A monocultural curriculum focuses on a single cultural perspective, often limiting students' understanding of diverse viewpoints and experiences. This approach can hinder critical thinking and diminish the appreciation of multiculturalism in an increasingly globalized world. Explore the rest of the article to discover the benefits of integrating a multicultural curriculum into your educational framework.
Table of Comparison
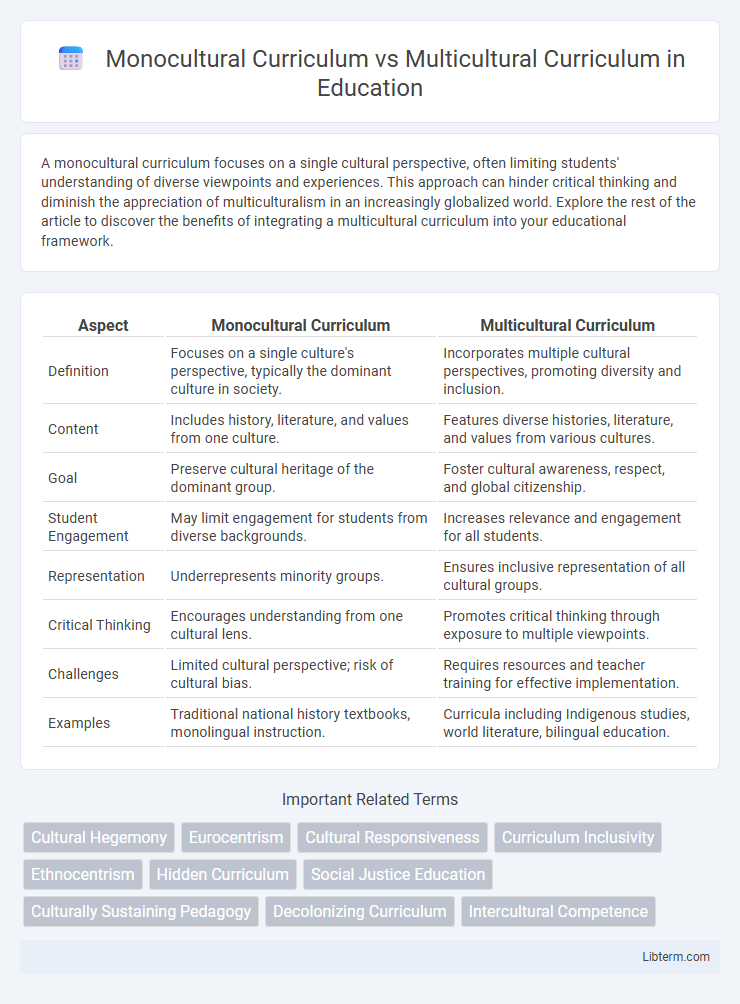
| Aspect | Monocultural Curriculum | Multicultural Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Focuses on a single culture's perspective, typically the dominant culture in society. | Incorporates multiple cultural perspectives, promoting diversity and inclusion. |
| Content | Includes history, literature, and values from one culture. | Features diverse histories, literature, and values from various cultures. |
| Goal | Preserve cultural heritage of the dominant group. | Foster cultural awareness, respect, and global citizenship. |
| Student Engagement | May limit engagement for students from diverse backgrounds. | Increases relevance and engagement for all students. |
| Representation | Underrepresents minority groups. | Ensures inclusive representation of all cultural groups. |
| Critical Thinking | Encourages understanding from one cultural lens. | Promotes critical thinking through exposure to multiple viewpoints. |
| Challenges | Limited cultural perspective; risk of cultural bias. | Requires resources and teacher training for effective implementation. |
| Examples | Traditional national history textbooks, monolingual instruction. | Curricula including Indigenous studies, world literature, bilingual education. |
Understanding Monocultural Curriculum
A monocultural curriculum centers predominantly on the values, histories, and perspectives of a single cultural group, often reflecting the dominant culture in society. This approach can limit students' exposure to diverse worldviews and reinforce ethnocentric attitudes, potentially hindering cross-cultural understanding and inclusivity. Research highlights the need for curriculum reform to promote cultural competence and equity by integrating multiple cultural narratives.
Key Features of Monocultural Curriculum
A Monocultural Curriculum centers on a single cultural perspective, often reflecting the dominant culture's values, history, and language within educational content. It typically prioritizes a standardized narrative that excludes diverse cultural backgrounds, resulting in limited cultural representation in textbooks, teaching materials, and assessments. The focus on uniformity aims to create a cohesive identity but may neglect the cultural pluralism present in multicultural societies.
Understanding Multicultural Curriculum
A multicultural curriculum emphasizes diverse perspectives by integrating content from various cultures, promoting cultural awareness, and fostering inclusivity in learning environments. It encourages critical thinking about social justice, equity, and the contributions of marginalized groups, enhancing students' empathy and global understanding. This approach contrasts with a monocultural curriculum that often centers on a single dominant culture, limiting students' worldview and cultural competence.
Core Principles of Multicultural Curriculum
The core principles of a multicultural curriculum emphasize inclusivity, cultural diversity, and equity by integrating multiple cultural perspectives into the learning process. This approach fosters critical thinking, respect for different identities, and the validation of historically marginalized voices, contrasting sharply with a monocultural curriculum that centers on a single dominant culture. Key elements include curriculum content that reflects diverse experiences, pedagogical strategies promoting student-centered learning, and assessment methods accommodating varied cultural backgrounds.
Historical Evolution of Educational Curricula
Educational curricula historically evolved from monocultural frameworks that prioritized dominant cultural narratives and perspectives, often marginalizing diverse groups. The shift towards multicultural curricula emerged in the late 20th century in response to growing social awareness and civil rights movements, emphasizing inclusion of diverse cultures, histories, and viewpoints. This evolution reflects an ongoing effort to create equitable and representative education systems that acknowledge and value cultural pluralism.
Benefits of a Multicultural Curriculum
A multicultural curriculum fosters cultural awareness and inclusivity by representing diverse perspectives, enhancing students' social empathy and global competence. It promotes critical thinking by exposing learners to varied historical narratives and experiences, reducing cultural biases and stereotypes. Studies show that students in multicultural programs demonstrate improved academic engagement and higher motivation compared to monocultural curriculums.
Limitations of Monocultural Curriculum
A monocultural curriculum limits students' exposure to diverse perspectives by focusing primarily on the dominant culture's values, histories, and narratives. This approach inadequately prepares learners for global citizenship and perpetuates cultural biases and stereotypes. Consequently, it hinders the development of critical thinking and empathy necessary for understanding multicultural societies.
Social Impact of Curriculum Choices
Monocultural curriculum reinforces dominant cultural narratives, often marginalizing minority perspectives and perpetuating social inequalities. Multicultural curriculum promotes inclusivity and cultural awareness, fostering empathy and social cohesion among diverse student populations. Curriculum choices shape students' understanding of societal diversity, directly influencing social integration and equity.
Strategies for Integrating Multiculturalism in Education
Effective strategies for integrating multiculturalism in education include incorporating diverse perspectives into curriculum content, using culturally relevant teaching materials, and fostering an inclusive classroom environment where all student backgrounds are valued. Training educators in cultural competence enables them to address biases and adapt instructional methods to meet the needs of diverse learners. Implementing collaborative projects and community engagement activities further enhances students' understanding and appreciation of multiculturalism.
Future Trends in Curriculum Development
Future trends in curriculum development emphasize a shift from monocultural to multicultural curricula to better prepare students for global citizenship and diverse workplaces. Integrating culturally responsive teaching methods and diverse perspectives fosters critical thinking, empathy, and inclusivity among learners. Emerging educational technologies and global collaboration platforms are driving personalized, culturally adaptive learning experiences that reflect the complexities of a multicultural society.
Monocultural Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com