis (DA) examines broader language use in social contexts, addressing power dynamics, ideology, and cultural frameworks embedded in texts or spoken communication. Key differences include CA's empirical emphasis on actual interaction patterns versus DA's interpretive approach to meaning and context across diverse communicative events.
Conversation Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com