Blended learning combines traditional face-to-face instruction with online educational resources, creating a dynamic and flexible learning environment tailored to individual needs. This approach enhances engagement and improves retention by allowing you to access materials anytime, anywhere, while benefiting from direct teacher support. Explore the rest of the article to discover how blended learning can transform your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
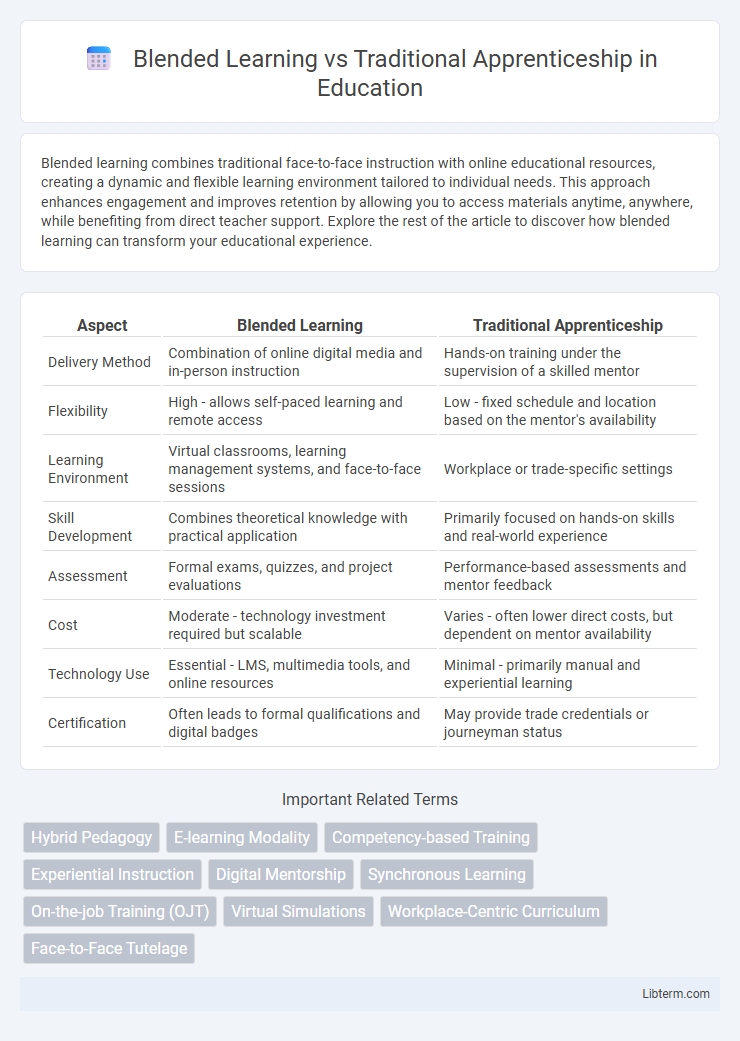
| Aspect | Blended Learning | Traditional Apprenticeship |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Method | Combination of online digital media and in-person instruction | Hands-on training under the supervision of a skilled mentor |
| Flexibility | High - allows self-paced learning and remote access | Low - fixed schedule and location based on the mentor's availability |
| Learning Environment | Virtual classrooms, learning management systems, and face-to-face sessions | Workplace or trade-specific settings |
| Skill Development | Combines theoretical knowledge with practical application | Primarily focused on hands-on skills and real-world experience |
| Assessment | Formal exams, quizzes, and project evaluations | Performance-based assessments and mentor feedback |
| Cost | Moderate - technology investment required but scalable | Varies - often lower direct costs, but dependent on mentor availability |
| Technology Use | Essential - LMS, multimedia tools, and online resources | Minimal - primarily manual and experiential learning |
| Certification | Often leads to formal qualifications and digital badges | May provide trade credentials or journeyman status |
Introduction to Blended Learning and Traditional Apprenticeship
Blended learning integrates digital tools with face-to-face instruction, enhancing flexibility and personalized skill development by combining online modules and hands-on practice. Traditional apprenticeship emphasizes direct mentorship and immersive on-the-job training, providing experiential learning through real-world tasks under expert supervision. The fusion of technology in blended learning offers scalable educational experiences, while traditional apprenticeship remains rooted in practical, skill-focused craftsmanship.
Core Principles of Blended Learning
Blended learning combines online digital media with traditional face-to-face instruction, emphasizing flexibility, personalized learning paths, and interactive content to enhance skill acquisition. Core principles include learner-centered approaches, active participation through multimedia resources, and continuous assessment to tailor experiences toward individual progress. This educative method contrasts traditional apprenticeship, which relies heavily on hands-on, mentor-guided experience without extensive digital integration.
Fundamentals of Traditional Apprenticeship
Traditional apprenticeships emphasize hands-on learning through direct mentorship, where novices acquire skills by working alongside experienced craftspeople in real-world environments. This model prioritizes tacit knowledge transfer, practical problem-solving, and gradual skill mastery over extended periods, fostering deep expertise. Structured progression, evaluation through demonstrated competence, and cultural immersion within a trade's community form the core fundamentals of traditional apprenticeship.
Flexibility and Accessibility Compared
Blended learning offers greater flexibility by combining online digital media with traditional face-to-face instruction, allowing apprentices to access training materials anytime and anywhere, which contrasts with the fixed schedules and locations typical of traditional apprenticeships. This approach enhances accessibility for learners with varying circumstances, such as those balancing work or family commitments, expanding opportunities to a wider demographic. Traditional apprenticeships, while effective in hands-on skill development, often lack the adaptability to accommodate diverse learning paces and remote participation.
Skill Acquisition and Practical Experience
Blended learning integrates digital tools with hands-on training, enhancing skill acquisition through interactive simulations and real-world practice, which accelerates competency development compared to traditional apprenticeship. Traditional apprenticeships offer immersive, on-site experience and direct mentorship, fostering deep practical knowledge grounded in real-time problem-solving. Combining virtual resources with face-to-face guidance optimizes both theoretical understanding and practical expertise, improving overall skill proficiency and adaptability in diverse work environments.
Technological Integration in Learning
Blended learning incorporates advanced digital tools and online platforms, enhancing accessibility and interactivity in skill acquisition compared to traditional apprenticeship methods. Traditional apprenticeship relies heavily on face-to-face mentorship and hands-on experience but lacks the scalability and flexibility provided by technology-enhanced learning environments. Integrating virtual simulations, multimedia resources, and real-time feedback systems in blended learning accelerates competency development while preserving practical component authenticity.
Learner Engagement and Motivation
Blended learning enhances learner engagement by combining digital tools with hands-on experiences, catering to varied learning styles and increasing motivation through interactive content and instant feedback. Traditional apprenticeships encourage motivation by providing real-world practice and direct mentorship, fostering deep skill acquisition and personal growth. Integrating technology in blended learning creates a dynamic environment that often surpasses the motivational impact of conventional apprenticeship methods.
Assessment Methods and Outcomes
Blended learning integrates digital assessments such as quizzes, simulations, and real-time feedback tools, enhancing continuous evaluation and personalized learning paths compared to traditional apprenticeships, which rely heavily on observational assessments and practical demonstrations under mentor supervision. The outcomes of blended learning often include measurable skill acquisition through data analytics and standardized testing, while traditional apprenticeships emphasize mastery through hands-on experience and direct mentor evaluation. This comparison highlights the growing effectiveness of blended learning in providing flexible, scalable, and quantifiable assessments alongside traditional, experience-based competency validation.
Industry Suitability and Application
Blended learning integrates digital tools with hands-on training, making it highly suitable for industries like IT, healthcare, and manufacturing where theoretical knowledge and practical skills must evolve rapidly. Traditional apprenticeship remains effective in trades such as carpentry, plumbing, and electrical work, where on-site experience and mentorship are critical for mastering tactile techniques. Combining both methods can optimize workforce development by addressing the unique demands of various industrial sectors.
Future Trends in Vocational Education
Blended learning integrates digital technology with hands-on training, enhancing flexibility and access in vocational education compared to traditional apprenticeships, which rely heavily on in-person mentorship and skill practice. Future trends indicate increasing adoption of virtual reality (VR) and artificial intelligence (AI) to simulate real-world environments, enabling more immersive and personalized learning experiences. These innovations aim to bridge skill gaps faster, catering to evolving industry demands and fostering lifelong learning in vocational sectors.
Blended Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com