Intuitive teaching harnesses natural understanding and instinctive learning processes to enhance educational experiences. By tapping into your innate abilities and allowing students to grasp concepts without excessive formal instruction, it fosters deeper engagement and retention. Explore the article to discover how intuitive teaching can transform your approach to education.
Table of Comparison
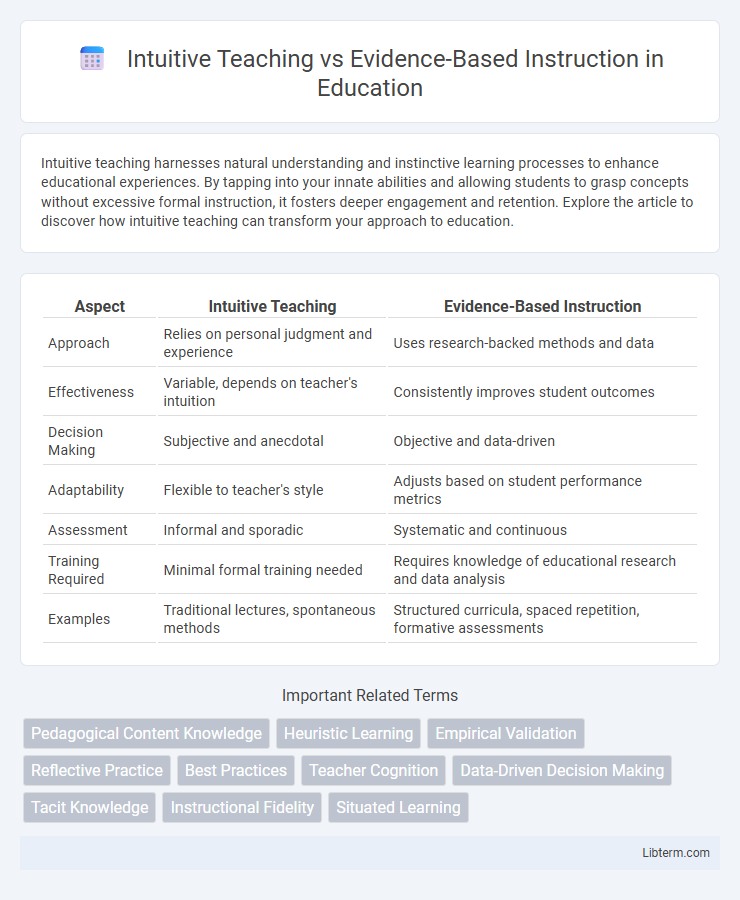
| Aspect | Intuitive Teaching | Evidence-Based Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Relies on personal judgment and experience | Uses research-backed methods and data |
| Effectiveness | Variable, depends on teacher's intuition | Consistently improves student outcomes |
| Decision Making | Subjective and anecdotal | Objective and data-driven |
| Adaptability | Flexible to teacher's style | Adjusts based on student performance metrics |
| Assessment | Informal and sporadic | Systematic and continuous |
| Training Required | Minimal formal training needed | Requires knowledge of educational research and data analysis |
| Examples | Traditional lectures, spontaneous methods | Structured curricula, spaced repetition, formative assessments |
Defining Intuitive Teaching and Evidence-Based Instruction
Intuitive teaching relies on educators' personal experience and instinct to guide instructional decisions, often lacking empirical validation or systematic evaluation. Evidence-based instruction, grounded in rigorous research and data, employs proven strategies and interventions validated through controlled studies and meta-analyses. This contrast highlights the importance of integrating scientific findings to enhance learning outcomes and instructional efficacy.
Historical Evolution of Teaching Approaches
The historical evolution of teaching approaches reveals a shift from intuitive teaching, which relies on personal experience and instinct, to evidence-based instruction grounded in scientific research and empirical data. Early educational methods were largely shaped by teachers' observations and traditional practices without systematic evaluation, whereas modern pedagogy emphasizes data-driven strategies validated through controlled studies and cognitive science. This transition reflects a broader movement toward accountability and effectiveness in education, highlighting the importance of measurable learning outcomes and replicable teaching techniques.
Core Principles Behind Intuitive Teaching
Intuitive teaching relies on educators' innate understanding and personal experiences to guide instruction, emphasizing adaptability and real-time responsiveness to student needs. Core principles include trusting teacher judgment, fostering creativity, and prioritizing student-teacher rapport to create a dynamic learning environment. This approach contrasts with evidence-based instruction, which depends on rigorously tested methods and empirical data to shape teaching practices.
Foundations of Evidence-Based Instruction
Evidence-based instruction relies on rigorous research and empirical data to inform teaching practices, ensuring methods are scientifically validated for effectiveness. This foundation prioritizes systematic reviews, meta-analyses, and controlled studies to design interventions that improve student outcomes. Intuitive teaching, while based on personal experience and instinct, lacks this empirical grounding and may not consistently produce reliable results.
Comparing Teacher Decision-Making Processes
Teacher decision-making in intuitive teaching relies heavily on personal experience, instincts, and spontaneous judgments, often leading to flexible but inconsistent instructional choices. In contrast, evidence-based instruction employs systematic analysis of research data and empirically validated strategies, fostering more objective and replicable teaching practices. Comparing these approaches highlights that intuitive methods may lack reliability, while evidence-based decisions enhance instructional efficacy through data-driven insights.
Impact on Student Outcomes
Evidence-based instruction significantly improves student outcomes by relying on research-backed strategies that enhance retention and comprehension. Intuitive teaching, while adaptable, can result in inconsistent learning gains due to lack of systematic validation. Implementing evidence-based methods fosters measurable academic progress and reduces achievement gaps across diverse student populations.
Challenges and Criticisms of Each Approach
Intuitive teaching often faces criticism for relying on personal experience and anecdotal evidence, which can lead to inconsistent outcomes and difficulty in measuring effectiveness, posing challenges in standardizing instruction across diverse classrooms. Evidence-based instruction, while grounded in research and data, encounters obstacles such as limited adaptability to individual student needs and the potential rigidity of strictly following protocols, which may hinder creativity and responsiveness. Both approaches grapple with balancing theoretical frameworks and practical application, impacting their efficacy and acceptance in varied educational settings.
Integrating Intuition and Evidence in Practice
Effective education balances intuitive teaching, which leverages a teacher's experiential insights and immediate responsiveness, with evidence-based instruction grounded in empirical research and proven methodologies. Integrating intuition with evidence involves using data-driven strategies while adapting flexibly to students' unique needs and contextual classroom dynamics. This approach enhances learning outcomes by combining the nuanced judgment of experienced educators with validated instructional techniques.
Case Studies in Classroom Applications
Case studies in classroom applications reveal that evidence-based instruction consistently improves student outcomes compared to intuitive teaching methods by utilizing data-driven strategies grounded in cognitive science. For example, randomized controlled trials demonstrate that evidence-based techniques like spaced repetition and formative assessment enhance retention and engagement more effectively than intuition-based approaches. These findings underscore the importance of integrating empirical research into teaching practices to optimize learning processes and ensure measurable academic progress.
Future Trends in Educational Methodologies
Emerging educational methodologies increasingly integrate evidence-based instruction with intuitive teaching to personalize learning experiences and improve student outcomes. Advances in artificial intelligence and learning analytics enable real-time assessment and adaptive feedback, fostering more effective knowledge retention and skill development. Future trends highlight the fusion of cognitive science research and educator intuition to create dynamic, data-driven classroom environments.
Intuitive Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com