Badges serve as symbols of achievement, recognition, or membership, often used across various platforms, organizations, and events. They enhance credibility and motivate individuals to engage more deeply with specific activities or communities. Discover how badges can impact your personal or professional growth by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
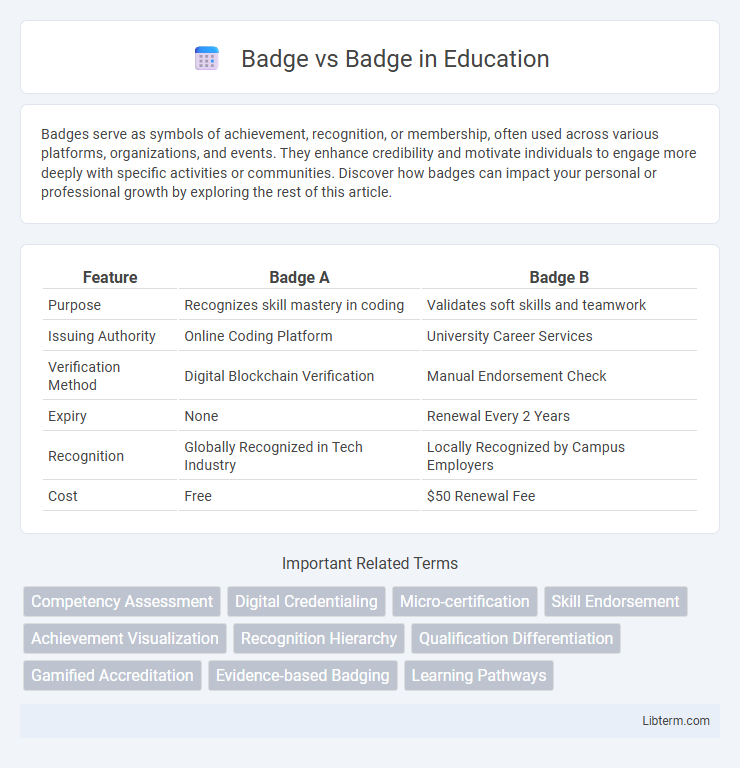
| Feature | Badge A | Badge B |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Recognizes skill mastery in coding | Validates soft skills and teamwork |
| Issuing Authority | Online Coding Platform | University Career Services |
| Verification Method | Digital Blockchain Verification | Manual Endorsement Check |
| Expiry | None | Renewal Every 2 Years |
| Recognition | Globally Recognized in Tech Industry | Locally Recognized by Campus Employers |
| Cost | Free | $50 Renewal Fee |
Introduction to Badge vs Badge
Badge vs Badge presents a comparative analysis of two distinct types of badges, emphasizing their design, purpose, and usage across various applications. It explores core differences in material composition, attachment mechanisms, and symbolic meanings assigned in organizational or digital contexts. Understanding these distinctions helps users select the appropriate badge type for identification, branding, or achievement recognition purposes.
Defining Badges: Digital vs Physical
Digital badges are virtual representations of achievements stored and shared online, offering instant verification and easy accessibility across platforms such as LinkedIn and digital portfolios. Physical badges, traditionally crafted from materials like metal or fabric, serve as tangible symbols displayed in workplaces or events to signify membership or accomplishments. While digital badges enhance portability and security through blockchain technology, physical badges provide a visible and lasting emblem often used for identification or ceremonial recognition.
Key Differences Between Badge Types
Key differences between badge types include their design, purpose, and application. Identification badges typically display personal information and affiliation, while achievement badges symbolize accomplishments or skills earned through activities. Access badges function as security devices granting entry to restricted areas, differing significantly in material and technology from other badge types.
Use Cases for Each Badge Format
Badge formats serve distinct purposes across digital and physical applications, with digital badges commonly used in e-learning platforms to certify skills, track progress, and motivate learners through verified credentials. Physical badges are prevalent in events, conferences, and workplaces for identification, access control, and fostering community engagement. Selecting the appropriate badge format depends on the context of use, such as digital badges for remote recognition and gamification, while physical badges excel in face-to-face environments where immediate identification is essential.
Benefits of Digital Badges
Digital badges enhance professional credibility by providing verifiable evidence of skills and achievements that traditional badges lack. They enable easy sharing across digital platforms such as LinkedIn, increasing visibility to employers and peers. Digital badges also support lifelong learning by tracking and showcasing continuous education and competency development over time.
Advantages of Physical Badges
Physical badges offer tangible recognition that enhances motivation through visible achievement symbols, fostering a sense of pride and accomplishment. They provide easy identification in events or workplaces, promoting networking and community building by displaying roles, ranks, or certifications. Durable materials ensure long-lasting use, making physical badges reliable tools for continuous branding and security purposes.
Credibility and Authentication
Badge and Badge systems both serve to enhance credibility and authentication by visually representing verified achievements or qualifications. Digital badges utilize cryptographic verification to ensure authenticity, allowing instant validation of skills and certifications across platforms. This secure authentication process builds trust among employers, educators, and peers by confirming an individual's verified competencies and accomplishments.
Cost and Accessibility Comparison
Badges typically vary in cost based on materials, design complexity, and production volume, with custom enamel badges costing between $2 to $10 per unit, while fabric badges can be as low as $0.50 each. Accessibility is influenced by manufacturing methods and distribution, as digital badges offer instant access and sharing capabilities compared to physical badges that require shipping and handling time. Organizations often choose digital badges for scalable, cost-effective recognition, whereas physical badges are preferred for tactile engagement despite higher expenses and logistical challenges.
Future Trends in Badge Systems
Future trends in badge systems emphasize enhanced interoperability across platforms, enabling seamless skill recognition in diverse digital ecosystems. Blockchain integration ensures badge authenticity and security, fostering trust among employers and learners. Adaptive badge frameworks leveraging AI analyze competency gaps and recommend personalized learning pathways, driving more efficient upskilling.
Choosing the Right Badge for Your Needs
Selecting the right badge depends on intended use, material durability, and visibility requirements. Plastic badges offer lightweight affordability for short-term events, while metal badges provide long-lasting professionalism for corporate or identification purposes. Customizable features such as size, color, and attachment type should align with specific environmental conditions and branding goals.
Badge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com