The chancellor plays a crucial role in shaping government policies and overseeing national administration. This position holds significant influence in economic planning, education, and legal frameworks, directly impacting your country's future. Explore the article to understand the responsibilities and importance of a chancellor in modern governance.
Table of Comparison
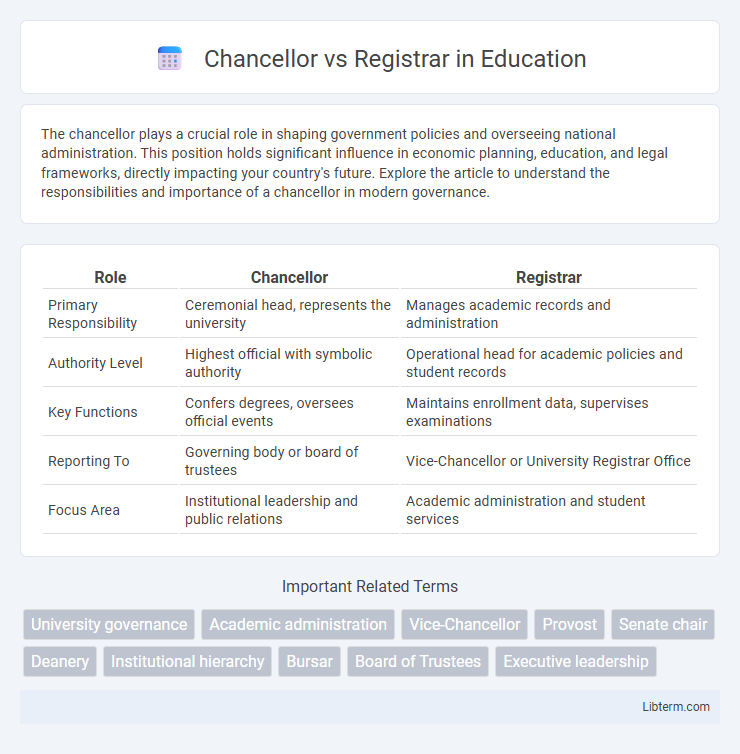
| Role | Chancellor | Registrar |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Responsibility | Ceremonial head, represents the university | Manages academic records and administration |
| Authority Level | Highest official with symbolic authority | Operational head for academic policies and student records |
| Key Functions | Confers degrees, oversees official events | Maintains enrollment data, supervises examinations |
| Reporting To | Governing body or board of trustees | Vice-Chancellor or University Registrar Office |
| Focus Area | Institutional leadership and public relations | Academic administration and student services |
Introduction to Chancellor and Registrar Roles
The Chancellor typically serves as the ceremonial head of a university, often responsible for presiding over convocations and representing the institution in formal capacities. The Registrar manages academic records, coordinates examination processes, and oversees student enrollment and registration systems. These roles are distinct yet complementary, ensuring both governance and administrative efficiency within educational institutions.
Historical Context of Chancellor vs Registrar
The historical context of the Chancellor and Registrar roles traces back to medieval European universities, where the Chancellor acted as the chief executive and ceremonial head representing royal or ecclesiastical authority. The Registrar emerged as a crucial administrative officer responsible for maintaining official university records, enrollment lists, and scholarly documentation. Over time, both roles evolved with the Chancellor focusing on governance and external relations, while the Registrar specialized in academic administration and compliance.
Core Responsibilities of a Chancellor
The Chancellor serves as the ceremonial head and chief executive officer of a university, overseeing its strategic direction, external relations, and major policy decisions. They play a pivotal role in fostering partnerships, securing funding, and representing the institution at significant academic and public events. Core responsibilities include guiding institutional mission, approving academic programs, and ensuring compliance with educational regulations.
Key Duties of a Registrar
The key duties of a Registrar include maintaining and managing academic records, ensuring compliance with institutional policies, overseeing student registration and enrollment processes, and coordinating graduation requirements. Registrars handle the certification of student transcripts, manage course scheduling, and collaborate with faculty to uphold academic standards. Their role is critical in data accuracy and administration to support student progression and institutional reporting.
Academic vs Administrative Functions
The Chancellor primarily holds the highest academic authority in a university, overseeing academic standards, policies, and long-term educational goals, often representing the institution in formal settings. The Registrar manages key administrative functions such as student enrollment, record-keeping, examination logistics, and maintaining academic databases. While the Chancellor's role centers on strategic academic leadership, the Registrar ensures the smooth operational administration essential for academic processes.
Decision-Making Authority: Chancellor vs Registrar
The Chancellor holds the highest decision-making authority in a university, overseeing major policies, administrative appointments, and strategic direction. The Registrar's decision-making is more operational, managing academic records, enrollment processes, and regulatory compliance. While the Chancellor's decisions shape institutional governance, the Registrar ensures these policies are executed efficiently within academic and administrative frameworks.
Interaction with Faculty, Staff, and Students
The Chancellor oversees the overall administration and strategic vision of the university, interacting extensively with faculty to align academic goals and policies, while guiding staff and student initiatives at a high level. The Registrar manages student records, enrollment processes, and academic scheduling, maintaining direct daily contact with students and faculty to ensure smooth operational flow. Collaboration between the Chancellor and Registrar is crucial for integrating administrative decisions with academic and student affairs.
Appointment Process and Qualifications
The Chancellor is typically appointed by the head of state or a governing board, often requiring extensive experience in higher education leadership or public service, with qualifications including advanced academic degrees and a proven record of administrative excellence. The Registrar is usually appointed by the university senate or administration, needing specialized knowledge in academic administration and records management, with qualifications such as a master's degree in education or management and expertise in regulatory compliance. Both roles demand strong leadership skills but differ in appointment authority and specific educational prerequisites tailored to their distinct administrative functions.
Chancellor and Registrar in Different Education Systems
Chancellors typically serve as ceremonial heads or senior executives in universities, responsible for overarching governance and representing the institution in many Commonwealth and European education systems. Registrars hold operational roles across global educational institutions, managing student records, academic policies, and administrative functions essential to daily university operations. The Chancellor's authority varies widely, often symbolic in some systems, while Registrars consistently ensure academic compliance and institutional efficiency across diverse education frameworks.
Impact on University Governance and Policy
The Chancellor primarily serves as the ceremonial head of a university, symbolizing institutional authority and often influencing high-level policy through advisory roles and external representation. The Registrar manages the administration of academic policies, ensuring compliance with governance structures by overseeing student records, examinations, and regulatory requirements. Together, their distinct functions impact university governance by balancing ceremonial leadership with effective operational policy implementation.
Chancellor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com