Priority-Based Budgeting in schools allocates financial resources according to key educational goals, ensuring funds directly support student learning outcomes and essential programs. This approach helps administrators make data-driven decisions, aligning expenditures with priorities like improving academic performance, technology integration, and teacher development. Discover how implementing priority-based budgeting can transform Your school's financial planning and boost overall educational success.
Table of Comparison
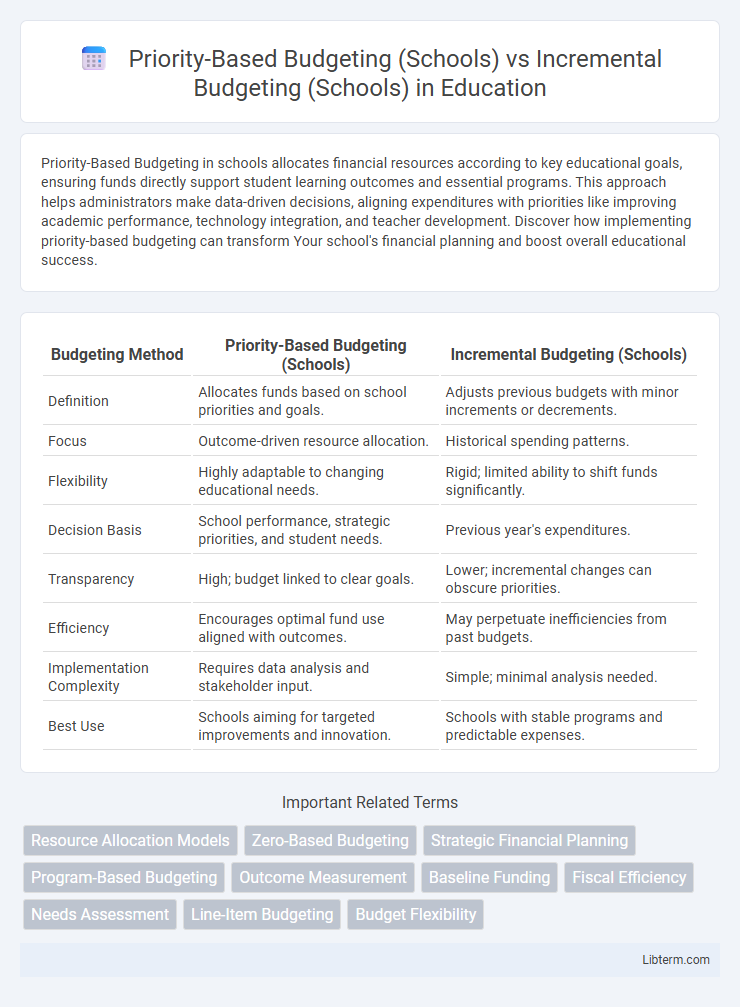
| Budgeting Method | Priority-Based Budgeting (Schools) | Incremental Budgeting (Schools) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allocates funds based on school priorities and goals. | Adjusts previous budgets with minor increments or decrements. |
| Focus | Outcome-driven resource allocation. | Historical spending patterns. |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to changing educational needs. | Rigid; limited ability to shift funds significantly. |
| Decision Basis | School performance, strategic priorities, and student needs. | Previous year's expenditures. |
| Transparency | High; budget linked to clear goals. | Lower; incremental changes can obscure priorities. |
| Efficiency | Encourages optimal fund use aligned with outcomes. | May perpetuate inefficiencies from past budgets. |
| Implementation Complexity | Requires data analysis and stakeholder input. | Simple; minimal analysis needed. |
| Best Use | Schools aiming for targeted improvements and innovation. | Schools with stable programs and predictable expenses. |
Introduction to School Budgeting Methods
Priority-Based Budgeting in schools allocates funds based on clearly defined goals and educational priorities, ensuring resources directly support student outcomes and instructional quality. Incremental Budgeting adjusts previous budgets with slight modifications, focusing on historical spending patterns rather than shifting educational needs. Understanding these methods helps school administrators balance innovation and stability in resource allocation for effective financial planning.
Overview of Priority-Based Budgeting in Schools
Priority-Based Budgeting in schools allocates funds by evaluating programs and services according to their impact on student outcomes and strategic goals. This method shifts resources towards high-priority initiatives such as literacy improvement, technology integration, and special education needs, enhancing overall educational effectiveness. Unlike Incremental Budgeting, which adjusts previous budgets incrementally, Priority-Based Budgeting promotes transparency, accountability, and data-driven decision-making in school financial planning.
Understanding Incremental Budgeting in Education
Incremental budgeting in schools allocates funds based on the previous year's budget with slight adjustments, maintaining financial stability and simplifying the budgeting process. This method often limits innovation, as it assumes existing expenditures are justified without rigorous evaluation, potentially perpetuating inefficiencies in resource allocation. Compared to priority-based budgeting, incremental budgeting provides predictability but may not effectively address changing educational needs or strategic goals.
Key Differences Between Priority-Based and Incremental Budgeting
Priority-Based Budgeting in schools allocates resources based on the alignment of programs with strategic goals and measurable outcomes, ensuring funds support high-impact initiatives. Incremental Budgeting adjusts previous year's allocations by small percentage increases or decreases without critically evaluating the effectiveness of expenditures. The key difference lies in Priority-Based Budgeting's emphasis on outcome-driven funding decisions versus Incremental Budgeting's reliance on historical spending patterns.
Advantages of Priority-Based Budgeting for Schools
Priority-Based Budgeting (PBB) allows schools to allocate resources according to strategic goals, improving resource efficiency and outcome alignment. It enhances transparency and accountability by clearly linking funds to specific priorities like student achievement and infrastructure. PBB fosters innovation and adaptability, enabling schools to respond effectively to changing educational needs compared to Incremental Budgeting's reliance on historical spending patterns.
Challenges of Implementing Priority-Based Budgeting
Priority-Based Budgeting (PBB) in schools faces challenges such as the complexity of accurately aligning expenditures with educational priorities and resistance from stakeholders accustomed to Incremental Budgeting's simplicity. Data collection and analysis demands for PBB require robust information systems often lacking in educational institutions, impeding effective implementation. Transitioning from Incremental Budgeting to PBB also involves substantial training and cultural shifts among school administrators and staff, which can slow adoption and reduce efficiency gains.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Incremental Budgeting in Schools
Incremental budgeting in schools offers simplicity and stability by building on previous budgets, ensuring consistent funding for ongoing programs and minimizing administrative workload. However, this method often perpetuates inefficiencies by allocating resources based on past spending rather than current needs, limiting flexibility for innovation or addressing shifting educational priorities. Consequently, incremental budgeting may hinder effective resource allocation in dynamic school environments requiring adaptive funding strategies.
Impact on Resource Allocation and Educational Outcomes
Priority-Based Budgeting in schools allocates funds by aligning resources directly with strategic educational goals, improving targeted program funding and potentially enhancing student achievement through focused investment. Incremental Budgeting, relying on historical expenditures plus incremental adjustments, often perpetuates existing resource distribution, which can limit innovation and responsiveness to changing educational needs. Studies indicate that Priority-Based Budgeting facilitates more effective resource allocation, fostering improved educational outcomes by prioritizing critical areas such as STEM programs and student support services.
Case Studies: Schools Using Priority-Based vs Incremental Budgeting
Case studies of schools implementing Priority-Based Budgeting (PBB) demonstrate enhanced resource allocation aligned with educational goals, improving student outcomes and operational efficiency. In contrast, schools using Incremental Budgeting typically maintain historical spending patterns, which often limit funding innovation and adaptability to emerging needs. Comparative analyses reveal that PBB schools report higher stakeholder engagement and clearer financial transparency than those relying on incremental approaches.
Choosing the Right Budgeting Approach for Your School
Priority-Based Budgeting in schools directs resources toward programs demonstrating the highest impact on student outcomes, ensuring funds align with strategic academic goals. Incremental Budgeting, by contrast, adjusts previous budgets with minor changes, which may perpetuate inefficient allocations and limit innovation in educational priorities. Selecting the right budgeting approach requires school leaders to evaluate their institutional goals, flexibility needs, and capacity for data-driven decision-making to optimize resource allocation effectively.
Priority-Based Budgeting (Schools) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com