Closed-ended assessments provide clear, concise answers that are easy to score and analyze, making them ideal for measuring specific knowledge or skills efficiently. They often include multiple-choice, true/false, or matching questions that limit response options to predefined choices. Explore the rest of the article to understand how closed-ended assessments can enhance your evaluation strategies effectively.
Table of Comparison
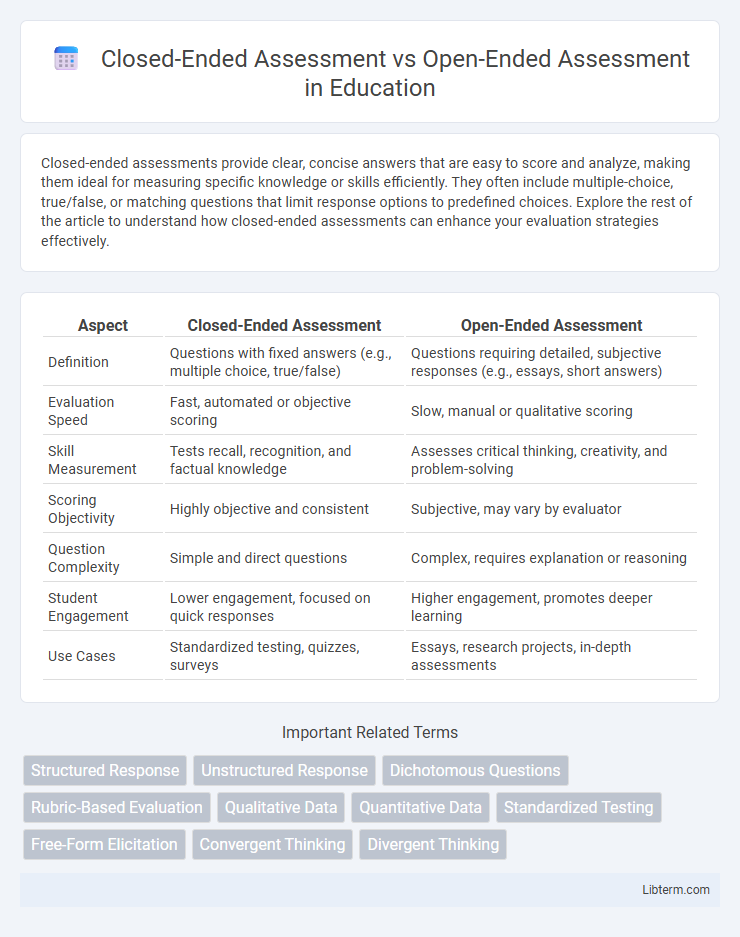
| Aspect | Closed-Ended Assessment | Open-Ended Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Questions with fixed answers (e.g., multiple choice, true/false) | Questions requiring detailed, subjective responses (e.g., essays, short answers) |
| Evaluation Speed | Fast, automated or objective scoring | Slow, manual or qualitative scoring |
| Skill Measurement | Tests recall, recognition, and factual knowledge | Assesses critical thinking, creativity, and problem-solving |
| Scoring Objectivity | Highly objective and consistent | Subjective, may vary by evaluator |
| Question Complexity | Simple and direct questions | Complex, requires explanation or reasoning |
| Student Engagement | Lower engagement, focused on quick responses | Higher engagement, promotes deeper learning |
| Use Cases | Standardized testing, quizzes, surveys | Essays, research projects, in-depth assessments |
Introduction to Assessment Types
Closed-ended assessments employ specific questions with predetermined answers, facilitating objective scoring and easy data analysis, commonly used in standardized testing. Open-ended assessments require respondents to generate their own responses, encouraging critical thinking and detailed feedback, ideal for evaluating deeper understanding and creativity. Both assessment types serve distinct educational purposes by balancing measurable outcomes with qualitative insights.
Defining Closed-Ended Assessment
Closed-ended assessment involves questions with predetermined answers, such as multiple-choice, true/false, or matching formats, enabling quick and objective scoring. This assessment type is effective for evaluating specific knowledge, factual recall, and comprehension across various subjects. By limiting response options, closed-ended assessments facilitate automated grading and statistical analysis, making them ideal for large-scale testing environments.
Defining Open-Ended Assessment
Open-ended assessment requires students to generate original responses, allowing for the demonstration of critical thinking, creativity, and in-depth understanding. Unlike closed-ended assessment, which limits answers to predetermined options like multiple-choice or true/false, open-ended questions encourage elaboration and explanation. This type of evaluation is essential for measuring higher-order cognitive skills and complex problem-solving abilities.
Key Differences Between Closed-Ended and Open-Ended Assessment
Closed-ended assessments use predefined answer choices, enabling quick grading and quantitative analysis, while open-ended assessments require respondents to generate their own answers, promoting critical thinking and deeper understanding. Closed-ended formats are ideal for measuring specific knowledge and comparing results across populations, whereas open-ended assessments capture nuanced insights and foster creativity by allowing elaborations. The primary difference lies in scoring objectivity and response freedom: closed-ended designs provide standardized metrics, whereas open-ended assessments demand qualitative evaluation.
Advantages of Closed-Ended Assessment
Closed-ended assessment offers clear advantages such as efficient grading and objective scoring, making it ideal for standardized testing and large-scale evaluations. Its structured format enables quick data analysis and reliable comparison of student performance across different groups. These assessments also minimize ambiguity, providing concise feedback on specific knowledge or skills.
Advantages of Open-Ended Assessment
Open-ended assessments promote critical thinking and creativity by encouraging students to construct their own responses rather than selecting from predetermined options. They provide deeper insights into student understanding and reasoning, enabling educators to identify misconceptions and assess higher-order cognitive skills. This type of assessment fosters personalized feedback and supports the development of communication skills essential for real-world problem solving.
Limitations of Closed-Ended Assessment
Closed-ended assessments limit students' ability to express complex ideas and critical thinking skills due to their fixed response options. These assessments often fail to capture the depth of understanding, creativity, and reasoning processes, leading to an incomplete evaluation of learning outcomes. The reliance on multiple-choice or true/false formats can encourage guessing and reduce opportunities for students to demonstrate problem-solving abilities and nuanced comprehension.
Limitations of Open-Ended Assessment
Open-ended assessments often face limitations such as subjective grading, which can lead to inconsistencies and potential bias in evaluation. They demand more time for both students to complete and instructors to assess, potentially reducing efficiency in large-scale testing environments. The lack of standardized responses also complicates automated grading and analysis, hindering scalability and quick feedback delivery.
Choosing the Right Assessment Method
Selecting the appropriate assessment method depends on the learning objectives and desired depth of understanding. Closed-ended assessments efficiently measure specific knowledge and produce quantifiable data ideal for large-scale testing. Open-ended assessments encourage critical thinking, creativity, and detailed responses, making them suitable for evaluating complex skills and higher-order learning outcomes.
Conclusion: Balancing Closed-Ended and Open-Ended Assessments
Balancing closed-ended and open-ended assessments enhances comprehensive evaluation by combining objective measurement with in-depth insight into student understanding. Closed-ended questions provide efficient scoring and clear data trends, while open-ended formats foster critical thinking and creativity. Integrating both types creates a holistic approach that supports diverse learning styles and accurately reflects student mastery.
Closed-Ended Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com