Annotations enhance understanding by providing concise explanations or notes that clarify complex information within a text. They enable you to quickly grasp key concepts and retain essential details for future reference. Explore the rest of this article to discover effective annotation techniques and tools.
Table of Comparison
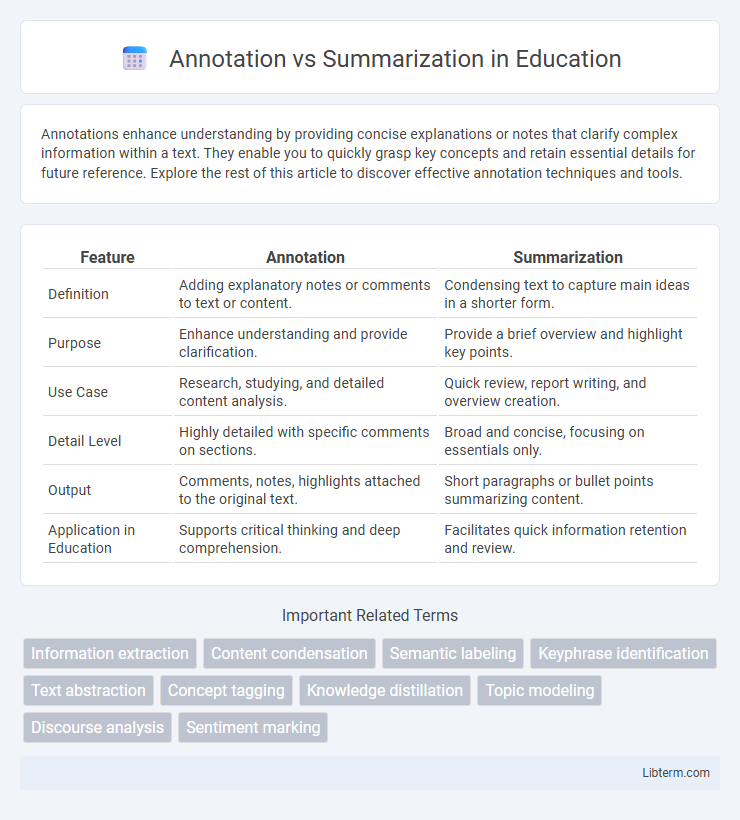
| Feature | Annotation | Summarization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adding explanatory notes or comments to text or content. | Condensing text to capture main ideas in a shorter form. |
| Purpose | Enhance understanding and provide clarification. | Provide a brief overview and highlight key points. |
| Use Case | Research, studying, and detailed content analysis. | Quick review, report writing, and overview creation. |
| Detail Level | Highly detailed with specific comments on sections. | Broad and concise, focusing on essentials only. |
| Output | Comments, notes, highlights attached to the original text. | Short paragraphs or bullet points summarizing content. |
| Application in Education | Supports critical thinking and deep comprehension. | Facilitates quick information retention and review. |
Introduction to Annotation and Summarization
Annotation involves adding explanatory notes or comments directly to a text to enhance understanding, highlight key points, or provide critical insights, serving as a detailed reference for readers or researchers. Summarization condenses the main ideas or essential information of a text into a shorter form, facilitating quick comprehension and overview without delving into detailed analysis. Both techniques support information processing but differ in depth and purpose, with annotation focusing on elaboration and summarization on brevity.
Defining Annotation: Key Characteristics
Annotation involves adding explanatory notes or comments to a text, enhancing understanding by highlighting important details, interpretations, or connections. Key characteristics include its interactive nature, context-specific insights, and the preservation of the original content's structure for reference. In contrast to summarization, annotation aims to deepen comprehension without reducing the text to a shorter form.
Understanding Summarization: Core Concepts
Summarization condenses lengthy content into concise versions, capturing the main ideas while excluding extraneous details. It involves techniques like extractive summarization, which selects key phrases directly from the text, and abstractive summarization, which generates new sentences to convey essential information. Effective summarization enhances information retrieval, improves readability, and supports rapid comprehension across diverse domains.
Types of Annotation Techniques
Annotation techniques include highlighting, underlining, margin notes, and digital tagging, each enabling deeper interaction with the text by marking key points or insights. Unlike summarization, which condenses the main ideas into brief overviews, annotations provide detailed, context-specific comments that enhance comprehension and recall. Common annotation types involve explanatory notes, questions, paraphrasing, and cross-references, facilitating a dynamic and personalized learning experience.
Types of Summarization Methods
Extractive summarization selects key sentences or phrases directly from the source text, preserving the original wording to highlight important information. Abstractive summarization generates new sentences that capture the core meaning, using advanced natural language processing techniques for more coherent and concise summaries. Hybrid summarization combines both extractive and abstractive methods to improve the quality and relevance of the final summary.
Annotation vs Summarization: Key Differences
Annotation involves adding explanatory notes or comments to a text to clarify meaning, while summarization condenses the original content into a brief overview capturing main ideas. Key differences include purpose, with annotation aimed at enhancing understanding and summarization focused on brevity and information extraction. Annotation preserves detailed context, whereas summarization transforms content into a compact format for quick comprehension.
Use Cases for Annotation
Annotation enhances document understanding by adding metadata, comments, or explanations directly onto text, images, or videos, making it ideal for educational purposes, legal document analysis, and content review processes. It supports collaborative workflows by enabling teams to highlight specific details, track changes, and provide contextual insights in research, software development, and quality assurance. Annotation is essential in machine learning training datasets to label features, improve model accuracy, and facilitate data categorization.
Practical Applications of Summarization
Summarization condenses large documents into concise versions, enhancing efficiency in information retrieval for research, news aggregation, and customer service. It enables quick understanding of key points in legal briefs, medical records, and scientific papers, saving time and improving decision-making. Summarization tools powered by AI support content management systems and educational platforms by providing clear, relevant overviews.
Challenges in Annotation and Summarization
Annotation faces challenges such as ensuring consistency across diverse annotators and managing the complexity of domain-specific labels, which can lead to variability and reduced data quality. Summarization struggles with capturing the essence of long or complex texts while maintaining factual accuracy and coherence, often requiring advanced natural language understanding to avoid information loss or distortion. Both tasks demand significant human effort and sophisticated algorithms to balance detail preservation and interpretability effectively.
Choosing Between Annotation and Summarization
Choosing between annotation and summarization depends on the specific goal of information processing. Annotation is ideal for highlighting key points and adding interpretive notes to facilitate deeper understanding and quick reference. Summarization condenses the main ideas into a brief overview, making it suitable for efficient information retrieval and quick comprehension.
Annotation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com