Experiential learning immerses you in hands-on activities that foster deeper understanding through direct experience and reflection. This approach enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by connecting theory with real-world practice. Discover how experiential learning can transform your educational journey in the full article ahead.
Table of Comparison
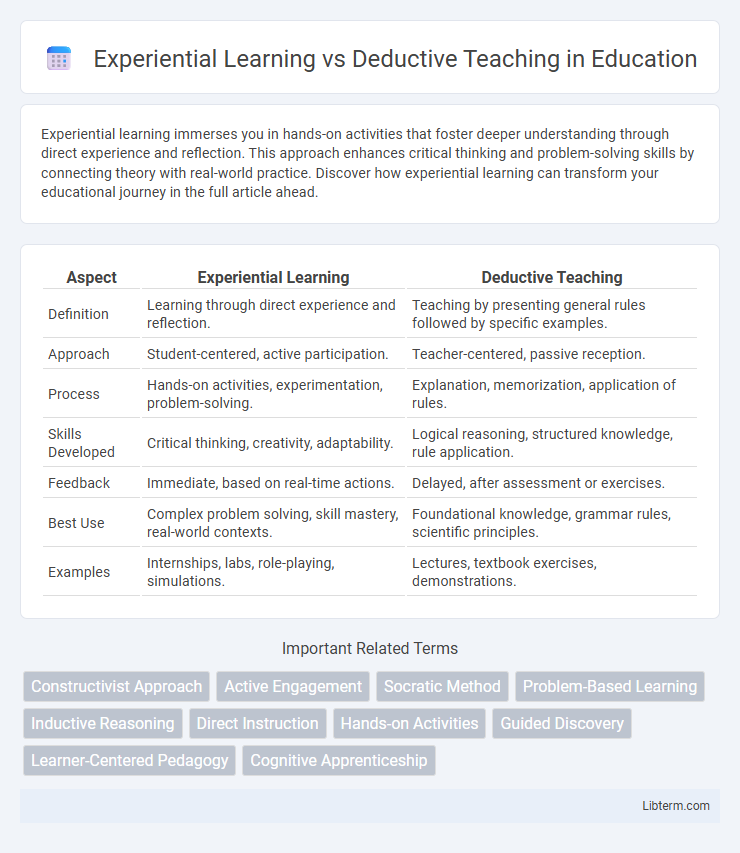
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Deductive Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection. | Teaching by presenting general rules followed by specific examples. |
| Approach | Student-centered, active participation. | Teacher-centered, passive reception. |
| Process | Hands-on activities, experimentation, problem-solving. | Explanation, memorization, application of rules. |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, creativity, adaptability. | Logical reasoning, structured knowledge, rule application. |
| Feedback | Immediate, based on real-time actions. | Delayed, after assessment or exercises. |
| Best Use | Complex problem solving, skill mastery, real-world contexts. | Foundational knowledge, grammar rules, scientific principles. |
| Examples | Internships, labs, role-playing, simulations. | Lectures, textbook exercises, demonstrations. |
Understanding Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on experiences and reflection to deepen understanding, allowing learners to actively engage with real-world situations and apply knowledge practically. This method contrasts with deductive teaching, which relies on presenting general principles followed by specific examples, often limiting student interaction to passive absorption. By fostering critical thinking and adaptability, experiential learning supports retention and skill development more effectively than traditional deductive approaches.
Defining Deductive Teaching
Deductive teaching is a structured instructional approach where general principles or rules are presented first, followed by specific examples and practice to reinforce understanding. This method emphasizes a top-down learning process, guiding learners to apply predefined concepts systematically. Deductive teaching contrasts with experiential learning by prioritizing clear explanations and direct instruction over hands-on exploration.
Key Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning centers on active engagement and reflection, where learners acquire knowledge through hands-on experiences and real-world problem-solving, fostering deeper understanding. Key principles include learning by doing, critical reflection on actions, and applying new insights in varied contexts to promote continuous growth. This contrasts with deductive teaching, which relies on structured, rule-based instruction and passive absorption of information.
Core Concepts of Deductive Teaching
Deductive teaching emphasizes presenting general principles or rules first, followed by specific examples and applications, ensuring clear and structured learning paths. It focuses on core concepts such as rule explanation, systematic instruction, and guided practice to reinforce understanding. This approach supports learners in grasping abstract concepts before engaging in practical activities, enhancing cognitive organization and retention.
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging learners in hands-on activities that simulate real-world scenarios, fostering deeper understanding and retention. It promotes active participation and intrinsic motivation, leading to improved learner confidence and adaptability in diverse situations. This approach bridges theory and practice, making knowledge more relevant and applicable compared to deductive teaching methods that rely primarily on passive information absorption.
Advantages of Deductive Teaching
Deductive teaching offers clear structure and predictable progression, enabling learners to grasp rules and concepts efficiently before applying them. This method enhances cognitive organization by providing explicit explanations, which is particularly beneficial for complex subjects requiring foundational knowledge. The focused approach supports rapid acquisition and assessment of specific skills, making it ideal in standardized academic settings.
Challenges of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning faces challenges such as the need for significant time and resource investment, which can strain educational institutions and instructors. It also requires learners to actively engage and reflect, but varying levels of motivation and prior knowledge may hinder effective participation and deeper understanding. Assessment of experiential learning outcomes remains complex due to its subjective and context-dependent nature.
Limitations of Deductive Teaching
Deductive teaching often limits critical thinking by presenting rules before students engage with concepts, which can suppress creativity and deeper understanding. It relies heavily on memorization, leading to passive learning and reduced long-term retention of knowledge. This method may also fail to address diverse learning styles, making it less effective for students who benefit from hands-on, experiential approaches.
Comparative Analysis: Which Approach Works Best?
Experiential learning, emphasizing hands-on experience and active participation, fosters deeper understanding and long-term retention compared to deductive teaching, which relies on rule-based instruction and abstract reasoning. Studies reveal that experiential methods enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging learners in real-world contexts, whereas deductive teaching efficiently conveys foundational knowledge but may limit practical application. Optimal educational outcomes often emerge from integrating both approaches, tailoring strategies to subject matter and learner needs for maximum effectiveness.
Integrating Experiential Learning and Deductive Teaching
Integrating experiential learning and deductive teaching enhances student engagement by combining hands-on activities with structured rule-based instruction, fostering deeper understanding and application of concepts. This blend encourages critical thinking as learners actively test hypotheses derived from deductive reasoning within real-world contexts, promoting retention and transfer of knowledge. Utilizing case studies, simulations, and guided discovery bridges theory and practice, optimizing educational outcomes through contextualized learning experiences.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com