Teacher assessment is a crucial process that evaluates the effectiveness and performance of educators through various methods such as classroom observations, student feedback, and standardized testing results. This evaluation helps identify strengths and areas for improvement, ensuring higher teaching quality and better student outcomes. Discover how comprehensive teacher assessments can transform educational experiences by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
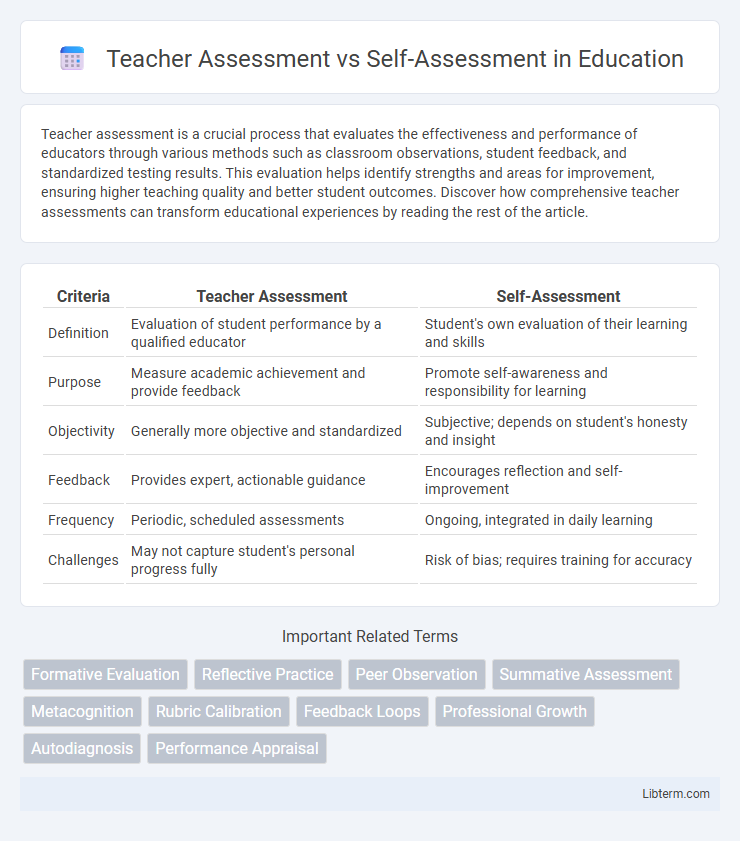
| Criteria | Teacher Assessment | Self-Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluation of student performance by a qualified educator | Student's own evaluation of their learning and skills |
| Purpose | Measure academic achievement and provide feedback | Promote self-awareness and responsibility for learning |
| Objectivity | Generally more objective and standardized | Subjective; depends on student's honesty and insight |
| Feedback | Provides expert, actionable guidance | Encourages reflection and self-improvement |
| Frequency | Periodic, scheduled assessments | Ongoing, integrated in daily learning |
| Challenges | May not capture student's personal progress fully | Risk of bias; requires training for accuracy |
Introduction to Assessment in Education
Teacher assessment provides an authoritative evaluation of student performance based on standardized criteria, ensuring consistent measurement of learning outcomes. Self-assessment encourages students to reflect on their own understanding and skills, promoting metacognition and personalized learning growth. Combining both methods in educational assessment fosters a comprehensive approach that enhances student engagement and accurate performance tracking.
Defining Teacher Assessment
Teacher assessment involves educators systematically evaluating student performance using established criteria to measure learning progress and mastery of subject matter. This process incorporates formative and summative methods, ensuring accurate feedback for students while informing instructional decisions. Effective teacher assessments rely on standardized tests, rubrics, and observational data to provide objective, consistent evaluations aligned with curriculum standards.
Understanding Self-Assessment
Understanding self-assessment involves recognizing its role in fostering metacognitive skills, allowing learners to evaluate their own progress and identify areas for improvement autonomously. Unlike teacher assessment, which provides external evaluation based on standardized criteria, self-assessment encourages reflective thinking and personal accountability in the learning process. Research indicates that effective self-assessment enhances motivation and deepens comprehension by engaging students in active goal-setting and self-regulation.
Key Differences Between Teacher Assessment and Self-Assessment
Teacher assessment involves an external evaluation where educators measure student performance based on standardized criteria, ensuring objectivity and alignment with curriculum standards. In contrast, self-assessment empowers students to reflect on their own learning process, fostering metacognitive skills and personal accountability. The key differences lie in the source of evaluation, with teacher assessment being formal and summative, while self-assessment is informal and formative, promoting ongoing self-improvement.
Benefits of Teacher Assessment
Teacher assessment provides objective evaluations based on expertise, ensuring consistency and accuracy in measuring student performance and progress. It helps identify specific learning gaps and tailor instructional strategies to meet diverse educational needs effectively. Moreover, teacher assessments contribute to standardized grading and accountability, promoting fairness and transparency in educational outcomes.
Benefits of Self-Assessment
Self-assessment enhances students' metacognitive skills by encouraging reflection on their own learning processes and identifying areas for improvement. It fosters greater autonomy and intrinsic motivation, leading to increased engagement and responsibility in educational outcomes. Research indicates that self-assessment can improve academic performance by promoting continuous self-monitoring and personalized goal-setting.
Challenges in Teacher Assessment
Challenges in teacher assessment include subjectivity in grading, inconsistent evaluation criteria, and potential biases impacting fairness and accuracy. Limited time and resources hinder comprehensive observations and feedback, reducing the effectiveness of assessments. Moreover, teachers may face pressure to conform to standardized testing outcomes, which can detract from holistic evaluation of student learning.
Challenges in Self-Assessment
Self-assessment challenges include student bias, limited self-awareness, and lack of objective criteria, which can lead to inaccurate evaluations of learning progress. Students often struggle with identifying their strengths and weaknesses due to inadequate metacognitive skills, resulting in overestimation or underestimation of performance. These limitations emphasize the importance of combining self-assessment with teacher assessment for a comprehensive evaluation strategy.
Combining Assessment Approaches for Optimal Learning
Combining teacher assessment with self-assessment enhances learning by integrating objective evaluation and personal reflection, fostering deeper understanding and self-regulation. This blended approach allows learners to identify their strengths and weaknesses while benefiting from expert guidance, creating a comprehensive feedback loop. Incorporating both methods supports adaptive teaching strategies and promotes continuous improvement in student performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Assessment Method
Teacher assessment provides objective evaluation based on standardized criteria and professional expertise, while self-assessment encourages student reflection and personal growth. Selecting the right assessment method depends on the learning goals, context, and desired outcomes, with a blended approach often optimizing both accuracy and learner engagement. Effective assessment strategies balance external feedback and self-evaluation to enhance overall educational development.
Teacher Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com