Inquiry-based learning fosters critical thinking by encouraging students to ask questions and explore topics deeply. This approach promotes active engagement and helps develop problem-solving skills essential for real-world situations. Discover how this method can transform Your educational experience in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
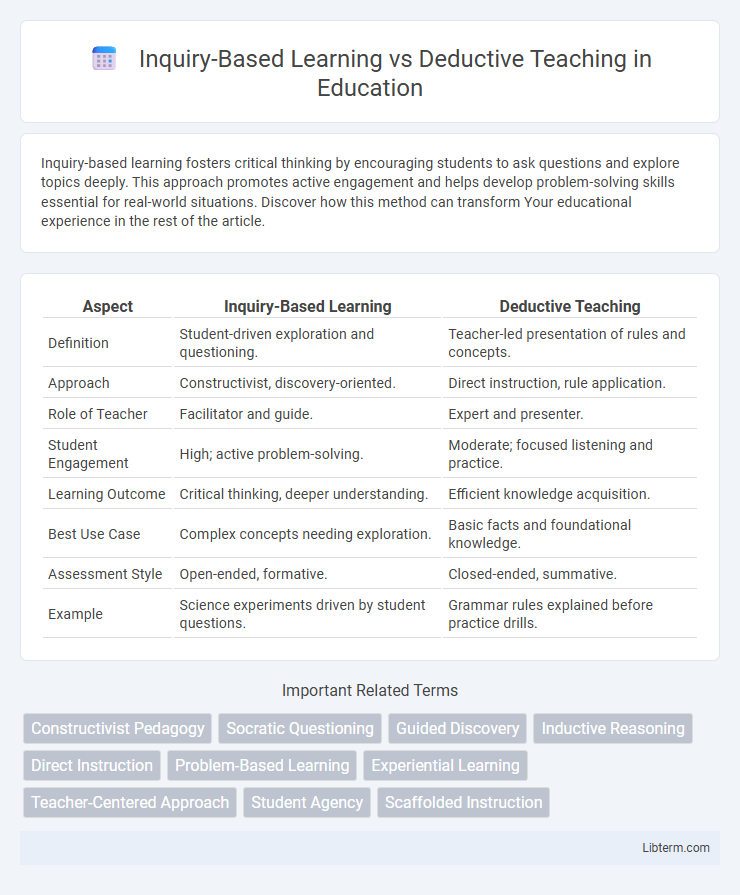
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Deductive Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-driven exploration and questioning. | Teacher-led presentation of rules and concepts. |
| Approach | Constructivist, discovery-oriented. | Direct instruction, rule application. |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide. | Expert and presenter. |
| Student Engagement | High; active problem-solving. | Moderate; focused listening and practice. |
| Learning Outcome | Critical thinking, deeper understanding. | Efficient knowledge acquisition. |
| Best Use Case | Complex concepts needing exploration. | Basic facts and foundational knowledge. |
| Assessment Style | Open-ended, formative. | Closed-ended, summative. |
| Example | Science experiments driven by student questions. | Grammar rules explained before practice drills. |
Understanding Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes active student engagement by encouraging exploration, questioning, and investigation to construct knowledge. This approach fosters critical thinking and deeper understanding through hands-on experiences and open-ended problems. Unlike Deductive Teaching, which starts with rules and moves to examples, Inquiry-Based Learning promotes discovery and learner autonomy.
Defining Deductive Teaching
Deductive teaching is a traditional instructional approach where educators present general rules or principles first, followed by specific examples to illustrate these concepts. This method emphasizes direct instruction and systematic explanation, allowing students to apply given rules to concrete problems. It contrasts with inquiry-based learning by prioritizing structured guidance over exploratory discovery.
Key Principles of Inquiry-Based Methods
Inquiry-based learning centers on student-driven exploration, encouraging learners to ask questions, investigate problems, and construct knowledge through active engagement. It emphasizes the development of critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and deeper understanding by allowing learners to formulate hypotheses and test them in real-world contexts. This method contrasts with deductive teaching, which delivers facts and rules upfront, focusing on direct instruction rather than experiential discovery.
Main Features of Deductive Instruction
Deductive instruction centers on explicitly presenting rules and principles followed by guided practice to reinforce understanding. This teaching method emphasizes teacher-led explanations and structured learning sequences, ensuring students grasp core concepts before applying them. The main features include clear instruction, systematic presentation of material, and immediate feedback to solidify knowledge acquisition.
Comparing Student Engagement Levels
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters higher student engagement by encouraging active exploration and critical thinking, allowing learners to ask questions and discover concepts independently. In contrast, Deductive Teaching often results in lower engagement as students receive pre-defined information with limited opportunities for interaction or creativity. Research indicates that classrooms employing inquiry-based methods report increased motivation, participation, and deeper conceptual understanding compared to traditional deductive approaches.
Impact on Critical Thinking Skills
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking by encouraging students to ask questions, explore, and actively construct knowledge through investigation. Deductive Teaching often emphasizes the application of established principles, reinforcing logical reasoning but limiting opportunities for independent problem-solving. Research indicates that Inquiry-Based Learning significantly enhances critical thinking skills by promoting deeper understanding and cognitive engagement compared to traditional deductive methods.
Flexibility and Adaptability in Classroom Settings
Inquiry-Based Learning offers greater flexibility in classroom settings by allowing students to explore topics at their own pace and follow personalized learning paths. Deductive Teaching, while structured and efficient for delivering specific content, often lacks adaptability to diverse student needs and learning styles. The dynamic nature of Inquiry-Based Learning enables educators to tailor lessons responsively, fostering deeper understanding through active engagement.
Teacher’s Role in Each Approach
In Inquiry-Based Learning, the teacher acts as a facilitator, guiding students to explore, ask questions, and discover knowledge independently, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. In Deductive Teaching, the teacher serves as the primary source of information, delivering structured content and ensuring students understand specific concepts through direct instruction. The teacher's role in Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes mentorship and scaffolding, whereas in Deductive Teaching, it centers on clarity, explanation, and reinforcement of predetermined material.
Assessment and Evaluation Techniques
Inquiry-based learning emphasizes formative assessment techniques such as observation, reflective journals, and open-ended questioning to gauge student understanding and promote critical thinking. Deductive teaching primarily relies on summative evaluations like quizzes, standardized tests, and structured problem-solving tasks to assess mastery of specific concepts. Both methods benefit from rubrics and feedback mechanisms, but inquiry-based learning prioritizes ongoing assessment aligned with investigation processes and conceptual development.
Choosing the Best Approach for Your Students
Inquiry-Based Learning promotes active student engagement by encouraging exploration and critical thinking, making it ideal for learners who thrive on discovery and problem-solving. Deductive Teaching offers structured guidance and clear explanations, benefiting students who prefer direct instruction and step-by-step understanding of concepts. Selecting the best approach depends on evaluating students' learning styles, curriculum goals, and classroom dynamics to maximize comprehension and motivation.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com