Kinesthetic learning involves acquiring knowledge through hands-on activities and physical movement, engaging your body to enhance memory and understanding. This approach benefits individuals who thrive on active participation rather than passive listening or reading. Discover how kinesthetic learning techniques can transform your educational experience by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
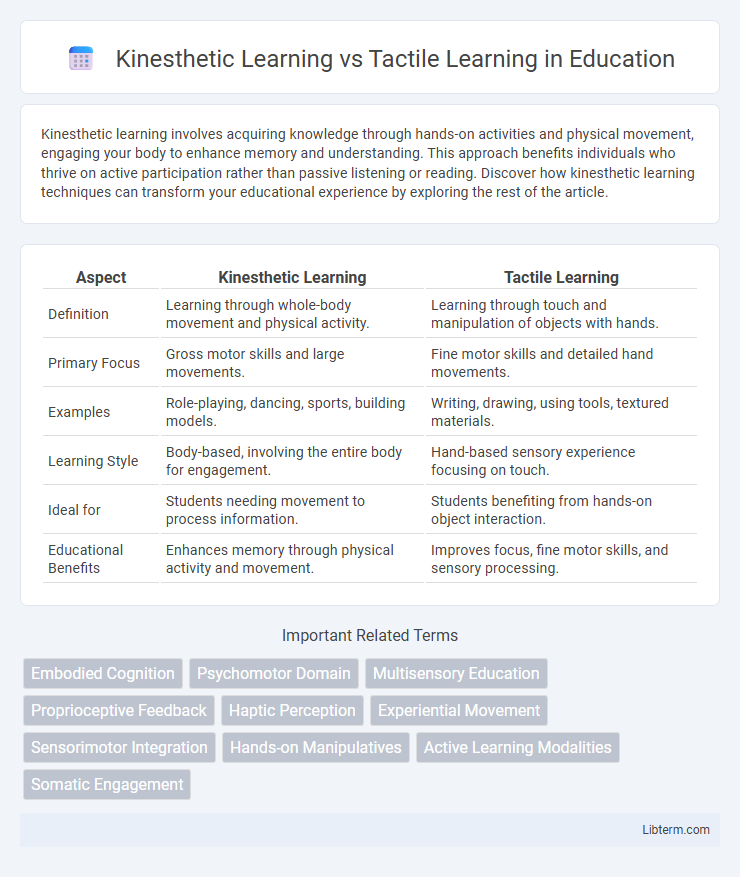
| Aspect | Kinesthetic Learning | Tactile Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through whole-body movement and physical activity. | Learning through touch and manipulation of objects with hands. |
| Primary Focus | Gross motor skills and large movements. | Fine motor skills and detailed hand movements. |
| Examples | Role-playing, dancing, sports, building models. | Writing, drawing, using tools, textured materials. |
| Learning Style | Body-based, involving the entire body for engagement. | Hand-based sensory experience focusing on touch. |
| Ideal for | Students needing movement to process information. | Students benefiting from hands-on object interaction. |
| Educational Benefits | Enhances memory through physical activity and movement. | Improves focus, fine motor skills, and sensory processing. |
Understanding Kinesthetic Learning
Kinesthetic learning involves acquiring knowledge through whole-body movement and physical activities, engaging large muscle groups to process and retain information. It emphasizes active participation, such as role-playing, dancing, or hands-on experiments, allowing learners to internalize concepts through motion and coordination. Understanding kinesthetic learning highlights its effectiveness in enhancing memory and comprehension by linking cognitive tasks with bodily movements.
Defining Tactile Learning
Tactile learning refers to acquiring knowledge through touch and physical manipulation of objects, emphasizing hands-on activities such as feeling textures or handling tools. It differs from kinesthetic learning, which involves whole-body movement to engage with the environment and enhance understanding. Tactile learning plays a crucial role in sensory development and supports learners who benefit from direct physical interaction with educational materials.
Core Differences Between Kinesthetic and Tactile Learning
Kinesthetic learning involves acquiring knowledge through whole-body movement and physical activities, engaging large muscle groups to enhance memory and skill retention. Tactile learning centers on the sense of touch and manipulation of objects, focusing on fine motor skills and hand-eye coordination to process information. The core difference lies in kinesthetic learning's emphasis on gross motor movements versus tactile learning's concentration on touch-based interactions and sensory feedback.
Key Characteristics of Kinesthetic Learners
Kinesthetic learners excel through physical movement and whole-body activities, often preferring hands-on experiences to grasp concepts effectively. They demonstrate strong coordination, spatial awareness, and a preference for learning by doing rather than passive observation. Key characteristics include a high need for physical engagement, difficulty sitting still for long periods, and enhanced memory retention when activities involve motion or manipulation of objects.
Hallmarks of Tactile Learners
Tactile learners excel through hands-on activities, relying on touch and manual manipulation to process information effectively. They benefit from using physical objects, textures, and movements to grasp concepts, exhibiting strong fine motor skills and an aptitude for crafts or writing-intensive tasks. Hallmarks of tactile learners include a preference for kinesthetic engagement, difficulty sitting still for long periods, and a tendency to learn best when actively involved in creating or handling materials.
Teaching Strategies for Kinesthetic Learners
Kinesthetic learners thrive through movement-based activities that engage large muscle groups, making teaching strategies such as role-playing, hands-on experiments, and interactive simulations highly effective. Incorporating physical activities like building models, using gestures, or incorporating movement breaks enhances retention and comprehension for these learners. Providing real-world applications and allowing exploration through active participation ensures kinesthetic learners remain engaged and deepen their understanding.
Effective Techniques for Tactile Learners
Tactile learning emphasizes hands-on activities that engage the sense of touch, making techniques such as using textured materials, building models, and writing notes by hand highly effective. Incorporating tools like clay, fabric samples, or interactive simulations enhances memory retention and comprehension for tactile learners. This approach contrasts with kinesthetic learning, which involves whole-body movement and physical activity to grasp concepts.
Common Misconceptions: Kinesthetic vs. Tactile
Kinesthetic learning involves whole-body movement and physical activity to process information, whereas tactile learning specifically focuses on using the sense of touch through hands-on manipulation. A common misconception is that these terms are interchangeable, but tactile learning is a subset of kinesthetic learning centered on fine motor skills and texture exploration. Clarifying this distinction enhances targeted educational strategies that cater to students' sensory and movement preferences.
Assessing Learning Preferences: Kinesthetic and Tactile Methods
Assessing learning preferences involves distinguishing kinesthetic learners, who comprehend best through whole-body movement and physical activities, from tactile learners, who benefit primarily from hands-on manipulation of objects. Educators use observation and specialized assessments to identify whether a student excels in dynamic movement tasks or detailed touch-based exercises. Tailoring instructional strategies to these specific modalities enhances engagement and retention by aligning with the learner's dominant sensory processing style.
Integrating Both Learning Styles in the Classroom
Integrating kinesthetic and tactile learning styles in the classroom enhances student engagement and retention by combining whole-body movement with hands-on activities that stimulate sensory experiences. Strategies such as incorporating interactive labs, role-playing, and the use of manipulatives support diverse learners and improve comprehension in subjects like science and math. Tailoring lesson plans to include both active movement and tactile exploration fosters an inclusive environment that boosts cognitive development and practical skill acquisition.
Kinesthetic Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com