Self-assessment is a critical process that helps you evaluate your strengths, weaknesses, and areas for growth, fostering personal and professional development. By regularly reflecting on your achievements and challenges, you can set realistic goals that align with your values and ambitions. Discover how effective self-assessment techniques can transform your approach by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
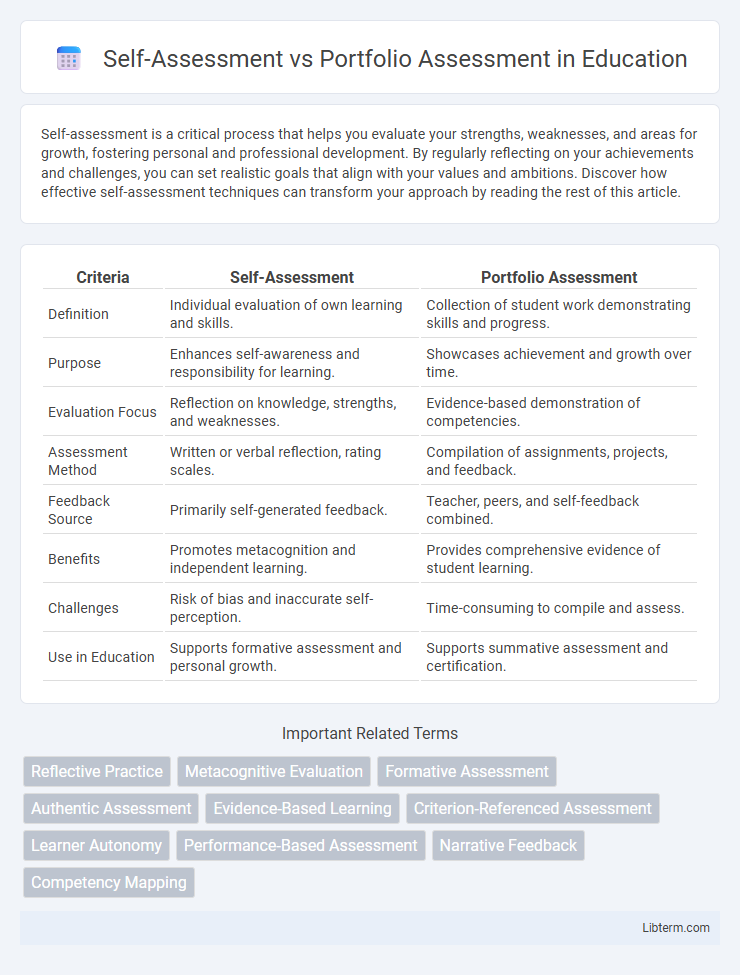
| Criteria | Self-Assessment | Portfolio Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual evaluation of own learning and skills. | Collection of student work demonstrating skills and progress. |
| Purpose | Enhances self-awareness and responsibility for learning. | Showcases achievement and growth over time. |
| Evaluation Focus | Reflection on knowledge, strengths, and weaknesses. | Evidence-based demonstration of competencies. |
| Assessment Method | Written or verbal reflection, rating scales. | Compilation of assignments, projects, and feedback. |
| Feedback Source | Primarily self-generated feedback. | Teacher, peers, and self-feedback combined. |
| Benefits | Promotes metacognition and independent learning. | Provides comprehensive evidence of student learning. |
| Challenges | Risk of bias and inaccurate self-perception. | Time-consuming to compile and assess. |
| Use in Education | Supports formative assessment and personal growth. | Supports summative assessment and certification. |
Defining Self-Assessment and Portfolio Assessment
Self-assessment involves individuals evaluating their own skills, knowledge, and performance against set criteria, fostering personal reflection and self-regulated learning. Portfolio assessment compiles a curated collection of a learner's work over time, providing comprehensive evidence of their achievements, skills development, and progress. Both methods emphasize learner involvement but differ in approach, with self-assessment centered on introspection and portfolio assessment focusing on documentation and demonstration of proficiency.
Key Differences between Self-Assessment and Portfolio Assessment
Self-assessment requires learners to evaluate their own understanding and skills, promoting self-reflection and personal responsibility, whereas portfolio assessment involves compiling diverse work samples that demonstrate learning progress and achievements over time. Self-assessment emphasizes internal judgment and metacognitive skills, while portfolio assessment provides external evidence for educators to review comprehensive performance. The primary differentiation lies in self-assessment's introspective nature versus portfolio assessment's focus on tangible artifacts and longitudinal evaluation.
Benefits of Self-Assessment in Learning
Self-assessment enhances learner autonomy by encouraging reflection on personal strengths and weaknesses, fostering deeper understanding and self-regulation. It promotes critical thinking skills as students actively evaluate their own progress against set criteria, leading to targeted improvements. Empowering learners this way increases motivation and engagement, resulting in more effective and personalized learning experiences.
Advantages of Portfolio Assessment
Portfolio assessment offers a comprehensive view of a learner's progress by showcasing diverse work samples and reflections over time, providing tangible evidence of skills and growth. It encourages critical thinking and self-reflection, fostering deeper engagement with the material compared to self-assessment alone. Educators benefit from portfolio evaluations as they obtain a multifaceted and authentic representation of student achievement that supports personalized feedback and targeted instruction.
Challenges Faced in Self-Assessment
Self-assessment challenges include bias and lack of objectivity, where learners may overestimate or underestimate their abilities. Insufficient self-awareness can lead to inaccurate evaluations, hindering skill development and progress tracking. Time constraints and limited guidance further complicate effective self-assessment in educational and professional settings.
Common Issues with Portfolio Assessment
Portfolio assessment often faces issues such as inconsistent evaluation criteria, leading to subjective grading and reduced reliability. Challenges also include the time-consuming nature of compiling and reviewing portfolios, which can hinder timely feedback and assessment efficiency. Additionally, portfolios may lack standardization, making comparisons across students difficult and affecting the overall validity of the assessment process.
Roles of Teachers in Both Assessment Types
Teachers act as facilitators in self-assessment by guiding students to set personal learning goals and reflect on their progress, fostering metacognitive skills and autonomy. In portfolio assessment, educators take on the role of curators and evaluators, selecting diverse student work samples to provide comprehensive feedback and track growth over time. Both assessment types require teachers to create supportive environments that encourage honest self-evaluation and meaningful documentation of learning achievements.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Self-assessment cultivates intrinsic motivation by encouraging students to reflect on their learning progress and set personal goals, which enhances engagement through ownership of their educational journey. Portfolio assessment provides tangible evidence of growth and accomplishments, fostering sustained motivation by visibly tracking development over time. Both methods promote active learning, but portfolios often increase engagement by integrating creativity and self-expression, while self-assessment deepens metacognitive skills and self-regulation.
Best Practices for Combining Both Methods
Combining self-assessment and portfolio assessment enhances student learning by fostering reflective practice and showcasing diverse skills and achievements. Best practices include setting clear criteria for both methods, encouraging regular self-reflection tied to portfolio evidence, and providing timely, constructive feedback to guide improvement. Integrating digital tools allows seamless documentation and analysis, supporting a holistic evaluation that captures growth over time.
Choosing the Right Assessment for Your Context
Self-assessment empowers learners to reflect on their own progress and identify strengths and weaknesses, fostering autonomy and metacognitive skills, while portfolio assessment provides tangible evidence of learning through curated work samples and documentation over time. Choose self-assessment when encouraging independence and self-regulation is a priority, especially in formative settings, and opt for portfolio assessment when comprehensive evaluation of skills, growth, and achievements is required, particularly in summative or performance-based contexts. Aligning the assessment method with your educational goals, learner needs, and available resources ensures an accurate and meaningful measure of competence.
Self-Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com