Outcome refers to the result or consequence of an action, decision, or event, shaping future possibilities and understanding. Effective evaluation of outcomes helps you measure success and identify areas for improvement. Explore the full article to uncover how to optimize outcomes in various contexts.
Table of Comparison
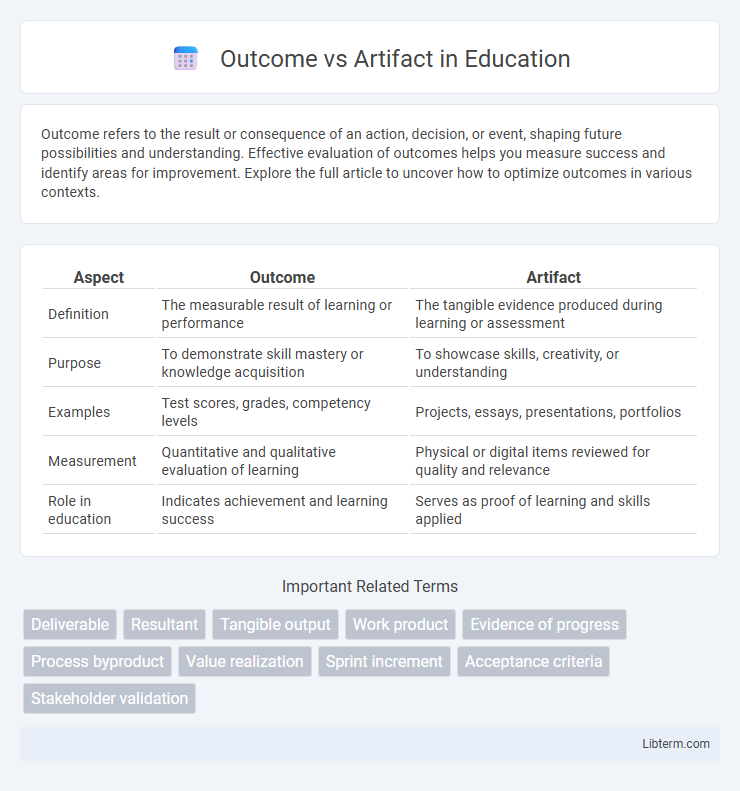
| Aspect | Outcome | Artifact |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The measurable result of learning or performance | The tangible evidence produced during learning or assessment |
| Purpose | To demonstrate skill mastery or knowledge acquisition | To showcase skills, creativity, or understanding |
| Examples | Test scores, grades, competency levels | Projects, essays, presentations, portfolios |
| Measurement | Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of learning | Physical or digital items reviewed for quality and relevance |
| Role in education | Indicates achievement and learning success | Serves as proof of learning and skills applied |
Understanding the Concept of Outcome vs Artifact
Understanding the concept of outcome versus artifact is essential in project management and software development. An outcome refers to the measurable impact or result achieved from a process, such as increased user engagement or improved customer satisfaction. An artifact, on the other hand, is a tangible byproduct or deliverable created during the project, including documents, prototypes, or code, which serve as tools to achieve the desired outcome.
Key Differences Between Outcomes and Artifacts
Outcomes represent the measurable results or impacts achieved after completing a project or process, while artifacts are the tangible products or documents created during the project lifecycle. Key differences between outcomes and artifacts include that outcomes focus on the value and effectiveness realized, such as increased customer satisfaction or revenue growth, whereas artifacts serve as evidence of work performed, such as reports, design documents, or code. Outcomes are often dynamic and linked to goals or objectives, whereas artifacts are static, preserved for reference, compliance, or further development.
Importance of Differentiating Outcomes and Artifacts
Differentiating outcomes and artifacts is crucial for effective project management and performance measurement, as outcomes represent the actual impact or results achieved, while artifacts are the tangible items produced during the process. Clear distinction ensures accurate evaluation of success criteria and guides strategic adjustments by focusing on meaningful change instead of merely completed deliverables. Understanding this difference enables organizations to prioritize value generation and optimize resource allocation for sustained business growth.
Real-World Examples of Outcomes and Artifacts
Outcomes represent measurable effects like increased customer satisfaction scores or higher sales revenue, while artifacts are tangible deliverables such as product prototypes or project documentation. For instance, a software development team's artifact could be the final application code, whereas the outcome is the improved user experience and reduced support tickets. In marketing, a campaign strategy is an artifact, but the outcome reflects brand awareness growth and lead generation metrics.
Measuring Success: Outcomes vs Artifacts
Measuring success through outcomes emphasizes the tangible impact and value delivered, such as increased revenue, user engagement, or customer satisfaction, rather than merely the presence of artifacts like reports or prototypes. Outcomes reflect real-world changes and business goals achieved, while artifacts serve as tools or milestones in the process without guaranteeing success. Prioritizing outcome-based metrics ensures alignment with strategic objectives and drives more meaningful evaluation of project effectiveness.
Impact on Project Management and Delivery
Outcomes represent the measurable results and benefits achieved through project execution, directly influencing stakeholder satisfaction and project success metrics. Artifacts encompass the tangible deliverables and documentation produced during project phases, serving as critical references for quality control, compliance, and knowledge transfer. Effective management of both outcomes and artifacts ensures accurate tracking, facilitates informed decision-making, and enhances overall project delivery efficiency.
Common Misconceptions About Outcomes and Artifacts
Outcomes represent the measurable impact or change resulting from a project, while artifacts are tangible deliverables or byproducts produced during the process. A common misconception is that artifacts, such as reports or prototypes, equate to successful outcomes, though they only serve as tools or evidence toward achieving desired goals. Understanding this distinction ensures teams prioritize lasting value and real-world effects over merely completing tasks or creating documents.
Role of Outcomes and Artifacts in Agile Methodologies
Outcomes in Agile methodologies represent the value delivered to customers and stakeholders, emphasizing goals such as improved user satisfaction and business performance. Artifacts, including product backlogs, sprint burndown charts, and increment demonstrations, serve as tangible tools that support transparency, planning, and review processes. Their role is to facilitate continuous feedback and iteration, ensuring that teams remain aligned with desired outcomes throughout the development lifecycle.
How to Focus Teams on Outcomes Over Artifacts
Focusing teams on outcomes over artifacts requires aligning goals with measurable customer value and business impact rather than just deliverables. Establishing clear key performance indicators (KPIs) and continuously communicating the desired results encourages teams to prioritize functionality and user benefits over documentation or feature count. Empowering teams with autonomy to iterate based on feedback enables a shift from producing static artifacts to achieving dynamic, outcome-driven success.
Best Practices for Aligning Outcomes and Artifacts
Aligning outcomes and artifacts requires establishing clear objectives that directly tie artifacts to desired business results and key performance indicators (KPIs). Best practices include using traceability matrices to map each artifact to specific outcomes, ensuring continual validation through iterative feedback and stakeholder involvement. This alignment maximizes project relevance, reduces scope creep, and accelerates value delivery.
Outcome Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com