A concept map visually organizes and represents knowledge by connecting ideas through labeled relationships, enhancing understanding and recall. This tool helps you identify key concepts and their associations, making complex information easier to grasp and communicate. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to create effective concept maps that boost your learning and productivity.
Table of Comparison
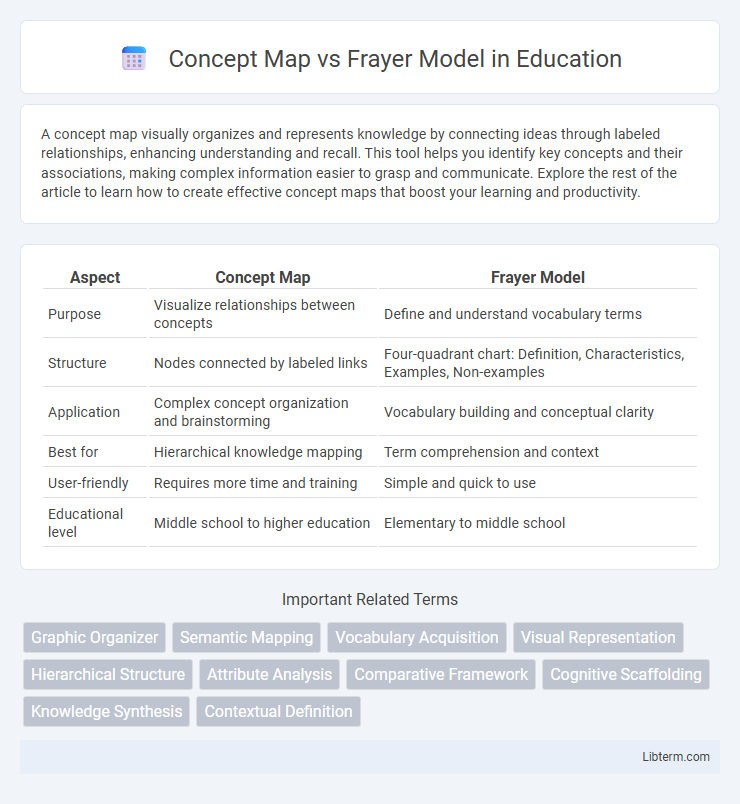
| Aspect | Concept Map | Frayer Model |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Visualize relationships between concepts | Define and understand vocabulary terms |
| Structure | Nodes connected by labeled links | Four-quadrant chart: Definition, Characteristics, Examples, Non-examples |
| Application | Complex concept organization and brainstorming | Vocabulary building and conceptual clarity |
| Best for | Hierarchical knowledge mapping | Term comprehension and context |
| User-friendly | Requires more time and training | Simple and quick to use |
| Educational level | Middle school to higher education | Elementary to middle school |
Introduction to Concept Mapping and the Frayer Model
Concept mapping organizes knowledge visually by linking key concepts with labeled relationships, enhancing comprehension and retention. The Frayer Model, a graphic organizer, defines vocabulary through four sections: definition, characteristics, examples, and non-examples, facilitating deep understanding of terms. Both tools support active learning by structuring information, but concept maps emphasize interconnected ideas while the Frayer Model centers on vocabulary mastery.
Key Features of Concept Maps
Concept maps visually represent relationships between concepts through nodes and labeled connecting lines, enabling hierarchical organization of information. They facilitate meaningful learning by illustrating cross-links and integrating new knowledge within existing cognitive structures. Key features include a focus on concept hierarchy, explicit relationship labeling, and the ability to capture complex, multi-dimensional connections.
Key Features of the Frayer Model
The Frayer Model features a four-quadrant design that promotes a deeper understanding of vocabulary by categorizing definitions, characteristics, examples, and non-examples. Its structured layout helps students distinguish between similar concepts and clarify meanings through real-world applications. This model emphasizes critical thinking and context, making it effective for vocabulary acquisition and concept clarification.
Visual Structure Comparison
Concept maps utilize nodes and labeled connections to represent hierarchical relationships and complex interdependencies between ideas, enabling a network-like structure for knowledge visualization. In contrast, the Frayer Model employs a four-quadrant box to define a concept through its definition, characteristics, examples, and non-examples, offering a more linear and categorical approach. The visual structure of concept maps promotes dynamic interaction and cross-linking among concepts, while the Frayer Model emphasizes clarity and specificity in understanding individual terms.
Applications in Education
Concept maps enhance students' critical thinking by visually organizing complex information and illustrating relationships between ideas, making them ideal for subjects like science and history. The Frayer Model supports vocabulary acquisition and deeper understanding of key terms by breaking down definitions, characteristics, examples, and non-examples, which benefits language arts and ESL learners. Both tools improve comprehension and retention but cater to different cognitive processes: concept maps emphasize connections across concepts, while the Frayer Model focuses on mastering specific vocabulary and definitions.
Strengths of Concept Maps
Concept maps excel at visually organizing complex information by illustrating relationships between multiple concepts, enhancing comprehension and retention. They support hierarchical structuring, making it easier to identify primary ideas and their interconnected subtopics. Their flexibility allows users to integrate new knowledge dynamically, fostering deeper critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
Strengths of the Frayer Model
The Frayer Model excels in reinforcing vocabulary acquisition by encouraging learners to define concepts, identify essential characteristics, and provide examples and non-examples, which deepens understanding. Its structured four-quadrant design promotes critical thinking and helps students differentiate complex terms effectively. This model is particularly beneficial in subjects requiring precise terminology mastery and conceptual clarity.
Limitations and Challenges
Concept maps often face challenges such as complexity in representing intricate relationships and potential cognitive overload for users, making it difficult to capture detailed hierarchies or abstract ideas. The Frayer Model, while effective for vocabulary building, is limited by its rigid four-quadrant structure, which can restrict deeper semantic connections and fails to accommodate multifaceted concepts beyond definitions and examples. Both tools require careful implementation to avoid oversimplification and ensure meaningful learning outcomes.
Choosing the Right Tool: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right tool between a Concept Map and a Frayer Model depends on the learning objective and complexity of the topic; Concept Maps excel in illustrating relationships between multiple concepts, while Frayer Models focus on defining and understanding a single term through examples and non-examples. For subjects requiring deep exploration of connections, such as science or history, Concept Maps provide visual clarity and hierarchical structure. In contrast, Frayer Models are ideal for vocabulary development and mastering specific concepts in language arts and social studies.
Conclusion: Which Is Best for Your Needs?
Choosing between a concept map and a Frayer Model depends on your specific educational goals and learning style preferences. Concept maps excel in visually organizing complex relationships among multiple concepts, making them ideal for learners needing a comprehensive overview. The Frayer Model, with its focus on defining terms, characteristics, examples, and non-examples, is best suited for reinforcing vocabulary and deepening understanding of individual concepts.
Concept Map Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com