Flipped Classroom transforms traditional teaching by delivering instructional content outside of the classroom, often through video lectures, enabling students to engage actively during in-class time. This approach promotes deeper understanding, personalized learning, and increased interaction between teachers and students. Discover how the flipped classroom model can revolutionize your learning experience by exploring the insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
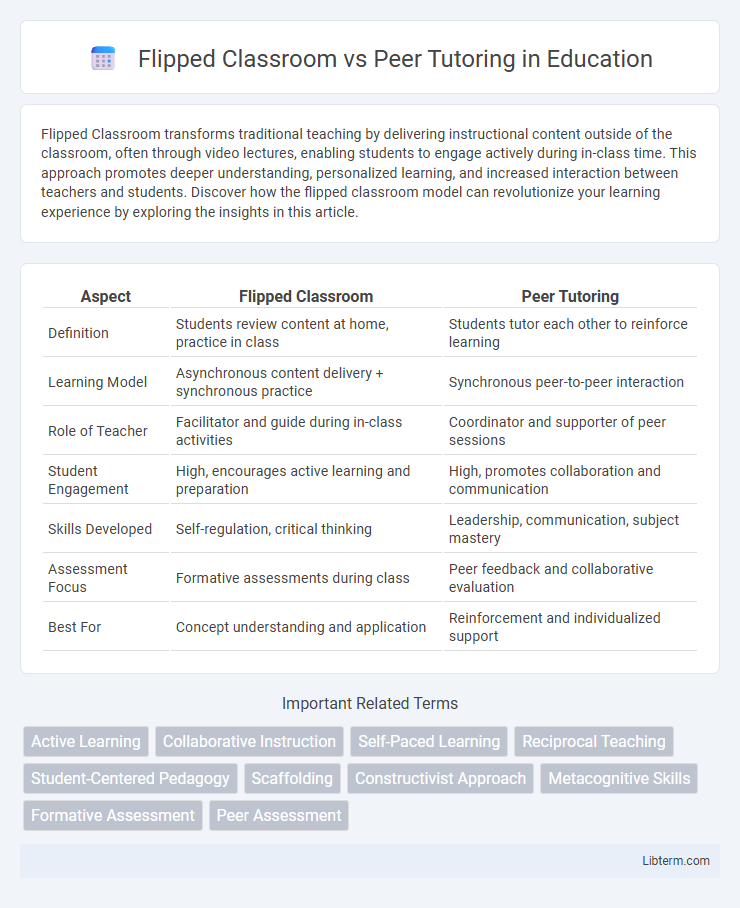
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Peer Tutoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students review content at home, practice in class | Students tutor each other to reinforce learning |
| Learning Model | Asynchronous content delivery + synchronous practice | Synchronous peer-to-peer interaction |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide during in-class activities | Coordinator and supporter of peer sessions |
| Student Engagement | High, encourages active learning and preparation | High, promotes collaboration and communication |
| Skills Developed | Self-regulation, critical thinking | Leadership, communication, subject mastery |
| Assessment Focus | Formative assessments during class | Peer feedback and collaborative evaluation |
| Best For | Concept understanding and application | Reinforcement and individualized support |
Introduction to Flipped Classroom and Peer Tutoring
The flipped classroom model transforms traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class, allowing in-person sessions to focus on interactive activities and personalized support. Peer tutoring involves students helping each other understand course material, promoting collaborative learning and reinforcing knowledge through explanation and discussion. Both methods enhance student engagement and improve academic performance by fostering active participation and deeper comprehension.
Core Principles of Flipped Classroom
The core principles of the flipped classroom emphasize moving direct instruction outside of traditional class time through pre-recorded lectures or digital content, allowing in-class time to focus on active learning and student engagement. This model prioritizes personalized learning and immediate feedback, enabling students to apply concepts collaboratively under the teacher's guidance. In contrast to peer tutoring, which relies on student-to-student instruction, the flipped classroom centers on technology-enhanced self-paced learning combined with interactive, teacher-led activities to deepen understanding.
Key Features of Peer Tutoring
Peer tutoring leverages collaborative learning by pairing students to enhance understanding through mutual teaching, fostering social interaction and individualized feedback. It promotes active engagement and reinforces content retention by allowing tutors to articulate knowledge while tutees receive personalized support tailored to their learning pace. This method improves academic achievement and builds communication skills, critical thinking, and confidence among participants.
Differences in Instructional Design
Flipped Classroom models invert traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class, enabling in-class time for interactive, application-based activities. Peer Tutoring relies on collaborative learning where students alternate roles as tutor and learner, emphasizing personalized support and immediate feedback. The former prioritizes structured content delivery through multimedia, while the latter centers on social interaction and individualized guidance within the learning process.
Student Engagement: Flipped vs Peer Tutoring
Flipped classrooms boost student engagement by encouraging active learning through pre-class video lectures and in-class problem-solving activities, fostering deeper comprehension. Peer tutoring enhances engagement by promoting collaboration and personalized feedback, allowing students to learn at their own pace while reinforcing knowledge through teaching others. Both methods increase participation, but flipped classrooms emphasize self-directed learning, whereas peer tutoring leverages social interaction for motivational support.
Teacher and Tutor Roles Compared
In a flipped classroom, the teacher primarily designs and delivers pre-class content, facilitating active learning during class while guiding student engagement and addressing misconceptions. Peer tutoring shifts instructional responsibility to trained student tutors, who provide personalized support and reinforce concepts through collaborative dialogue under the teacher's supervision. Both models emphasize interactive learning, but flipped classrooms rely more on teacher-led content curation, whereas peer tutoring centers on student-led knowledge reinforcement.
Academic Outcomes and Learning Gains
Flipped Classroom models significantly enhance academic outcomes by promoting active learning, resulting in higher test scores and improved knowledge retention compared to traditional teaching methods. Peer Tutoring fosters personalized learning gains through collaborative problem-solving and immediate feedback, which boosts student confidence and academic performance in diverse subjects. Combining both approaches can maximize learning efficiency by integrating structured content delivery with interactive, peer-supported engagement.
Technology Integration in Both Methods
Flipped Classroom leverages technology by utilizing video lectures and online resources, enabling students to engage with content at their own pace outside the classroom, while in-class time is dedicated to interactive discussions and problem-solving activities. Peer Tutoring integrates technology through collaborative platforms, enabling tutors and tutees to connect virtually, share digital resources, and track progress in real-time, enhancing personalized learning experiences. Both methods harness technology to foster active learning, improve student engagement, and support differentiated instruction.
Challenges and Limitations
Flipped Classroom challenges include student resistance to self-directed learning and varying access to technology, which can hinder effective preparation outside the classroom. Peer Tutoring faces limitations such as inconsistent tutor quality and potential reinforcement of misconceptions without proper oversight. Both methods require substantial instructor training and careful implementation to maximize educational outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Flipped Classroom emphasizes pre-class content engagement, allowing in-class time for active learning, ideal for classrooms with sufficient digital access and self-motivated students. Peer Tutoring leverages collaborative learning through student partnerships, fostering personalized support and social interaction, which suits diverse learning abilities and promotes peer accountability. Selecting the right approach depends on factors such as student learning styles, available resources, and educational goals to maximize engagement and academic achievement.
Flipped Classroom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com