Race to the Top is a competitive grant program designed to incentivize innovation and reforms in K-12 education across the United States. By focusing on student achievement, teacher effectiveness, and data-driven decision making, it aims to elevate educational standards and close achievement gaps. Discover how this initiative can impact Your school district and drive meaningful improvements throughout the article.
Table of Comparison
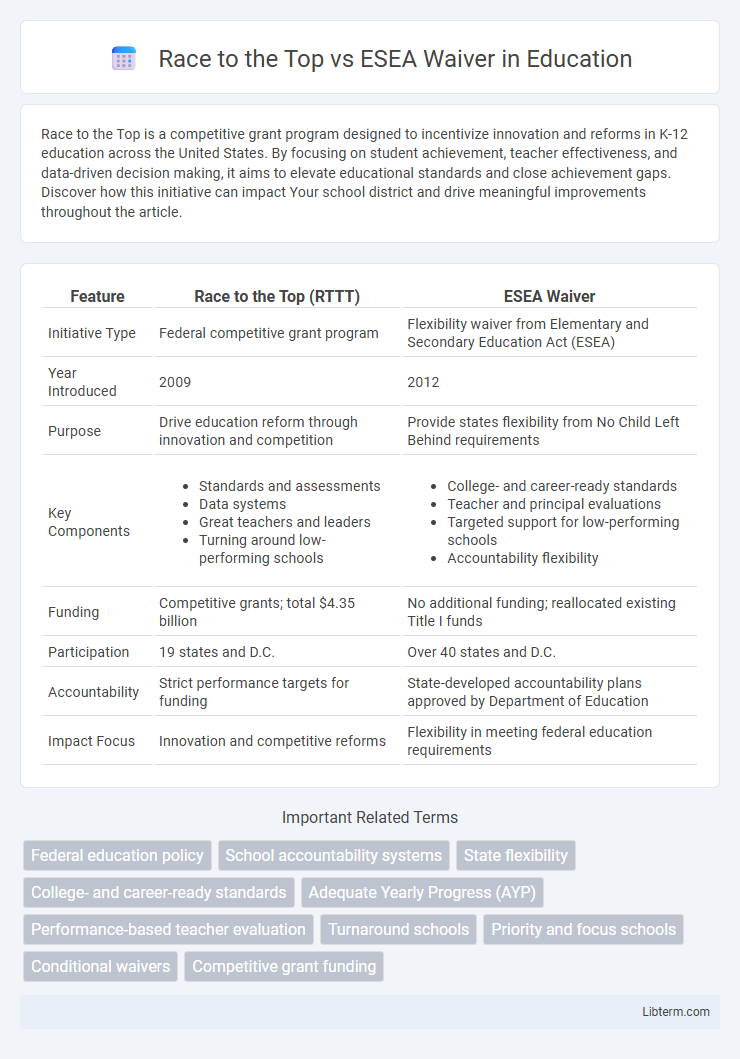
| Feature | Race to the Top (RTTT) | ESEA Waiver |
|---|---|---|
| Initiative Type | Federal competitive grant program | Flexibility waiver from Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) |
| Year Introduced | 2009 | 2012 |
| Purpose | Drive education reform through innovation and competition | Provide states flexibility from No Child Left Behind requirements |
| Key Components |
|
|
| Funding | Competitive grants; total $4.35 billion | No additional funding; reallocated existing Title I funds |
| Participation | 19 states and D.C. | Over 40 states and D.C. |
| Accountability | Strict performance targets for funding | State-developed accountability plans approved by Department of Education |
| Impact Focus | Innovation and competitive reforms | Flexibility in meeting federal education requirements |
Introduction: Understanding Race to the Top and ESEA Waiver
Race to the Top was a competitive grant program launched by the U.S. Department of Education in 2009 to incentivize states in implementing education reforms focused on student achievement, teacher effectiveness, and data-driven decision-making. The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) Waiver, introduced later, allowed states flexibility from certain No Child Left Behind requirements by adopting state-specific accountability systems aligned with the Elementary and Secondary Education Act's goals. Both initiatives aimed to improve public education through innovative policies, with Race to the Top emphasizing competitive funding and ESEA Waivers offering regulatory flexibility.
Historical Context of Federal Education Reform
The Race to the Top (RTTT) initiative, launched in 2009 under the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, marked a significant shift in federal education policy by incentivizing states to adopt standards like the Common Core and implement teacher evaluation systems tied to student performance. The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) Waiver, introduced in 2012, provided states with flexibility from No Child Left Behind (NCLB) requirements in exchange for commitments to college- and career-ready standards and improved accountability measures. Both policies reflect evolving federal strategies aimed at increasing educational equity and improving outcome-based accountability systems across public schools.
Core Objectives of Race to the Top
Race to the Top emphasized key educational reforms including improving standards and assessments, enhancing teacher effectiveness, and turning around low-performing schools. Its core objectives centered on raising student achievement through rigorous accountability, data-driven decision making, and expanding educational opportunities. Unlike ESEA Waivers, Race to the Top offered substantial competitive grants to states adopting innovative policies aligned with these goals.
Purpose and Provisions of the ESEA Waiver
The ESEA Waiver aimed to provide states flexibility from specific requirements of the No Child Left Behind Act by allowing personalized accountability systems, tailored interventions for struggling schools, and updated teacher evaluation methods. Its provisions included replacing Adequate Yearly Progress (AYP) with differentiated accountability, setting ambitious but attainable goals for all students, and supporting evidence-based school improvement plans. The waiver facilitated states' efforts to innovate education reforms while maintaining federal oversight and ensuring support for underperforming schools.
Funding and Incentives: Comparing Approaches
Race to the Top offered substantial competitive grants to states to encourage education reform, totaling $4.35 billion aimed at innovation and accountability improvements. In contrast, the ESEA Waiver provided flexibility from certain No Child Left Behind requirements in exchange for states adopting specific reforms, without direct grant funding but with the incentive of avoiding federal sanctions. Both approaches aimed to drive systemic change, but Race to the Top relied on financial awards while ESEA Waivers incentivized states through regulatory leniency and performance benchmarks.
Accountability Systems and Standards Alignment
Race to the Top emphasized rigorous accountability systems by rewarding states that developed comprehensive growth models and improved student outcomes through data-driven interventions. ESEA Waivers provided flexibility by allowing states to design differentiated accountability systems tailored to local priorities while maintaining alignment with college- and career-ready standards, often incorporating multiple measures of student achievement. Both initiatives aimed to align standards and accountability, but Race to the Top used competitive grants to enforce compliance, whereas ESEA Waivers focused on granting states autonomy within federal guidelines.
Impact on Teacher Evaluation and Effectiveness
The Race to the Top initiative significantly advanced teacher evaluation systems by promoting rigorous standards tied to student performance data and multiple measures of effectiveness. In contrast, ESEA Waivers offered states flexibility to design their own teacher evaluation frameworks while maintaining a focus on improving instructional quality and accountability. Both approaches emphasized using evaluation results to inform professional development and improve teacher effectiveness, though Race to the Top mandated more prescriptive criteria for implementation.
State Flexibility and Implementation Challenges
Race to the Top provided states with competitive grants encouraging innovative education reforms but required strict adherence to federal guidelines, limiting state flexibility. In contrast, the ESEA Waiver offered broader state flexibility by allowing exemptions from specific No Child Left Behind provisions while demanding states meet performance targets tied to college-and-career readiness. Implementation challenges for both included balancing federal oversight with local control, ensuring equitable resource allocation, and managing stakeholder resistance to significant policy shifts.
Student Achievement: Measuring Outcomes and Equity
Race to the Top emphasized rigorous student achievement metrics by incorporating Common Core standards and Annual Measurable Objectives (AMOs) to promote accountability and equity in education. ESEA Waivers replaced Adequate Yearly Progress (AYP) with multiple measures of student performance, including growth models and subgroup analyses, to better capture diverse student outcomes and close achievement gaps. Both initiatives sought to enhance equity by targeting support to underperforming schools and ensuring gains across all student demographics.
Long-Term Implications for U.S. Education Policy
Race to the Top introduced competitive grants that incentivized states to implement comprehensive education reforms, promoting innovation in standards and accountability systems. ESEA Waivers allowed states flexibility from No Child Left Behind requirements, enabling tailored approaches to improve student outcomes without strict federal mandates. Long-term implications include a shift toward state-led education policies emphasizing data-driven decision-making and local control, influencing federal-state dynamics in U.S. education governance.
Race to the Top Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com