Inquiry-based learning fosters critical thinking by encouraging students to explore questions and problems independently. This active learning process enhances curiosity, promotes deeper understanding, and develops problem-solving skills essential for real-world applications. Discover how this method can transform Your educational experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
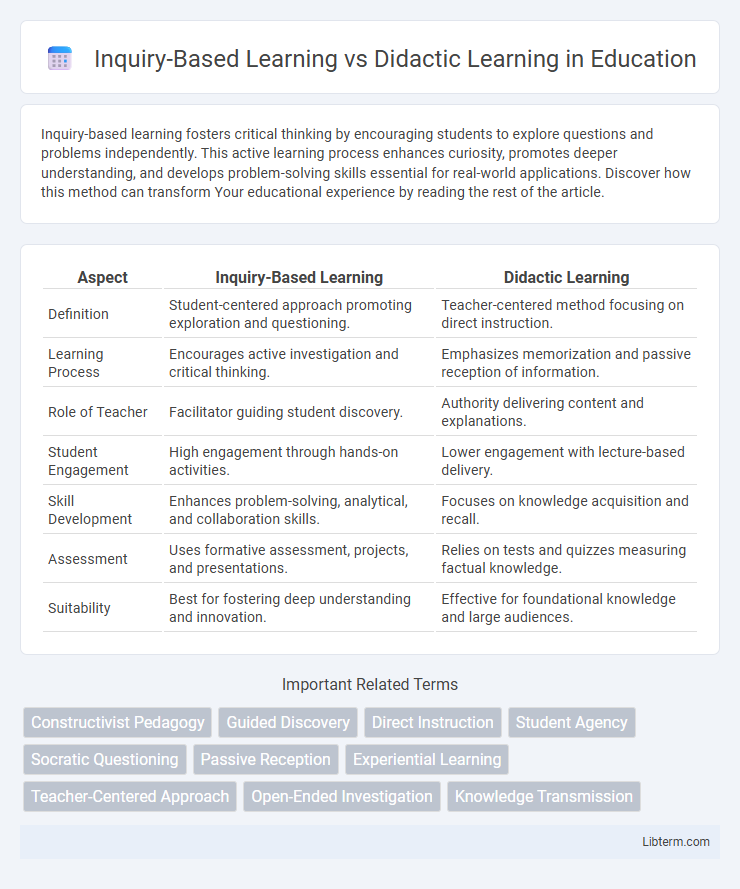
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Didactic Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach promoting exploration and questioning. | Teacher-centered method focusing on direct instruction. |
| Learning Process | Encourages active investigation and critical thinking. | Emphasizes memorization and passive reception of information. |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator guiding student discovery. | Authority delivering content and explanations. |
| Student Engagement | High engagement through hands-on activities. | Lower engagement with lecture-based delivery. |
| Skill Development | Enhances problem-solving, analytical, and collaboration skills. | Focuses on knowledge acquisition and recall. |
| Assessment | Uses formative assessment, projects, and presentations. | Relies on tests and quizzes measuring factual knowledge. |
| Suitability | Best for fostering deep understanding and innovation. | Effective for foundational knowledge and large audiences. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based Learning and Didactic Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes active student engagement through questioning, exploration, and critical thinking, fostering deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. Didactic Learning relies on direct instruction where the teacher delivers information in a structured, lecture-based format, prioritizing content accuracy and efficient knowledge transfer. Research shows Inquiry-Based Learning enhances problem-solving skills, while Didactic Learning ensures foundational knowledge acquisition, making both approaches valuable depending on educational goals.
Defining Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on student-driven exploration and questioning, encouraging critical thinking and problem-solving through active investigation. Unlike Didactic Learning, which relies on direct instruction and memorization, this approach fosters deeper understanding by allowing learners to construct knowledge through experience. Research shows Inquiry-Based Learning enhances engagement, creativity, and long-term retention compared to traditional teaching methods.
Understanding Didactic Learning
Didactic learning centers on direct instruction where educators deliver specific content and factual knowledge in a structured, teacher-led format that emphasizes memorization and repetition. This approach relies heavily on clear objectives, standardized assessments, and passive student participation to ensure mastery of established curricula. While effective for foundational knowledge acquisition, didactic methods may limit critical thinking and creativity by prioritizing content delivery over inquiry and exploration.
Historical Context and Educational Theories
Inquiry-based learning emerged from constructivist theories by Jean Piaget and John Dewey's advocacy for experiential education, emphasizing student-centered exploration and critical thinking. Didactic learning, rooted in the behaviorist tradition of B.F. Skinner and earlier classical education models, prioritizes direct instruction and knowledge transmission from teacher to student. Historically, the shift from didactic to inquiry-based methods reflects evolving educational theories favoring active learner engagement over passive reception.
Key Differences Between Inquiry-Based and Didactic Approaches
Inquiry-based learning emphasizes student exploration, critical thinking, and active problem-solving, whereas didactic learning relies on direct instruction and memorization of facts. In inquiry-based approaches, learners formulate questions and investigate topics, fostering deeper understanding and retention, while didactic methods center on teacher-led lectures and predefined content delivery. This contrast highlights the shift from passive reception to active engagement in education, impacting student motivation and cognitive development.
Benefits of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-based learning promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging students to explore questions and discover answers independently. This student-centered approach enhances engagement, motivation, and deeper understanding of concepts compared to traditional didactic learning, which often relies on passive memorization. Research indicates that inquiry-based learning supports long-term retention and fosters creativity by allowing learners to connect knowledge with real-world applications.
Advantages of Didactic Learning
Didactic learning offers structured content delivery, ensuring efficient coverage of core material in a consistent manner. It provides clear guidance and expert explanations, which help students grasp complex concepts quickly and reduce confusion. This method is especially effective in large groups where standardized knowledge acquisition is crucial for foundational subjects.
Common Challenges and Limitations
Inquiry-Based Learning often faces challenges such as limited student readiness, time constraints, and insufficient teacher training to effectively facilitate open-ended questioning. Didactic Learning can lead to passive student engagement, reduced critical thinking opportunities, and difficulties in accommodating diverse learning styles. Both approaches may struggle with balancing content coverage and depth of understanding within curriculum demands.
Impact on Student Engagement and Achievement
Inquiry-based learning promotes higher student engagement by encouraging curiosity and active problem-solving, which enhances critical thinking and retention of knowledge. Didactic learning, often centered on teacher-led instruction, may lead to passive participation and lower intrinsic motivation, potentially limiting deeper understanding. Research shows inquiry-based approaches improve academic achievement by fostering independent learning skills and adaptability in complex subjects.
Choosing the Right Approach for Diverse Learners
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving by encouraging students to explore and ask questions, making it ideal for learners who thrive on curiosity and active engagement. Didactic Learning provides structured, clear guidance and is effective for students needing direct instruction and foundational knowledge. Selecting the right approach depends on individual learner needs, cognitive styles, and the subject matter, ensuring optimal comprehension and skill development.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com