Content-Based Instruction focuses on teaching language through subject matter, allowing learners to acquire language skills naturally while engaging with meaningful content. This approach enhances both language proficiency and knowledge of the topic, making learning more relevant and motivating. Discover how Content-Based Instruction can transform your language learning experience in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
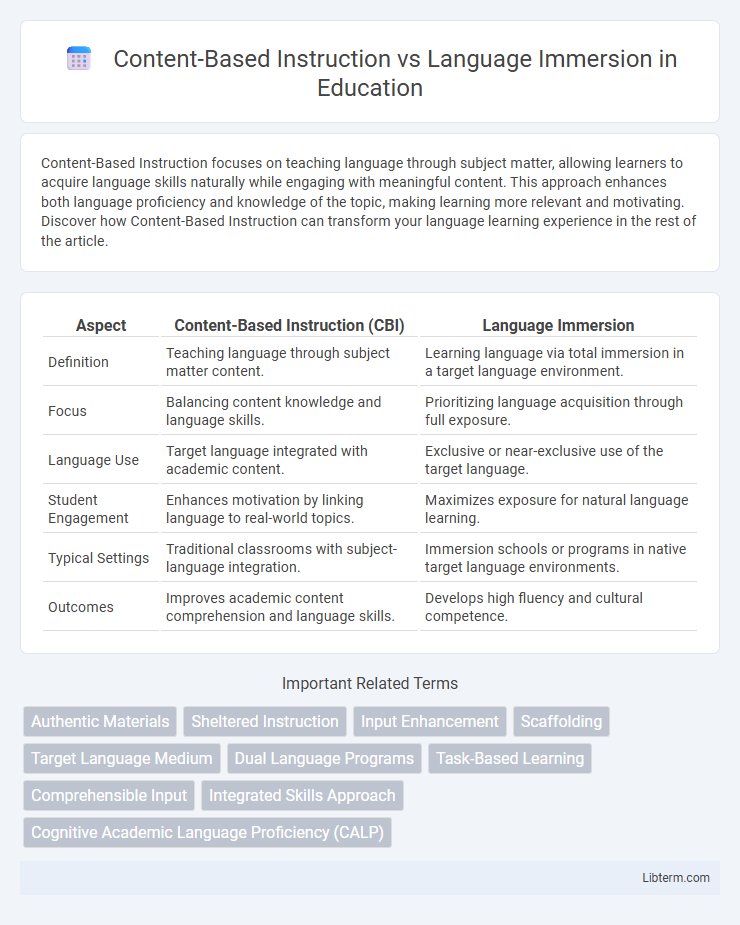
| Aspect | Content-Based Instruction (CBI) | Language Immersion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teaching language through subject matter content. | Learning language via total immersion in a target language environment. |
| Focus | Balancing content knowledge and language skills. | Prioritizing language acquisition through full exposure. |
| Language Use | Target language integrated with academic content. | Exclusive or near-exclusive use of the target language. |
| Student Engagement | Enhances motivation by linking language to real-world topics. | Maximizes exposure for natural language learning. |
| Typical Settings | Traditional classrooms with subject-language integration. | Immersion schools or programs in native target language environments. |
| Outcomes | Improves academic content comprehension and language skills. | Develops high fluency and cultural competence. |
Understanding Content-Based Instruction
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) integrates language learning with subject matter, emphasizing comprehension and use of academic content in the target language. This approach enhances cognitive skills alongside linguistic proficiency by focusing on meaningful communication in contexts such as science, history, or math. Unlike Language Immersion, which immerses learners entirely in the language environment, CBI strategically combines language objectives with content goals to promote both language acquisition and academic achievement.
Defining Language Immersion Programs
Language immersion programs engage students in learning a new language by surrounding them with that language in everyday contexts, promoting natural acquisition through consistent exposure. Content-Based Instruction integrates language learning with subject matter teaching, where language skills develop alongside academic content. Immersion programs emphasize full or partial language exposure to accelerate fluency by embedding communication within meaningful activities.
Objectives: CBI vs Language Immersion
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) targets simultaneous development of subject matter knowledge and language proficiency by integrating academic content with language learning objectives. Language Immersion prioritizes creating a naturalistic environment where learners acquire language skills primarily through contextual communication and cultural exposure. CBI emphasizes dual-focused cognitive skills in both language and content mastery, while Language Immersion seeks fluency and cultural competence through immersive social interaction.
Curriculum Structure and Design
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) integrates subject matter learning with language acquisition, aligning curriculum design to thematic units that promote vocabulary and grammar through academic content. Language Immersion programs structure curricula entirely around the target language, emphasizing natural language use by delivering all subjects through that language to foster fluency and cultural competence. Both approaches prioritize meaningful communication but differ in that CBI balances language goals with content mastery, while immersion focuses on language dominance in a content-rich environment.
Teacher Roles and Requirements
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) requires teachers to integrate subject matter expertise with language teaching skills, emphasizing scaffolded language input and contextualized vocabulary to enhance comprehension. Language Immersion teachers must possess high proficiency in the target language and the ability to create a fully immersive environment that promotes natural language acquisition through meaningful interaction. Both approaches demand strong classroom management and the capacity to adapt instruction to diverse learner needs while fostering language development within content learning.
Language Skills Development
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) enhances language skills through subject matter learning, integrating vocabulary, grammar, and communication within academic or thematic contexts. Language Immersion promotes fluency and comprehension by exposing learners to the target language exclusively, fostering natural language acquisition in real-life situations. Both methods develop speaking, listening, reading, and writing abilities but differ in instructional focus and learning environment intensity.
Student Engagement and Motivation
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) enhances student engagement by integrating meaningful subject matter with language learning, which increases motivation through relevance and real-world application. Language Immersion fosters motivation by surrounding students with the target language in authentic contexts, promoting natural acquisition and cultural connection. Both methods boost student participation, but CBI emphasizes cognitive engagement through content, while immersion focuses on immersive experiential learning.
Assessment Strategies
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) assessment strategies prioritize evaluating both language proficiency and subject matter comprehension through integrated tasks like project presentations and thematic tests. Language Immersion programs emphasize performance-based assessments and ongoing oral proficiency evaluations to measure real-time communication skills within immersive contexts. Both approaches benefit from formative assessments that track learner progress and adapt instruction to reinforce language acquisition and content mastery.
Advantages and Challenges
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) promotes language learning through subject matter engagement, enhancing cognitive skills and contextual vocabulary acquisition but demands proficient instructors skilled in both language and content. Language Immersion offers immersive linguistic environments that accelerate fluency and cultural understanding, yet poses challenges in balancing curriculum standards and supporting learners with limited prior knowledge. Both methods require careful program design to address diverse learner needs and optimize language proficiency outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Learners
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) integrates language learning with subject matter mastery, promoting cognitive engagement and contextual vocabulary acquisition ideal for learners needing academic or professional language skills. Language Immersion emphasizes total language exposure through environmental integration, fostering natural fluency and cultural understanding best suited for beginners or those seeking conversational proficiency. Selecting the right approach depends on learners' goals, proficiency levels, and learning environments to enhance motivation and achieve effective language acquisition outcomes.
Content-Based Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com