A deficit mindset focuses on limitations and perceived shortcomings rather than strengths and opportunities for growth, often hindering personal and professional development. Shifting away from this mindset enables you to embrace challenges and foster resilience, leading to greater success and fulfillment. Explore the rest of the article to discover strategies for overcoming a deficit mindset and unlocking your full potential.
Table of Comparison
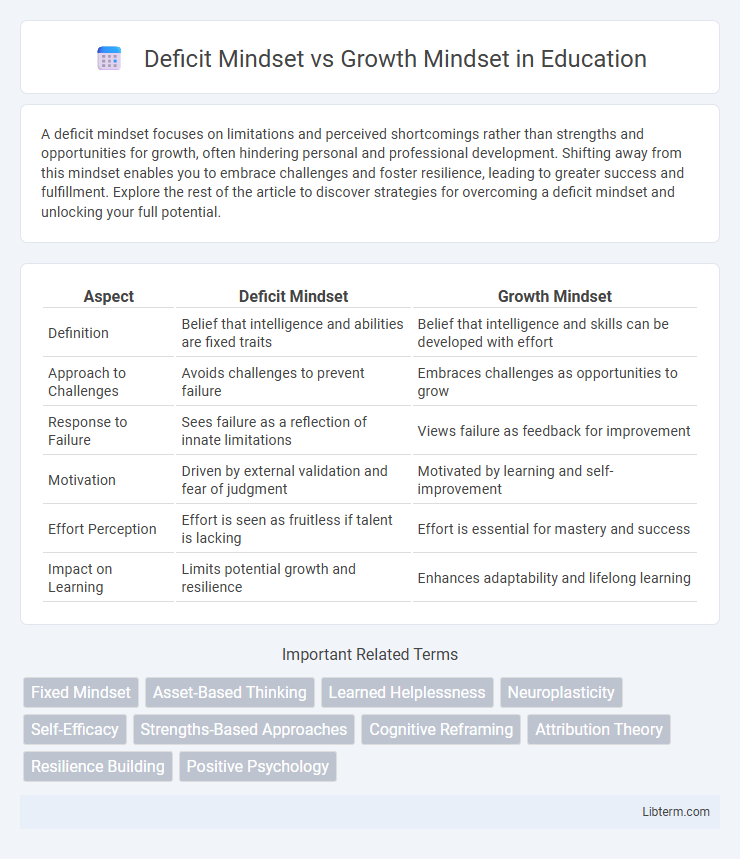
| Aspect | Deficit Mindset | Growth Mindset |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Belief that intelligence and abilities are fixed traits | Belief that intelligence and skills can be developed with effort |
| Approach to Challenges | Avoids challenges to prevent failure | Embraces challenges as opportunities to grow |
| Response to Failure | Sees failure as a reflection of innate limitations | Views failure as feedback for improvement |
| Motivation | Driven by external validation and fear of judgment | Motivated by learning and self-improvement |
| Effort Perception | Effort is seen as fruitless if talent is lacking | Effort is essential for mastery and success |
| Impact on Learning | Limits potential growth and resilience | Enhances adaptability and lifelong learning |
Understanding the Deficit Mindset
The deficit mindset centers on perceived limitations and fixed abilities, leading individuals to view challenges as threats rather than opportunities for growth. This perspective often results in self-doubt, fear of failure, and resistance to change, which can hinder learning and personal development. Recognizing the characteristics of a deficit mindset is crucial for shifting toward a growth mindset that embraces effort, resilience, and continuous improvement.
What is a Growth Mindset?
A growth mindset is the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through effort, learning, and perseverance. This perspective encourages embracing challenges, learning from feedback, and viewing failures as opportunities for improvement. Research by psychologist Carol Dweck highlights how adopting a growth mindset leads to higher motivation, resilience, and academic or professional success.
Key Differences Between Deficit and Growth Mindset
The deficit mindset emphasizes limitations and fixed abilities, often leading to fear of failure and avoidance of challenges. In contrast, the growth mindset views abilities as developable through effort, persistence, and learning from mistakes. Key differences include the perception of intelligence as static versus dynamic, and the approach to obstacles as threats versus opportunities for improvement.
Origins and Influences of Each Mindset
The deficit mindset often originates from early negative feedback or failure experiences that emphasize limitations and fixed abilities, fostering a belief in innate inadequacy. In contrast, the growth mindset is influenced by environments that reward effort, learning, and persistence, highlighting the brain's neuroplasticity and potential for development. Social interactions, educational practices, and cultural values play critical roles in shaping these mindsets by reinforcing either fixed or malleable perceptions of intelligence and talent.
Impact on Learning and Achievement
A deficit mindset, which centers on perceived limitations and fixed abilities, hinders learning by promoting fear of failure and reducing effort, ultimately stalling academic achievement. In contrast, a growth mindset encourages embracing challenges, persistence, and learning from mistakes, leading to improved cognitive development and higher achievement levels. Research from Stanford University highlights that students with a growth mindset demonstrate increased motivation, resilience, and superior academic performance compared to those with a deficit mindset.
Signs You May Have a Deficit Mindset
Signs you may have a deficit mindset include a persistent fear of failure, a tendency to avoid challenges, and a belief that abilities and intelligence are fixed traits. You might frequently criticize yourself for mistakes and feel threatened by the success of others. This mindset limits personal growth by fostering self-doubt and resistance to learning opportunities.
Strategies to Shift to a Growth Mindset
Embracing a growth mindset involves implementing strategies such as setting realistic goals, practicing self-reflection, and seeking feedback to foster continuous learning. Techniques like reframing failures as opportunities for improvement and cultivating curiosity enhance resilience and adaptability. Consistent use of positive affirmations and surrounding oneself with supportive environments accelerate the shift from a deficit mindset to a growth mindset.
Benefits of Cultivating a Growth Mindset
Cultivating a growth mindset enhances resilience by promoting the belief that abilities can be developed through effort, leading to increased perseverance in the face of challenges. This mindset fosters continuous learning and adaptability, essential for personal and professional growth in dynamic environments. Embracing a growth mindset also improves problem-solving skills and encourages constructive feedback, which drives innovation and higher achievement.
Overcoming Common Mindset Barriers
Overcoming common mindset barriers involves shifting from a deficit mindset, which fixates on limitations and fear of failure, to a growth mindset that embraces challenges and views mistakes as learning opportunities. Cultivating self-awareness and resilience enables individuals to reframe obstacles as chances for development rather than insurmountable problems. Research by psychologist Carol Dweck highlights that individuals adopting a growth mindset demonstrate higher motivation, improved problem-solving skills, and greater overall achievement.
Building a Mindset for Lifelong Success
A growth mindset fosters resilience and continuous learning by embracing challenges and viewing failures as opportunities for development, which contrasts sharply with a deficit mindset that limits potential through fixed beliefs and fear of failure. Cultivating a growth mindset enhances problem-solving skills, adaptability, and motivation, essential components for lifelong success in personal and professional domains. Neuroscience research supports that brain plasticity enables skill improvement and cognitive growth throughout life, reinforcing the value of mindset in shaping long-term achievement.
Deficit Mindset Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com