Inquiry-based education fosters critical thinking and deep understanding by encouraging students to ask questions and explore topics independently. It emphasizes active learning and real-world problem-solving, making lessons more engaging and relevant. Discover how this approach can transform Your learning experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
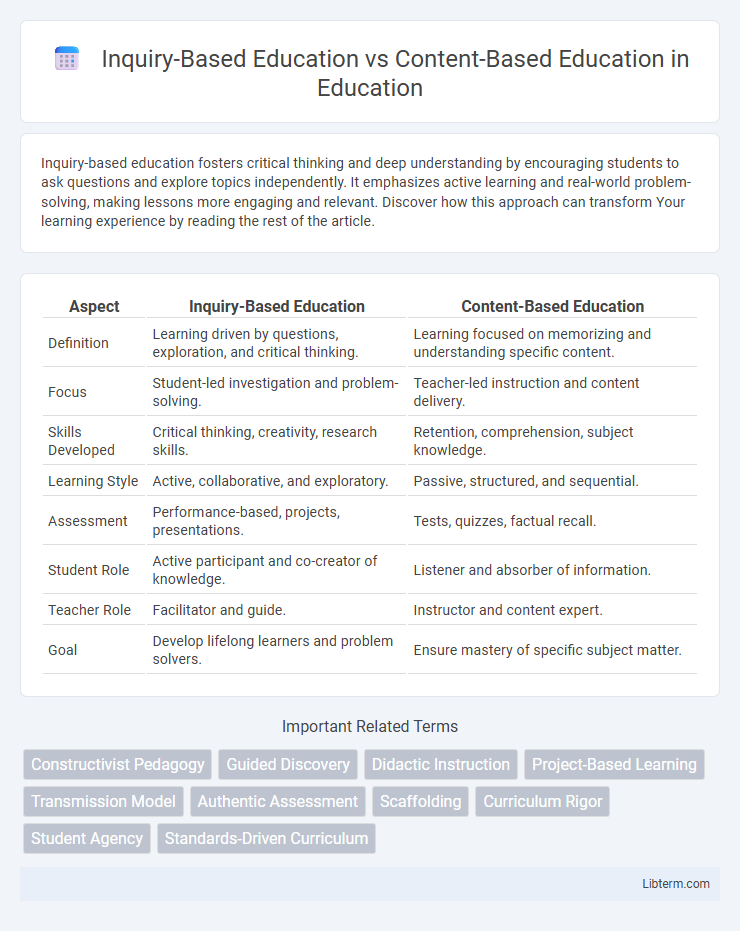
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Education | Content-Based Education |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning driven by questions, exploration, and critical thinking. | Learning focused on memorizing and understanding specific content. |
| Focus | Student-led investigation and problem-solving. | Teacher-led instruction and content delivery. |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, creativity, research skills. | Retention, comprehension, subject knowledge. |
| Learning Style | Active, collaborative, and exploratory. | Passive, structured, and sequential. |
| Assessment | Performance-based, projects, presentations. | Tests, quizzes, factual recall. |
| Student Role | Active participant and co-creator of knowledge. | Listener and absorber of information. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and guide. | Instructor and content expert. |
| Goal | Develop lifelong learners and problem solvers. | Ensure mastery of specific subject matter. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based and Content-Based Education
Inquiry-Based Education emphasizes student-centered learning through exploration, questioning, and critical thinking, fostering deeper understanding by engaging learners actively in the knowledge construction process. Content-Based Education prioritizes delivering structured subject matter knowledge, focusing on mastering core concepts and facts through direct instruction. Both approaches serve distinct educational goals: Inquiry-Based methods cultivate analytical skills and curiosity, while Content-Based methods ensure comprehensive coverage of essential information.
Defining Inquiry-Based Education
Inquiry-Based Education centers on student-driven exploration and critical thinking, emphasizing the process of questioning, investigating, and constructing knowledge rather than memorizing facts. This educational approach fosters deeper understanding by encouraging learners to actively engage with material through hands-on activities and problem-solving tasks. Unlike Content-Based Education, which prioritizes the transmission of established information, Inquiry-Based Education develops skills in inquiry, analysis, and independent learning.
Understanding Content-Based Education
Content-Based Education centers on delivering subject-specific knowledge through structured curricula, emphasizing mastery of facts, concepts, and skills within disciplines such as math, science, and language arts. This approach uses direct instruction, standardized assessments, and sequential content delivery to ensure students acquire foundational expertise essential for academic progression. The methodology prioritizes measurable learning outcomes, enabling educators to evaluate student comprehension through tests and assignments aligned with established educational standards.
Key Differences Between Inquiry and Content Approaches
Inquiry-based education emphasizes student-driven exploration and critical thinking skills by encouraging learners to ask questions, investigate, and construct understanding through active engagement. Content-based education focuses on the systematic delivery of predetermined subject matter, prioritizing memorization and mastery of specific facts and concepts. Key differences include the active learning process and skill development in inquiry-based approaches versus the structured, teacher-led content transmission in content-based methods.
Benefits of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-based education enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging students to ask questions and explore topics independently. This approach fosters deeper understanding and retention by actively engaging learners in the discovery process. Unlike content-based education, inquiry-based learning cultivates creativity and adaptability essential for real-world applications.
Advantages of Content-Based Instruction
Content-Based Instruction (CBI) enhances language acquisition by integrating subject matter learning with language development, promoting deeper cognitive engagement and contextual understanding. It offers structured content that supports vocabulary expansion and grammar acquisition tailored to specific academic or professional disciplines. This approach facilitates practical language use in real-world scenarios, improving both comprehension and communication skills efficiently.
Challenges of Inquiry-Based Education
Inquiry-based education presents challenges such as the need for highly skilled teachers capable of guiding open-ended questioning without imposing answers, which demands extensive training and experience. Students may struggle with the ambiguity and self-direction inherent in inquiry-based learning, leading to frustration or disengagement if support structures are insufficient. Additionally, the assessment of inquiry-based learning outcomes remains complex, as standardized tests often fail to capture critical thinking and problem-solving skills developed through this approach.
Limitations of Content-Based Methods
Content-Based Education often limits critical thinking by emphasizing memorization and passive absorption of information rather than active engagement. This approach can restrict students' ability to apply knowledge in real-world contexts and hinders the development of problem-solving skills. Furthermore, content-heavy curricula may overwhelm learners, reducing motivation and creativity in the learning process.
Impact on Student Engagement and Critical Thinking
Inquiry-based education significantly enhances student engagement by fostering curiosity and active participation, leading to deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. It promotes critical thinking through open-ended questioning, problem-solving, and exploration, encouraging students to analyze, synthesize, and evaluate information independently. In contrast, content-based education often emphasizes memorization and passive learning, which may limit opportunities for critical thinking and reduce intrinsic motivation.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Inquiry-Based Education emphasizes student-driven exploration and critical thinking, fostering deeper understanding by encouraging curiosity and problem-solving skills. Content-Based Education focuses on structured delivery of subject matter to ensure mastery of specific knowledge and skills, often aligning with standardized curriculum requirements. Selecting the right approach depends on classroom goals, student needs, and subject complexity, blending inquiry methods with content rigor often yields the most effective learning outcomes.
Inquiry-Based Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com