Differentiated instruction tailors teaching methods and materials to meet the diverse learning needs and abilities of each student. It enhances engagement and comprehension by using varied strategies such as flexible grouping, personalized content, and ongoing assessment. Discover how applying differentiated instruction can transform your classroom experience in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
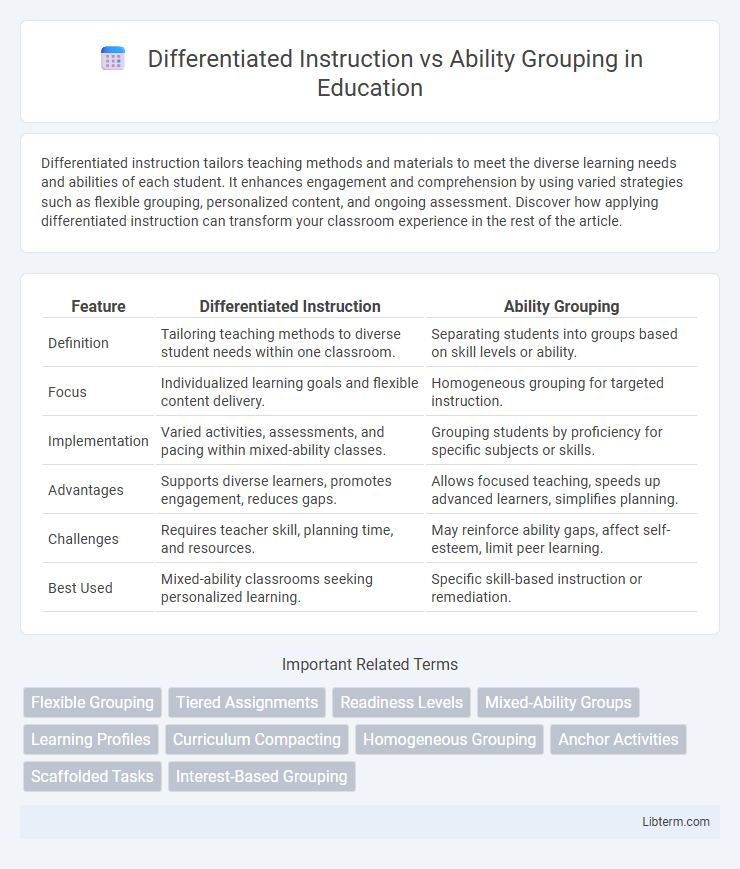
| Feature | Differentiated Instruction | Ability Grouping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tailoring teaching methods to diverse student needs within one classroom. | Separating students into groups based on skill levels or ability. |
| Focus | Individualized learning goals and flexible content delivery. | Homogeneous grouping for targeted instruction. |
| Implementation | Varied activities, assessments, and pacing within mixed-ability classes. | Grouping students by proficiency for specific subjects or skills. |
| Advantages | Supports diverse learners, promotes engagement, reduces gaps. | Allows focused teaching, speeds up advanced learners, simplifies planning. |
| Challenges | Requires teacher skill, planning time, and resources. | May reinforce ability gaps, affect self-esteem, limit peer learning. |
| Best Used | Mixed-ability classrooms seeking personalized learning. | Specific skill-based instruction or remediation. |
Understanding Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated Instruction tailors teaching methods and materials to accommodate diverse student learning styles, readiness levels, and interests within a single classroom. It emphasizes flexible grouping, varied content, and adaptive assessments to promote individual growth and engagement. This approach contrasts with Ability Grouping, which sorts students strictly by skill level, often limiting personalized learning opportunities.
What Is Ability Grouping?
Ability grouping is an educational strategy that organizes students into groups based on their skill levels or academic achievement for specific subjects or tasks. This method aims to tailor instruction to the group's proficiency, allowing teachers to target lessons more precisely and address diverse learning needs. Unlike differentiated instruction, which customizes teaching within heterogeneous classrooms, ability grouping creates more homogeneous groups to streamline content delivery and pacing.
Key Differences Between Differentiated Instruction and Ability Grouping
Differentiated instruction customizes teaching strategies and resources to meet individual student needs within a diverse classroom setting, promoting inclusive learning and continuous assessment; in contrast, ability grouping segregates students based on skill level into homogeneous groups for targeted instruction, which can potentially limit peer interaction and reinforce ability-based tracking. Differentiated instruction emphasizes flexible grouping and adapts content, process, and product according to student readiness, interests, and learning profiles, whereas ability grouping primarily organizes students by proficiency or performance in fixed groups. Evidence suggests differentiated instruction supports equitable learning opportunities and boosts engagement by responding to student diversity, while ability grouping may accelerate learning for high achievers but risks stigmatizing lower-performing groups.
Benefits of Differentiated Instruction for Student Learning
Differentiated instruction enhances student learning by tailoring teaching methods and materials to individual needs, promoting better engagement and understanding. It supports diverse learning styles and paces, helping students build on their strengths while addressing weaknesses effectively. This approach fosters a more inclusive classroom environment, improving academic outcomes compared to rigid ability grouping.
Advantages and Challenges of Ability Grouping
Ability grouping enhances tailored instruction by clustering students based on skill levels, allowing educators to address specific learning needs more efficiently. This method can boost student motivation and engagement by providing appropriately challenging materials, yet it risks reinforcing achievement gaps and limiting peer diversity, potentially reducing collaborative learning opportunities. Teachers face challenges in balancing group dynamics and ensuring equitable resource allocation while avoiding stigma or lowered expectations for lower-ability groups.
Impact on Student Engagement and Motivation
Differentiated instruction tailors teaching methods and materials to meet diverse student needs, resulting in higher engagement and intrinsic motivation by addressing individual learning styles and interests. In contrast, ability grouping can lead to fixed mindset issues and decreased motivation among lower-ability groups, as students may feel labeled or stigmatized. Research indicates differentiated instruction fosters a more inclusive environment, promoting sustained student motivation and active participation across varied academic levels.
Addressing Equity and Inclusivity Concerns
Differentiated instruction promotes equity and inclusivity by tailoring teaching methods and materials to diverse student needs within heterogeneous classrooms, ensuring all learners receive appropriate challenges and support. Ability grouping, while potentially increasing instructional efficiency, risks reinforcing achievement gaps and stigmatizing lower-ability students by segregating them, which can limit social integration and reduce access to high-quality curriculum. Implementing differentiated instruction with culturally responsive pedagogy fosters an inclusive learning environment that values diverse abilities and backgrounds, enhancing educational equity.
Practical Strategies for Implementing Differentiated Instruction
Differentiated instruction employs tailored teaching methods such as flexible grouping, tiered assignments, and ongoing assessment to meet diverse learner needs, contrasting with ability grouping's fixed student clusters. Practical strategies include pre-assessment to identify readiness levels, using varied modalities to present content, and providing choice in learning activities to promote engagement. Incorporating technology tools like adaptive software enhances personalization, enabling instructors to address individual strengths and challenges effectively within heterogeneous classrooms.
Best Practices for Effective Ability Grouping
Effective ability grouping requires precise assessment of student skill levels to create homogeneous groups that enhance targeted instruction. Best practices include regularly rotating groups to prevent stigmatization and ensuring flexible grouping to address diverse learning needs. Consistent progress monitoring and tailored instructional strategies within groups foster optimal student engagement and achievement.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Differentiated instruction tailors teaching methods and materials to meet diverse student needs within a mixed-ability classroom, promoting individual growth and engagement. Ability grouping, by contrast, organizes students into homogeneous groups based on skill level, allowing for targeted instruction but risking stigmatization and reduced peer interaction. Choosing the right approach depends on classroom goals, student diversity, and available resources, with many educators blending both strategies to optimize learning outcomes.
Differentiated Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com