Traditional lecture-based science teaching often relies heavily on passive learning, where students listen to the instructor without engaging in hands-on activities or critical thinking exercises. This method may limit your ability to fully grasp complex scientific concepts and apply them in real-world scenarios. Explore the rest of the article to discover more effective teaching strategies that enhance your understanding and retention of science.
Table of Comparison
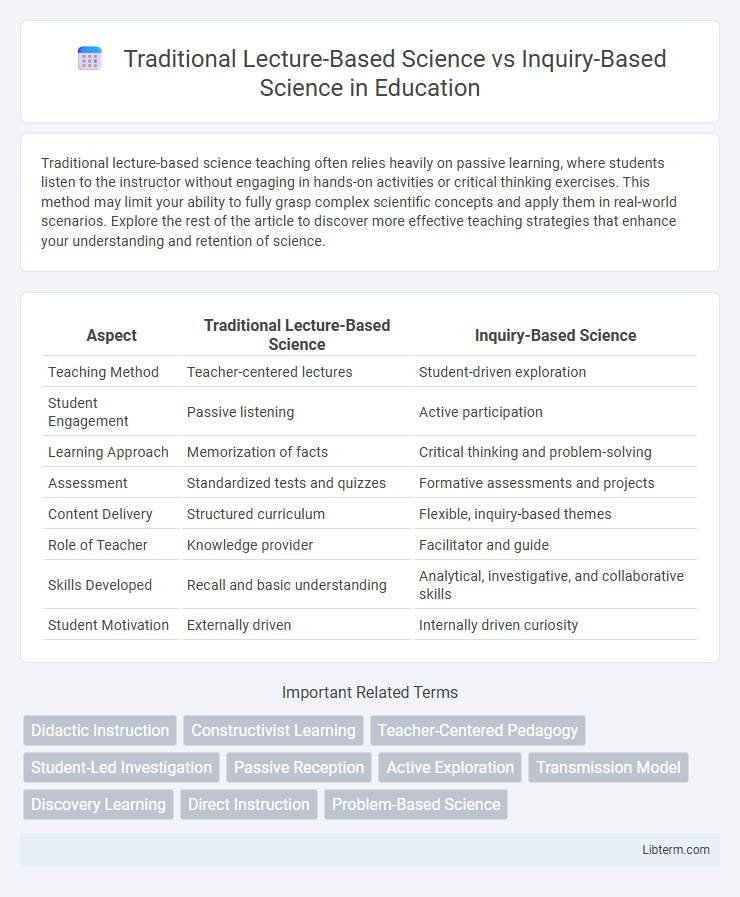
| Aspect | Traditional Lecture-Based Science | Inquiry-Based Science |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching Method | Teacher-centered lectures | Student-driven exploration |
| Student Engagement | Passive listening | Active participation |
| Learning Approach | Memorization of facts | Critical thinking and problem-solving |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and quizzes | Formative assessments and projects |
| Content Delivery | Structured curriculum | Flexible, inquiry-based themes |
| Role of Teacher | Knowledge provider | Facilitator and guide |
| Skills Developed | Recall and basic understanding | Analytical, investigative, and collaborative skills |
| Student Motivation | Externally driven | Internally driven curiosity |
Introduction to Science Teaching Methods
Traditional lecture-based science teaching emphasizes direct instruction, where teachers deliver content through lectures and students passively receive information. Inquiry-based science teaching engages students actively in the learning process by encouraging exploration, questioning, and hands-on experimentation to develop scientific understanding. Research shows inquiry-based methods improve critical thinking and retention compared to traditional approaches that focus on memorization.
Defining Traditional Lecture-Based Science
Traditional Lecture-Based Science emphasizes instructor-centered delivery, where the teacher presents scientific concepts through direct lectures, often relying on textbooks and passive student note-taking. This method prioritizes memorization and the transmission of established scientific knowledge, with limited student interaction or hands-on experimentation. The approach is characterized by structured lessons and standardized assessments designed to evaluate content retention rather than critical thinking or problem-solving skills.
Exploring Inquiry-Based Science Education
Inquiry-based science education emphasizes active student engagement through hands-on experiments and critical thinking, fostering deeper understanding of scientific concepts. Unlike traditional lecture-based science, which relies on passive information delivery, inquiry-based approaches promote skills such as hypothesis formulation, data analysis, and collaborative problem-solving. This method enhances scientific literacy and encourages lifelong curiosity by immersing students in real-world scientific practices.
Key Differences Between the Two Approaches
Traditional lecture-based science emphasizes passive learning where students receive information through direct instruction and memorize content, prioritizing factual knowledge acquisition. Inquiry-based science encourages active participation by engaging students in questioning, experimenting, and discovering concepts, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. The key difference lies in the student's role: passive recipient in traditional methods versus active investigator in inquiry-based approaches, influencing engagement and depth of understanding.
Advantages of Traditional Lecture-Based Science
Traditional lecture-based science provides a structured and efficient delivery of foundational knowledge, ensuring consistent coverage of essential concepts across diverse student populations. This format allows educators to control the pacing and sequence of content, facilitating clarity and minimizing misconceptions early in learning. Moreover, lectures can efficiently reach large groups, making them cost-effective for resource-limited educational settings.
Benefits of Inquiry-Based Science Learning
Inquiry-based science learning promotes critical thinking and problem-solving skills through hands-on experiments and active student engagement. This method enhances knowledge retention by encouraging exploration and fostering curiosity, leading to deeper understanding of scientific concepts. Studies indicate improved academic performance and increased motivation among students exposed to inquiry-based approaches compared to traditional lecture-based instruction.
Challenges and Limitations of Lecture-Based Methods
Lecture-based science teaching often faces challenges such as limited student engagement and passive learning, resulting in lower retention and understanding of complex scientific concepts. This method restricts critical thinking and creativity, as students primarily receive information without opportunities for hands-on experimentation or inquiry. Furthermore, lecture-based approaches may inadequately address diverse learning styles and fail to promote collaboration or problem-solving skills essential for scientific literacy.
Addressing Difficulties in Inquiry-Based Approaches
Inquiry-based science learning faces challenges such as student frustration with open-ended problems and inconsistent guidance, which can hinder deep understanding. Effective strategies include scaffolding complex tasks, providing timely formative feedback, and fostering collaborative learning environments to support cognitive development. Research in science education emphasizes that adaptive support and structured inquiry sequences significantly improve student engagement and conceptual mastery in inquiry-based settings.
Impact on Student Engagement and Learning Outcomes
Traditional lecture-based science often results in passive student participation, limiting opportunities for critical thinking and reducing overall engagement. Inquiry-based science promotes hands-on experimentation and collaborative problem-solving, significantly enhancing student motivation and deepening conceptual understanding. Research shows that inquiry-based methods lead to higher retention rates and improved performance on assessments compared to traditional lecture formats.
Choosing the Right Science Teaching Strategy
Selecting the appropriate science teaching strategy depends on learning objectives and student engagement levels; traditional lecture-based science efficiently delivers foundational knowledge and systematic content coverage, while inquiry-based science fosters critical thinking, hands-on experimentation, and deeper conceptual understanding. Inquiry-based approaches enhance student motivation and adaptability by encouraging exploration and problem-solving in real-world contexts. Balancing both methods can optimize comprehension and skill development across diverse learner needs and educational goals.
Traditional Lecture-Based Science Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com