Intra-curricular activities are integrated within the regular academic curriculum to enhance students' learning experiences and skill development. These activities promote critical thinking, collaboration, and practical application of theoretical knowledge. Explore the article to discover how intra-curricular programs can enrich your educational journey effectively.
Table of Comparison
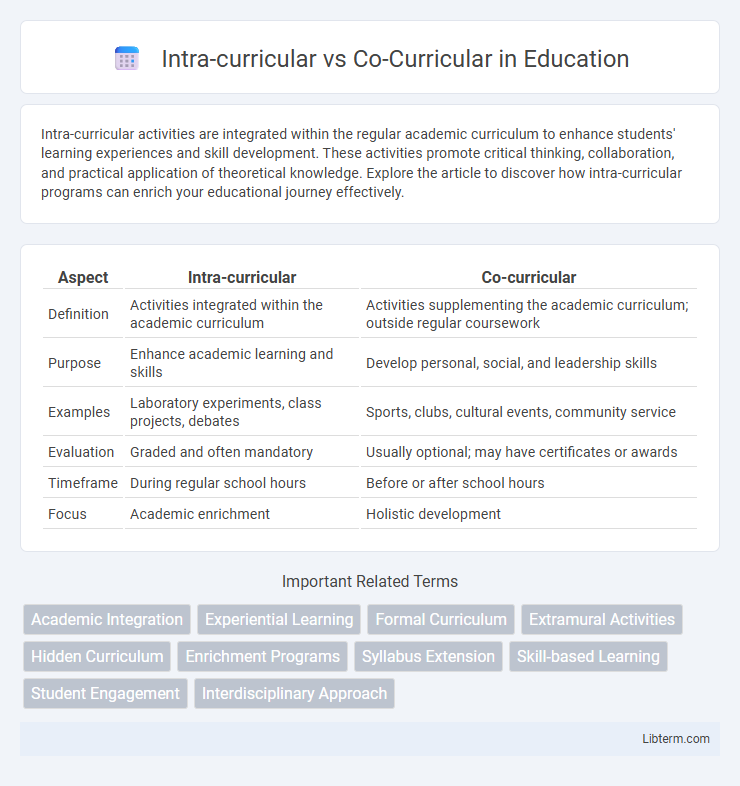
| Aspect | Intra-curricular | Co-curricular |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Activities integrated within the academic curriculum | Activities supplementing the academic curriculum; outside regular coursework |
| Purpose | Enhance academic learning and skills | Develop personal, social, and leadership skills |
| Examples | Laboratory experiments, class projects, debates | Sports, clubs, cultural events, community service |
| Evaluation | Graded and often mandatory | Usually optional; may have certificates or awards |
| Timeframe | During regular school hours | Before or after school hours |
| Focus | Academic enrichment | Holistic development |
Introduction to Intra-Curricular and Co-Curricular Activities
Intra-curricular activities are structured learning experiences integrated directly within the academic curriculum, such as science experiments, group projects, and classroom debates. Co-curricular activities complement the academic syllabus by promoting skills and values through practical engagement, including sports, music clubs, and student councils. Both types of activities enhance student development, fostering cognitive, social, and emotional growth alongside traditional education.
Defining Intra-Curricular Activities
Intra-curricular activities are educational tasks integrated directly into the core curriculum, enhancing students' understanding of academic subjects through practical application and structured learning experiences. These activities include laboratory experiments, class projects, and subject-specific competitions that align with academic goals and assessment criteria. Unlike co-curricular activities, intra-curricular programs focus on reinforcing classroom instruction and academic achievement within the formal educational framework.
What are Co-Curricular Activities?
Co-curricular activities complement the academic curriculum by enhancing students' personal, social, and intellectual development outside traditional classroom lessons. These activities include sports, music, drama, debates, and clubs that foster teamwork, leadership, and practical skills. Participation in co-curricular programs promotes holistic education, improving student engagement and overall academic performance.
Key Differences Between Intra-Curricular and Co-Curricular
Intra-curricular activities are integrated within the formal academic curriculum and directly support educational objectives, such as laboratory experiments and class debates, enhancing subject-specific knowledge and skills. Co-curricular activities occur outside the standard curriculum but complement classroom learning by developing broader skills, including sports teams, clubs, and community service. The key difference lies in their alignment to academic schedules and their role in holistic student development, with intra-curricular activities mandatory and co-curricular often voluntary yet equally vital for soft skill enhancement.
Benefits of Intra-Curricular Activities for Students
Intra-curricular activities enhance student engagement by integrating practical skills directly into the academic curriculum, which promotes deeper understanding and retention of subject matter. These activities foster critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration within a structured learning environment, aligning closely with educational goals. Research shows that students involved in intra-curricular programs tend to achieve higher academic performance and improved time management skills compared to their peers.
Advantages of Co-Curricular Activities
Co-curricular activities enhance students' social skills, leadership abilities, and teamwork through practical experiences outside the traditional curriculum. These activities foster creativity and critical thinking by encouraging participation in arts, sports, and community service, complementing academic learning. Engagement in co-curricular activities also improves time management and self-discipline, contributing to holistic personal and academic development.
The Role of Both Activities in Holistic Education
Intra-curricular activities are integrated within the academic curriculum and directly reinforce subject knowledge, while co-curricular activities complement education by promoting social skills, creativity, and physical development outside the classroom. Both types of activities are essential in holistic education, as they collectively foster intellectual growth, emotional intelligence, and interpersonal skills. Research shows that students engaged in balanced intra- and co-curricular activities exhibit higher academic performance, greater motivation, and improved overall well-being.
Integrating Intra-Curricular and Co-Curricular for Better Outcomes
Integrating intra-curricular activities, which are embedded within the formal academic curriculum, with co-curricular activities like clubs, sports, and community service enhances holistic learning by reinforcing theoretical knowledge through practical application. This combined approach fosters critical thinking, leadership, and interpersonal skills, creating a dynamic educational environment that supports diverse learning styles. Research indicates that students engaged in both intra-curricular and co-curricular programs demonstrate higher academic performance, improved motivation, and better social-emotional development.
Challenges in Balancing Intra-Curricular and Co-Curricular Activities
Balancing intra-curricular and co-curricular activities presents challenges such as time management conflicts, where students struggle to allocate sufficient time for rigorous academic tasks and extracurricular commitments. Academic performance may decline if co-curricular involvement consumes excessive hours, leading to stress and burnout. Effective planning and institutional support are essential to optimize student engagement without compromising educational outcomes.
Conclusion: Importance of a Balanced Educational Approach
A balanced educational approach integrating both intra-curricular and co-curricular activities enhances holistic student development by fostering academic knowledge alongside critical life skills such as teamwork, leadership, and time management. Schools that prioritize this synergy report improved student engagement, higher academic performance, and better preparedness for real-world challenges. Emphasizing an equitable blend ensures students receive comprehensive education crucial for personal growth and future success.
Intra-curricular Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com