Sheltered Instruction is a teaching approach designed to make academic content comprehensible for English Language Learners (ELLs) while promoting their language development. It integrates language objectives with content objectives, ensuring that Your students build both language skills and subject knowledge simultaneously. Discover how Sheltered Instruction can transform your classroom by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
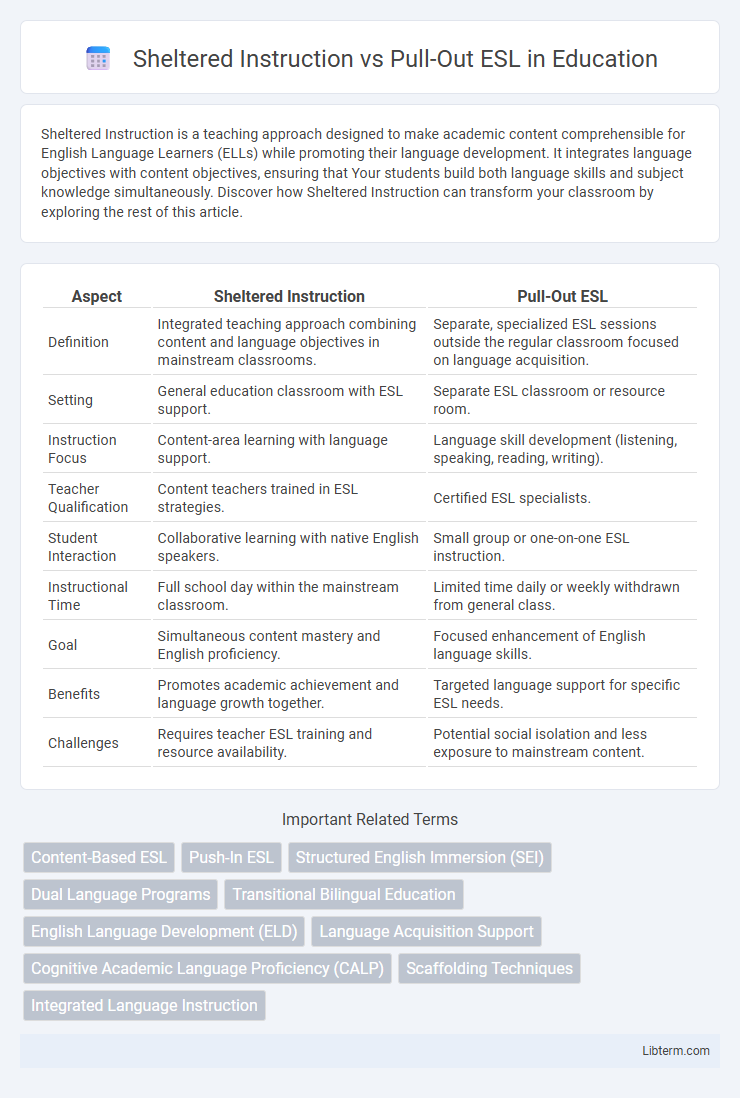
| Aspect | Sheltered Instruction | Pull-Out ESL |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrated teaching approach combining content and language objectives in mainstream classrooms. | Separate, specialized ESL sessions outside the regular classroom focused on language acquisition. |
| Setting | General education classroom with ESL support. | Separate ESL classroom or resource room. |
| Instruction Focus | Content-area learning with language support. | Language skill development (listening, speaking, reading, writing). |
| Teacher Qualification | Content teachers trained in ESL strategies. | Certified ESL specialists. |
| Student Interaction | Collaborative learning with native English speakers. | Small group or one-on-one ESL instruction. |
| Instructional Time | Full school day within the mainstream classroom. | Limited time daily or weekly withdrawn from general class. |
| Goal | Simultaneous content mastery and English proficiency. | Focused enhancement of English language skills. |
| Benefits | Promotes academic achievement and language growth together. | Targeted language support for specific ESL needs. |
| Challenges | Requires teacher ESL training and resource availability. | Potential social isolation and less exposure to mainstream content. |
Introduction to Sheltered Instruction and Pull-Out ESL
Sheltered Instruction integrates language support within content-area classrooms, enabling English Language Learners (ELLs) to develop academic skills while acquiring English in real-time. Pull-Out ESL provides targeted language instruction in separate sessions outside the mainstream classroom, focusing primarily on language proficiency development. Both models aim to address ELLs' needs but differ in instructional context and integration with grade-level standards.
Core Principles of Sheltered Instruction
Sheltered Instruction emphasizes integrating language and content learning through techniques like explicit vocabulary teaching, use of visual aids, and interactive strategies tailored for English Language Learners (ELLs). It maintains grade-level content standards while scaffolding instruction to make academic concepts comprehensible. Core principles include contextualized language instruction, student engagement in meaningful communication, and ongoing assessment of both language proficiency and content understanding.
Key Features of Pull-Out ESL Programs
Pull-Out ESL programs feature targeted instruction where students are temporarily removed from mainstream classrooms to receive specialized English language support, typically focusing on vocabulary, grammar, and conversational skills. These sessions are often individualized or conducted in small groups, allowing for tailored language development based on students' proficiency levels. This model emphasizes direct language teaching outside of content lessons, aiming to improve English fluency without altering the core academic curriculum during pull-out times.
Instructional Strategies in Sheltered Instruction
Sheltered Instruction employs instructional strategies that integrate language development with content learning, emphasizing techniques such as visual aids, graphic organizers, and hands-on activities to support English Learners (ELs) in comprehending academic concepts. This approach uses scaffolding methods like modeling, sentence frames, and interactive discussions to facilitate language acquisition within subject matter lessons. Teachers also modify speech by adjusting pace and vocabulary complexity, ensuring ELs engage meaningfully with grade-level content.
Student Experience in Pull-Out ESL Settings
Pull-out ESL settings often isolate English learners from mainstream classrooms, which can limit their exposure to grade-level content and reduce opportunities for meaningful social interaction with native speakers. Students in pull-out programs may experience a fragmented learning process, where language instruction is separate from academic subjects, potentially impacting their overall engagement and language development. However, individualized attention in pull-out ESL can address specific language needs, though it may not fully support integration into the broader school community or academic environment.
Academic Outcomes: Sheltered Instruction vs Pull-Out ESL
Sheltered Instruction consistently demonstrates stronger academic outcomes compared to Pull-Out ESL by integrating language support within grade-level content, fostering higher student engagement and comprehension. Research shows that students in Sheltered Instruction programs achieve better standardized test scores and improved subject mastery due to sustained exposure to academic language in context. Pull-Out ESL, while offering targeted language therapy, often leads to fragmented learning experiences and lower achievement in core academic subjects.
Teacher Roles and Qualifications
Sheltered Instruction teachers require specialized training in content-area pedagogy combined with ESL strategies to support English language learners within general classrooms. Pull-Out ESL instructors typically possess ESL certification and focus on targeted language acquisition skills in separate settings, emphasizing individualized support. Both roles demand proficiency in second-language acquisition theories, but Sheltered Instruction teachers must integrate language objectives with academic content, whereas Pull-Out ESL teachers concentrate primarily on language development.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Sheltered Instruction often faces challenges such as limited content coverage and the need for teachers to simultaneously address language development and academic standards, which can strain instructional time and resources. Pull-Out ESL programs may lead to social isolation and fragmented learning experiences as students are removed from mainstream classrooms, causing potential gaps in content knowledge and limited peer interaction. Both approaches require careful coordination and support to mitigate limitations like inconsistent language exposure and varying student proficiency levels.
Best Practices for Effective English Learner Instruction
Sheltered Instruction integrates content and language objectives within mainstream classrooms, utilizing strategies like scaffolding, visual aids, and cooperative learning to support English learners' comprehension and engagement. Pull-Out ESL programs provide targeted language development in separate settings, emphasizing individualized instruction tailored to students' proficiency levels and specific language needs. Effective English learner instruction combines sheltered instruction's contextualized learning with pull-out ESL's focused language practice, fostering both academic achievement and language proficiency through ongoing formative assessment and culturally responsive teaching.
Choosing the Right ESL Model for Your School
Selecting the appropriate ESL model--Sheltered Instruction or Pull-Out ESL--depends on student proficiency levels and available resources within your school. Sheltered Instruction integrates language learning with content instruction, promoting academic achievement for English learners in mainstream classrooms. Pull-Out ESL offers targeted language support in separate sessions but may limit exposure to grade-level content, impacting integration and overall progress.
Sheltered Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com