Special education provides tailored instructional methods and resources designed to meet the unique learning needs of students with disabilities or challenges. These programs foster inclusion, promote skill development, and support academic achievement through individualized education plans (IEPs). Explore the article to understand how special education can empower your child's learning journey.
Table of Comparison
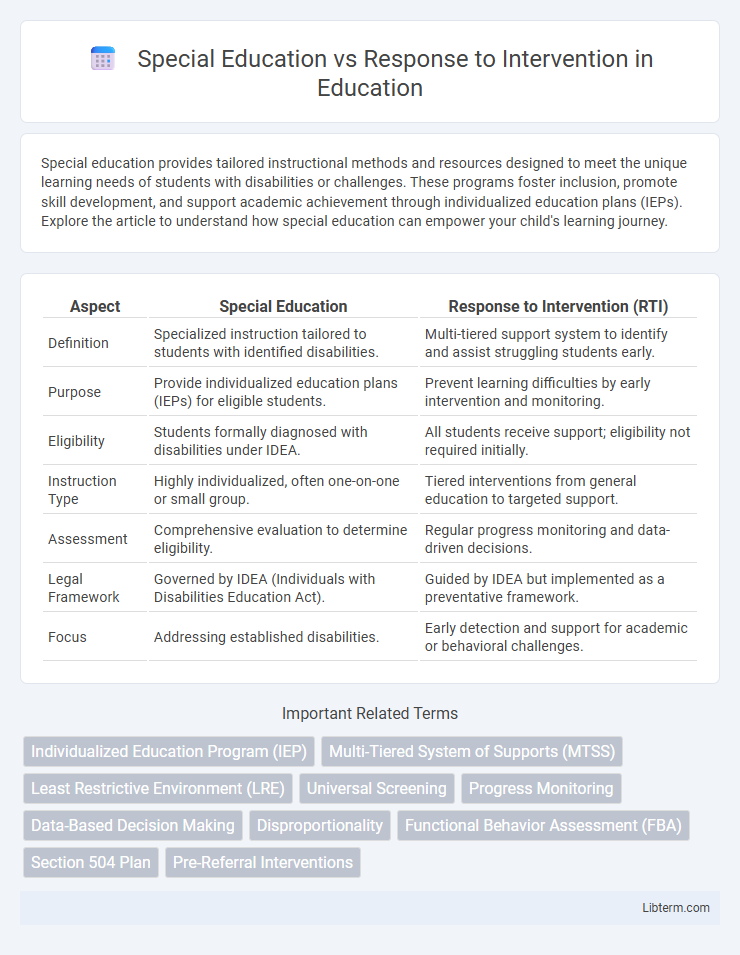
| Aspect | Special Education | Response to Intervention (RTI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specialized instruction tailored to students with identified disabilities. | Multi-tiered support system to identify and assist struggling students early. |
| Purpose | Provide individualized education plans (IEPs) for eligible students. | Prevent learning difficulties by early intervention and monitoring. |
| Eligibility | Students formally diagnosed with disabilities under IDEA. | All students receive support; eligibility not required initially. |
| Instruction Type | Highly individualized, often one-on-one or small group. | Tiered interventions from general education to targeted support. |
| Assessment | Comprehensive evaluation to determine eligibility. | Regular progress monitoring and data-driven decisions. |
| Legal Framework | Governed by IDEA (Individuals with Disabilities Education Act). | Guided by IDEA but implemented as a preventative framework. |
| Focus | Addressing established disabilities. | Early detection and support for academic or behavioral challenges. |
Understanding Special Education: An Overview
Special Education provides tailored instructional services to students with identified disabilities to support their unique learning needs. It involves individualized education programs (IEPs) that specify specialized goals, accommodations, and modifications in alignment with legal mandates such as the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA). Understanding Special Education requires recognizing its focus on personalized support, multisensory teaching approaches, and collaboration among educators, families, and specialists to promote equitable access to education.
What is Response to Intervention (RTI)?
Response to Intervention (RTI) is a multi-tiered approach designed to identify and support students with learning and behavioral needs through early intervention. RTI involves systematic monitoring and data-driven instruction across three tiers, providing increasingly intensive support based on student responsiveness. This framework aims to prevent academic failure by addressing difficulties before considering special education eligibility.
Key Differences Between Special Education and RTI
Special Education provides specialized instruction tailored to students with identified disabilities under IDEA, focusing on individualized education plans (IEPs) to address specific learning needs. Response to Intervention (RTI) uses a tiered approach to early identification and support, delivering varying levels of interventions based on student performance without initially classifying disabilities. Key differences include RTI's proactive, data-driven model for prevention and monitoring versus Special Education's reactive, legally mandated support system for students with formal disability diagnoses.
Core Objectives: Special Education vs RTI
Special Education primarily targets individualized academic and behavioral support for students with identified disabilities, emphasizing tailored instruction and specialized services to meet unique learning needs. Response to Intervention (RTI) focuses on early identification and prevention by providing tiered, evidence-based interventions to all students, aiming to address learning difficulties before considering special education placement. Both frameworks prioritize improving student outcomes, but Special Education caters to legally qualified disabilities while RTI enhances general education through systematic monitoring and targeted interventions.
Legal Frameworks Governing Both Approaches
The legal frameworks governing Special Education and Response to Intervention (RTI) are primarily anchored in the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA), which mandates Free Appropriate Public Education (FAPE) for eligible students with disabilities and outlines evaluation procedures for special education services. RTI operates within the framework of IDEA as a pre-referral process to identify students struggling academically or behaviorally, aiming to provide early interventions before special education eligibility is determined. Both approaches require adherence to state and federal regulations ensuring procedural safeguards, parental rights, and evidence-based instructional support to promote equitable educational outcomes.
Eligibility Criteria for Special Education and RTI
Eligibility criteria for Special Education require a documented disability that adversely affects educational performance and necessitates specialized instruction under IDEA guidelines. In contrast, Response to Intervention (RTI) eligibility is based on a tiered approach assessing student progress through evidence-based interventions without initial formal disability identification. RTI serves as a proactive framework to prevent academic failure, while Special Education eligibility requires comprehensive evaluations confirming a specific disability.
Intervention Strategies: Tailored vs Tiered Support
Special Education employs tailored intervention strategies designed to meet the unique needs of students with identified disabilities, offering individualized instruction and accommodations. Response to Intervention (RTI) utilizes a tiered support system that provides increasing levels of assistance based on student progress, starting with universal interventions and escalating to more intensive support. Both approaches emphasize early identification and support, but Special Education centers on personalized plans, whereas RTI focuses on data-driven, multi-tiered preventative measures.
Roles of Teachers and Specialists in Each Model
Teachers in Special Education develop individualized education plans (IEPs) tailored to students with disabilities, collaborating closely with specialists such as speech therapists and occupational therapists to address specific learning needs. In the Response to Intervention (RTI) model, general education teachers implement tiered interventions and monitor student progress, while specialists provide targeted support and data analysis to refine instructional strategies. Both models rely on a multidisciplinary team approach, emphasizing continuous assessment and adjustment to optimize student outcomes.
Measuring Student Progress: IEPs vs RTI Data
Measuring student progress in special education relies heavily on Individualized Education Programs (IEPs), which provide tailored goals and benchmarks for students with disabilities. Response to Intervention (RTI) data tracks student performance through universal screenings and ongoing progress monitoring across tiers, emphasizing early identification and support. The contrast lies in IEPs offering customized, legally mandated objectives, while RTI uses data-driven interventions to guide instructional decisions and prevent academic failure.
Choosing the Right Approach for Student Success
Choosing the right approach between Special Education and Response to Intervention (RTI) depends on a student's unique learning needs and academic performance data. Special Education offers tailored, legally mandated services for students with identified disabilities, while RTI provides tiered, early support to prevent academic failure through targeted interventions and progress monitoring. Educators can enhance student success by using RTI to address learning difficulties and reserving Special Education for cases where intensive, individualized support is necessary.
Special Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com