Thematic analysis is a qualitative research method focused on identifying, analyzing, and reporting patterns within data, providing a rich and detailed understanding of complex information. It enables you to organize your data into meaningful themes that reveal insights into participants' experiences and perspectives. Explore the rest of this article to learn practical steps and tips for conducting an effective thematic analysis.
Table of Comparison
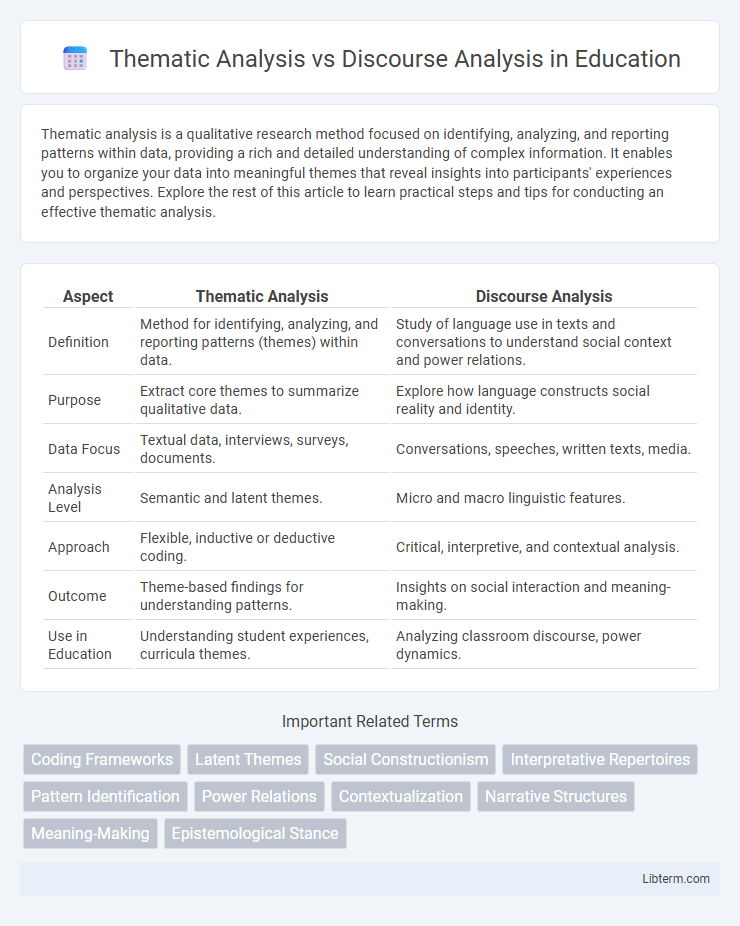
| Aspect | Thematic Analysis | Discourse Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Method for identifying, analyzing, and reporting patterns (themes) within data. | Study of language use in texts and conversations to understand social context and power relations. |
| Purpose | Extract core themes to summarize qualitative data. | Explore how language constructs social reality and identity. |
| Data Focus | Textual data, interviews, surveys, documents. | Conversations, speeches, written texts, media. |
| Analysis Level | Semantic and latent themes. | Micro and macro linguistic features. |
| Approach | Flexible, inductive or deductive coding. | Critical, interpretive, and contextual analysis. |
| Outcome | Theme-based findings for understanding patterns. | Insights on social interaction and meaning-making. |
| Use in Education | Understanding student experiences, curricula themes. | Analyzing classroom discourse, power dynamics. |
Introduction to Thematic and Discourse Analysis
Thematic Analysis systematically identifies, analyzes, and reports patterns or themes within qualitative data, offering a flexible approach to understanding participants' experiences. Discourse Analysis examines language use beyond the sentence level, focusing on social context, power relations, and how meaning is constructed through communication. Both methods provide critical insights into qualitative research, with Thematic Analysis emphasizing thematic patterns and Discourse Analysis concentrating on language and social interaction dynamics.
Defining Thematic Analysis
Thematic Analysis is a qualitative research method focused on identifying, analyzing, and reporting patterns or themes within textual data, offering detailed insights into participants' experiences and perceptions. It involves coding data to categorize themes, enabling researchers to capture semantic and latent meanings across a dataset. Unlike Discourse Analysis, which examines language use and social context, Thematic Analysis emphasizes the content of the data without requiring extensive attention to linguistic structures or power relations.
Defining Discourse Analysis
Discourse Analysis examines language use beyond the sentence level, focusing on how social context, power relations, and ideology shape communication patterns within texts and conversations. It explores how meaning is constructed through interaction and how language reflects and influences societal structures. This method contrasts with Thematic Analysis, which identifies patterns or themes within data without emphasizing the broader social and linguistic contexts.
Key Differences Between Thematic and Discourse Analysis
Thematic Analysis identifies and categorizes patterns or themes within qualitative data to understand underlying meanings, focusing primarily on content across the dataset. Discourse Analysis examines language use, context, and social interaction in communication, emphasizing how language constructs social realities and power relations. Key differences include Thematic Analysis's broader aim to reveal common themes versus Discourse Analysis's detailed investigation of language structures and social context.
When to Use Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis is ideal for identifying and interpreting patterns across qualitative data, making it useful when the goal is to explore common themes and experiences within participant responses. It is preferred in studies aiming to summarize key ideas without delving into language use or social context nuances. Researchers use thematic analysis when they seek a flexible and accessible method to organize large datasets into meaningful themes for insights into shared meanings.
When to Use Discourse Analysis
Discourse analysis is ideal for examining how language constructs social realities, power relations, and identities within specific contexts, making it suitable for studying political speeches, media narratives, and institutional communication. It focuses on the interactional and interpretive aspects of language rather than just thematic content, allowing researchers to uncover underlying social structures and ideological frameworks. Choose discourse analysis when the goal is to explore the role of language in shaping social practices and meaning beyond surface-level themes.
Methodological Steps in Thematic Analysis
Thematic Analysis involves systematic coding of qualitative data to identify, analyze, and report patterns or themes, typically following six key steps: familiarization with data, generating initial codes, searching for themes, reviewing themes, defining and naming themes, and producing the final report. This method emphasizes organizing data into meaningful clusters to interpret underlying meanings and experiences, contrasting with Discourse Analysis that focuses on language use and social context. The clarity and flexibility of Thematic Analysis make it a widely adopted approach in qualitative research for addressing complex datasets.
Methodological Steps in Discourse Analysis
Discourse Analysis involves systematic examination of language use in social contexts, emphasizing the identification of patterns, power relations, and ideologies through detailed transcription, coding, and interpretative stages. Key methodological steps include selecting discourse data, segmenting texts into meaningful units, identifying discursive constructions, analyzing language features such as metaphors and modality, and situating findings within broader socio-political contexts. This approach contrasts with Thematic Analysis, which primarily focuses on categorizing themes across qualitative data without extensive linguistic or contextual analysis.
Strengths and Limitations of Each Approach
Thematic Analysis excels in identifying and organizing patterns within large qualitative datasets, offering flexibility and clarity in presenting key themes but may overlook the broader social or contextual influences embedded in language use. Discourse Analysis provides deep insight into power dynamics, social constructs, and language functions within conversations, highlighting the role of context and interaction, yet it can be time-intensive and less structured for comparing large volumes of data systematically. Each method's strengths and limitations depend on research goals: Thematic Analysis suits broad pattern detection, while Discourse Analysis uncovers nuanced socio-linguistic meanings.
Choosing the Right Analysis for Your Research
Choosing the right analysis for your research depends on your objectives: Thematic Analysis excels in identifying and interpreting patterns or themes within qualitative data, making it ideal for exploring participants' experiences and perceptions. Discourse Analysis, on the other hand, focuses on language use and social context, examining how power, identity, and ideology are constructed through communication. For studies centered on meaning and narrative structure, Thematic Analysis is preferable, whereas Discourse Analysis suits research investigating language-in-use and social interactions.
Thematic Analysis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com