Mastery-based assessment focuses on ensuring students achieve a deep understanding of material before moving on to new topics, prioritizing comprehension over speed. This approach allows learners to progress at their own pace, fostering long-term retention and application of knowledge. Discover how mastery-based assessment can transform your educational experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
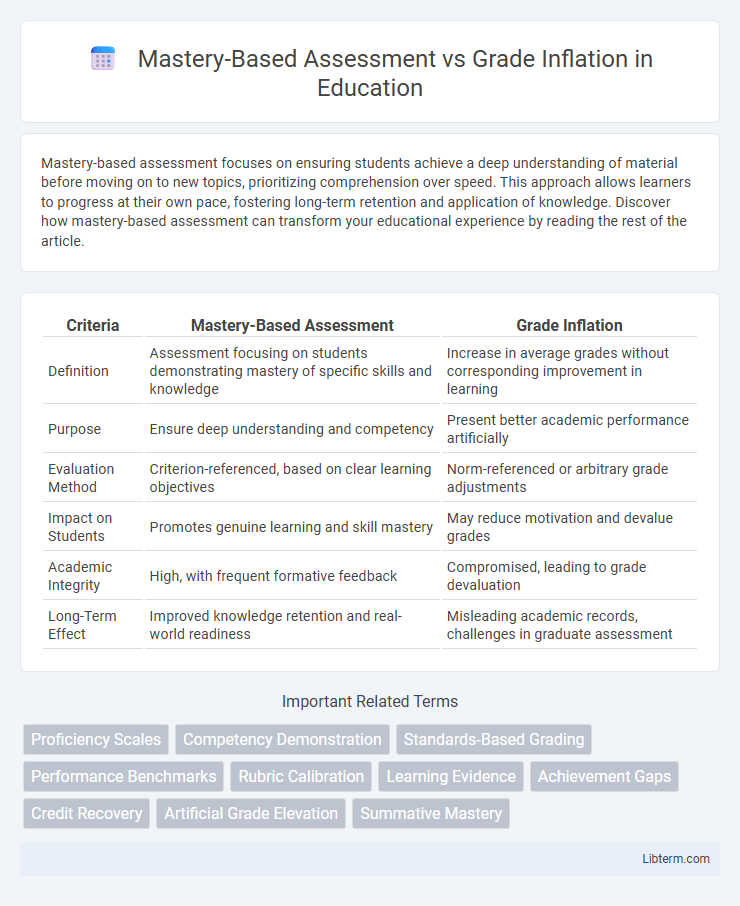
| Criteria | Mastery-Based Assessment | Grade Inflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Assessment focusing on students demonstrating mastery of specific skills and knowledge | Increase in average grades without corresponding improvement in learning |
| Purpose | Ensure deep understanding and competency | Present better academic performance artificially |
| Evaluation Method | Criterion-referenced, based on clear learning objectives | Norm-referenced or arbitrary grade adjustments |
| Impact on Students | Promotes genuine learning and skill mastery | May reduce motivation and devalue grades |
| Academic Integrity | High, with frequent formative feedback | Compromised, leading to grade devaluation |
| Long-Term Effect | Improved knowledge retention and real-world readiness | Misleading academic records, challenges in graduate assessment |
Understanding Mastery-Based Assessment
Mastery-based assessment evaluates students' comprehension and skills by requiring demonstration of proficiency before progressing, unlike traditional grading systems prone to grade inflation. This method emphasizes deep learning and personalized feedback, ensuring students achieve a thorough understanding of subject matter. By aligning assessments with clear learning objectives, mastery-based approaches reduce grade inflation and promote genuine academic achievement.
Defining Grade Inflation in Education
Grade inflation in education refers to the gradual increase in student grades without a corresponding rise in learning or achievement levels, often leading to diminished academic standards. Mastery-based assessment contrasts this trend by emphasizing student proficiency and mastery of specific skills or knowledge before advancing, ensuring grades reflect true understanding. This approach addresses the pitfalls of grade inflation by maintaining rigorous evaluation criteria aligned with learning outcomes.
Key Differences Between Mastery and Traditional Grading
Mastery-based assessment evaluates students on their ability to demonstrate deep understanding and proficiency in specific skills or concepts, emphasizing continuous improvement and personalized learning progress. Traditional grading often relies on averaged scores and percentage points that may mask true comprehension, contributing to grade inflation by rewarding partial knowledge or effort instead of mastery. Key differences include the focus on demonstrating competency versus accumulating points, and mastery assessments provide clearer feedback on specific strengths and weaknesses rather than a single generalized score.
Causes and Consequences of Grade Inflation
Grade inflation primarily results from lenient grading standards, pressure to meet institutional enrollment goals, and teacher biases favoring higher marks to support student motivation. Consequences of grade inflation include devalued academic credentials, difficulty distinguishing student abilities, and reduced incentives for students to achieve mastery of content. Mastery-based assessments aim to counteract these issues by emphasizing demonstrated competency and providing clear benchmarks, thereby preserving academic integrity and fostering genuine learning outcomes.
Benefits of Mastery-Based Assessment Systems
Mastery-based assessment systems promote deep understanding by requiring students to demonstrate proficiency before advancing, reducing the risk of grade inflation that often comes from traditional grading methods. These systems provide clearer feedback on student learning, enabling targeted interventions and personalized support that enhance overall educational outcomes. By emphasizing mastery, schools foster long-term retention and skill development, ensuring that grades truly reflect competency rather than inflated averages.
Challenges Faced in Implementing Mastery Approaches
Mastery-based assessment faces challenges including inconsistent standardization, which complicates comparability across institutions and can obscure true academic ability. Educators often encounter resistance due to the increased time and resources required for personalized feedback and repeated assessments to ensure skill mastery. These factors contribute to difficulties in balancing accurate competency measurement with pressures that may inadvertently encourage grade inflation.
Impact on Student Motivation and Learning Outcomes
Mastery-based assessment emphasizes demonstrating proficiency in specific skills, which fosters intrinsic motivation and deeper understanding in students. Grade inflation, often resulting from lenient grading practices, can undermine authentic learning by diminishing the value of grades and reducing students' drive to improve. Research indicates that mastery-based approaches lead to higher engagement and better long-term retention compared to inflated grading systems.
Teacher Perspectives: Mastery vs. Inflated Grades
Teachers favor mastery-based assessments for their ability to accurately reflect student understanding and skill acquisition, minimizing the distortions caused by grade inflation. Educators highlight that mastery grading promotes deeper learning and clearer feedback, contrasting with inflated grades that often mask gaps in knowledge and undermine academic standards. This perspective underscores the importance of aligning assessment practices with true competency rather than inflated numerical scores.
Policy Implications for Educational Institutions
Mastery-based assessment emphasizes demonstrating competency over accumulating points, reducing grade inflation by aligning grades with actual skill acquisition. Educational institutions must revise policies to incorporate clear mastery criteria, standardized performance metrics, and ongoing formative feedback to ensure accurate student evaluation. Shifting to mastery-based assessment requires policy adjustments that promote transparency, equity, and long-term academic integrity while mitigating pressures that contribute to inflated grades.
Recommendations for Fair and Effective Assessment Practices
Mastery-based assessment prioritizes demonstration of skills and knowledge over accumulating points, reducing risks of grade inflation by aligning grades with actual learning outcomes. Implementing clear rubrics, frequent formative assessments, and personalized feedback ensures fair evaluation and supports student progress. Institutions should integrate mastery criteria with transparent grading policies to balance rigor and equity in assessment practices.
Mastery-Based Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com