Modular instruction breaks down complex content into smaller, manageable units, enhancing learner comprehension and retention. This approach allows customization to fit Your specific learning pace and needs, promoting efficient knowledge acquisition. Explore the rest of the article to discover how modular instruction can transform Your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
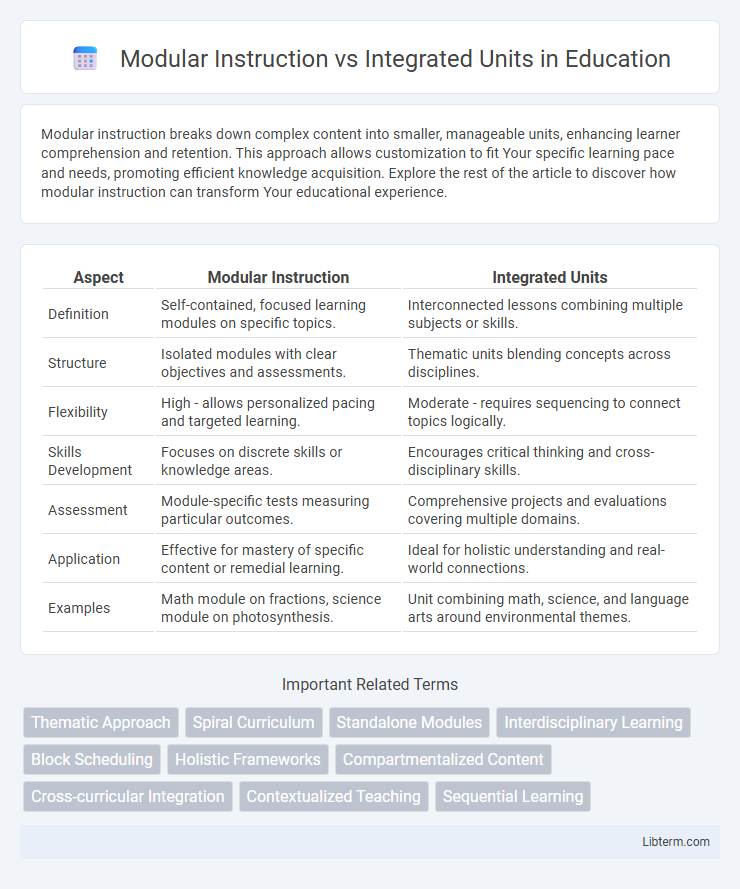
| Aspect | Modular Instruction | Integrated Units |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Self-contained, focused learning modules on specific topics. | Interconnected lessons combining multiple subjects or skills. |
| Structure | Isolated modules with clear objectives and assessments. | Thematic units blending concepts across disciplines. |
| Flexibility | High - allows personalized pacing and targeted learning. | Moderate - requires sequencing to connect topics logically. |
| Skills Development | Focuses on discrete skills or knowledge areas. | Encourages critical thinking and cross-disciplinary skills. |
| Assessment | Module-specific tests measuring particular outcomes. | Comprehensive projects and evaluations covering multiple domains. |
| Application | Effective for mastery of specific content or remedial learning. | Ideal for holistic understanding and real-world connections. |
| Examples | Math module on fractions, science module on photosynthesis. | Unit combining math, science, and language arts around environmental themes. |
Understanding Modular Instruction: Key Features
Modular instruction breaks content into self-contained, focused units designed for mastery of specific skills or concepts, enhancing learner autonomy and pacing. Each module includes clear objectives, assessments, and resources tailored to targeted outcomes, ensuring concentrated and efficient knowledge acquisition. This approach contrasts with integrated units by emphasizing discrete, sequential learning segments rather than interdisciplinary or thematic connections.
What Are Integrated Units? An Overview
Integrated units combine multiple subject areas into a cohesive learning experience, enhancing cross-disciplinary understanding and real-world application. They allow students to explore interconnected concepts through thematic lessons, promoting deeper engagement and retention. This approach contrasts with modular instruction, which divides subjects into isolated segments focusing on specific skills or knowledge.
Historical Development of Modular and Integrated Approaches
The historical development of modular instruction began in the mid-20th century as educators sought to break down complex subjects into self-contained, manageable units to enhance individualized learning and assessment. Integrated units emerged later, responding to critiques of fragmentation by promoting interdisciplinary connections that mirror real-world contexts, fostering deeper cognitive engagement through thematic, holistic curricula. Both approaches evolved through educational research emphasizing student-centered learning, with modular instruction rooted in behaviorist theory and integrated units influenced by constructivist principles.
Comparing Curriculum Organization: Modular vs Integrated
Modular instruction divides curriculum into distinct, self-contained units focusing on specific skills or topics, enabling targeted learning and easy assessment of individual competencies. Integrated units blend multiple subject areas around common themes or problems, promoting interdisciplinary understanding and holistic skill development. Curriculum organization in modular approaches allows flexibility and depth in discrete subjects, whereas integrated units foster connections across disciplines for broader cognitive engagement.
Advantages of Modular Instruction for Learners
Modular instruction offers learners flexibility by allowing them to progress at their own pace, which enhances individualized learning and better retention of information. This method supports targeted skill development through clearly defined modules, making it easier for learners to focus on specific competencies. Furthermore, modular instruction facilitates easier assessment and tracking of learner progress, improving both motivation and accountability.
Benefits of Integrated Units in Fostering Connections
Integrated units enhance interdisciplinary learning by weaving together multiple subjects, promoting deeper understanding and real-world application of knowledge. These units encourage critical thinking and creativity by allowing students to draw connections across different content areas, fostering a holistic educational experience. The collaborative nature of integrated units supports social skills development and increases student engagement through cohesive, meaningful instruction.
Potential Challenges in Implementing Modular Instruction
Implementing modular instruction presents potential challenges such as ensuring consistent alignment between modules and curriculum standards, which can lead to gaps in student learning if not managed carefully. Teachers may face difficulties in pacing and sequencing content effectively without the integration and thematic cohesion found in integrated units. Limited opportunities for interdisciplinary learning and real-world application may also reduce student engagement and critical thinking development.
Obstacles Faced with Integrated Unit Planning
Integrated unit planning often encounters obstacles such as the complexity of aligning cross-disciplinary standards and objectives, which can lead to inconsistent learning outcomes. Coordinating collaborative efforts among teachers from different subject areas requires significant time and communication, impacting the feasibility of cohesive unit development. Limited resources and lack of professional development specific to interdisciplinary teaching further hinder the effective implementation of integrated instructional units.
Assessment Strategies: Modular Instruction vs Integrated Units
Modular Instruction emphasizes frequent, focused assessments aligned with individual learning modules, enabling targeted feedback and mastery checks for specific skills or knowledge areas. Integrated Units employ holistic assessment strategies that evaluate cumulative understanding across multiple subjects, promoting critical thinking and application of interdisciplinary concepts. Both approaches benefit from formative and summative assessments but differ in scope, with modular assessments being more granular and integrated unit assessments assessing broader learning outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between modular instruction and integrated units depends on curriculum goals, student learning styles, and subject complexity. Modular instruction offers flexible, targeted content delivery suited for mastery of specific skills, while integrated units promote interdisciplinary connections and holistic understanding. Evaluating the balance between focused skill development and thematic integration is essential for tailoring instructional strategies to maximize student engagement and achievement.
Modular Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com