The National Curriculum establishes a standardized framework for education, ensuring consistency in learning objectives across schools. It emphasizes core subjects such as mathematics, science, and literacy while promoting critical thinking and creativity. Discover how the National Curriculum impacts your child's education and what it means for their academic success in the full article.
Table of Comparison
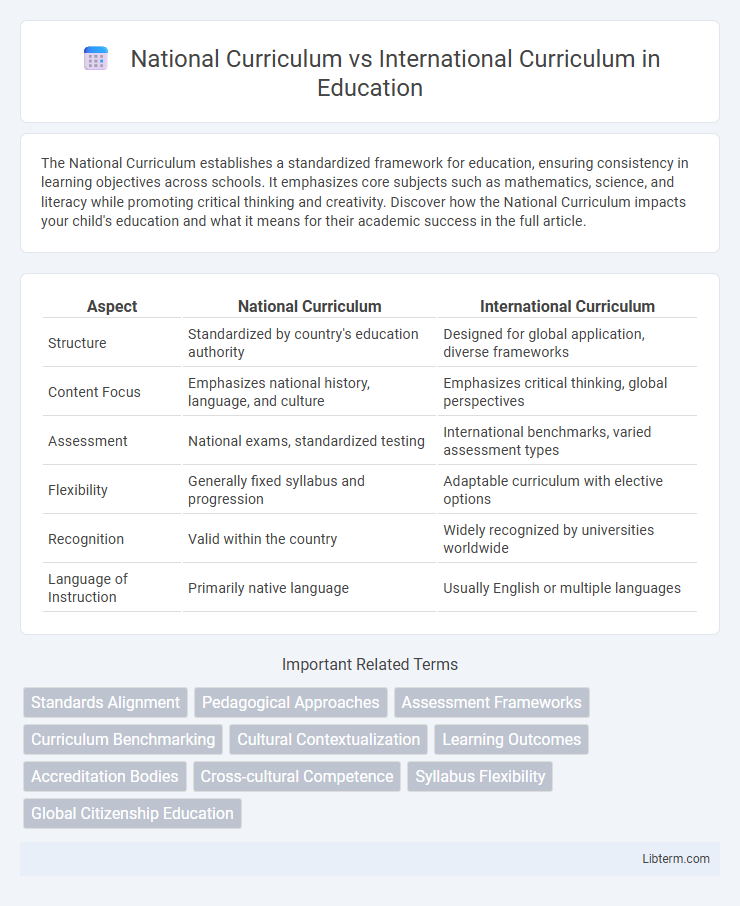
| Aspect | National Curriculum | International Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Standardized by country's education authority | Designed for global application, diverse frameworks |
| Content Focus | Emphasizes national history, language, and culture | Emphasizes critical thinking, global perspectives |
| Assessment | National exams, standardized testing | International benchmarks, varied assessment types |
| Flexibility | Generally fixed syllabus and progression | Adaptable curriculum with elective options |
| Recognition | Valid within the country | Widely recognized by universities worldwide |
| Language of Instruction | Primarily native language | Usually English or multiple languages |
Introduction to National and International Curricula
National curricula are developed by individual countries to reflect their cultural heritage, history, and educational standards, ensuring students gain knowledge relevant to their national identity. International curricula, such as the International Baccalaureate (IB) and Cambridge Assessment International Education, offer a standardized framework designed for global recognition, promoting critical thinking and multicultural understanding. These curricula provide diverse pathways tailored to different educational goals and student needs worldwide.
Defining National Curriculum: Key Features
The National Curriculum is a government-mandated framework that outlines the mandatory subjects, learning objectives, and assessment standards for schools within a specific country. It emphasizes cultural relevance, national history, language proficiency, and citizenship education tailored to the country's social and economic context. Key features include standardized assessments, compulsory adherence by public schools, and alignment with national education policies and workforce needs.
Understanding International Curriculum: Core Elements
International Curriculum emphasizes global perspectives, multilingual proficiency, and intercultural understanding to prepare students for a competitive world. Core elements include inquiry-based learning, critical thinking, and collaboration skills, fostering adaptability and innovation. It integrates diverse cultural contexts while maintaining rigorous academic standards aligned with international benchmarks.
Historical Evolution and Philosophical Foundations
The National Curriculum originated from country-specific educational reforms aiming to preserve cultural heritage and promote national identity, whereas the International Curriculum emerged in response to globalization, emphasizing cross-cultural competence and global citizenship. Historically, national curricula reflect localized pedagogical traditions shaped by political and social contexts, while international curricula like the IB and Cambridge developed through collaborations among multiple countries to standardize educational quality. Philosophically, the national approach centers on fostering patriotism and social cohesion, contrasting with the international curriculum's foundation in constructivism, critical thinking, and intercultural understanding.
Curriculum Content and Subject Offerings
The National Curriculum emphasizes local history, culture, and language, integrating standardized subjects like mathematics, science, and social studies tailored to national educational standards. International Curriculum frameworks, such as the International Baccalaureate (IB) or Cambridge Assessment International Education, offer a broader, globally-focused content with diverse subject offerings including global languages, interdisciplinary studies, and skills for international mindedness. Subject offerings in international curricula often include unique components like Theory of Knowledge, Global Perspectives, and a wider range of elective languages compared to the more traditional, nationally-oriented curriculum structure.
Approaches to Assessment and Evaluation
National curriculum assessment typically emphasizes standardized testing aligned with specific country education standards, focusing on measurable academic outcomes and uniform benchmarks. International curriculum approaches, such as the IB or Cambridge systems, prioritize formative and summative assessments that foster critical thinking, creativity, and global competencies through diverse evaluation methods like portfolios, projects, and oral presentations. These contrasting assessment strategies reflect differing educational philosophies, with national curricula prioritizing knowledge retention and international curricula emphasizing holistic student development and intercultural understanding.
Teacher Qualifications and Training Requirements
Teacher qualifications for National Curriculum programs typically require certifications aligned with government education standards and localized pedagogical training focused on national history, language, and culture. In contrast, International Curriculum educators often need internationally recognized credentials such as the International Baccalaureate (IB) diploma or Cambridge International examinations, emphasizing global teaching methodologies and cross-cultural communication skills. Training requirements for International Curriculum teachers prioritize ongoing professional development in diverse instructional strategies to cater to multinational student bodies, while National Curriculum training usually concentrates on compliance with standardized national education policies and assessment criteria.
Cultural Relevance and Global Perspectives
National curriculum emphasizes cultural relevance by incorporating local history, language, and traditions, fostering students' connection to their heritage and community identity. International curriculum integrates diverse global perspectives, promoting cross-cultural understanding, critical thinking, and preparation for participation in a globalized world. Balancing national cultural values with international outlooks equips students to navigate both local and global contexts effectively.
Student Outcomes and University Admissions
National curriculums emphasize standardized knowledge aligned with local educational standards, resulting in strong foundational skills but limited global exposure, often affecting students' adaptability in international university environments. International curriculums like the IB and Cambridge offer holistic learning, critical thinking, and global perspectives, enhancing university admissions prospects worldwide by aligning with diverse tertiary education requirements. Studies indicate students from international curriculums have higher acceptance rates in top universities due to their rigorous academic training and well-rounded skill development.
Choosing the Right Curriculum: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right curriculum involves evaluating academic standards, cultural relevance, and future opportunities; the National Curriculum emphasizes local history and languages, ensuring alignment with national university requirements, while the International Curriculum offers global perspectives and flexibility for expatriate families. Consider the child's learning style, language proficiency, and long-term educational goals when deciding between curricula like the British GCSE/A-Levels or the International Baccalaureate (IB). Schools' accreditation, recognition by higher education institutions, and extracurricular support also play critical roles in making an informed choice.
National Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com