Curricular design plays a crucial role in shaping effective educational experiences tailored to learners' needs and goals. Integrating diverse teaching methodologies and assessment strategies ensures comprehensive skill development and knowledge retention. Explore the rest of the article to discover how your curricular choices can transform student engagement and achievement.
Table of Comparison
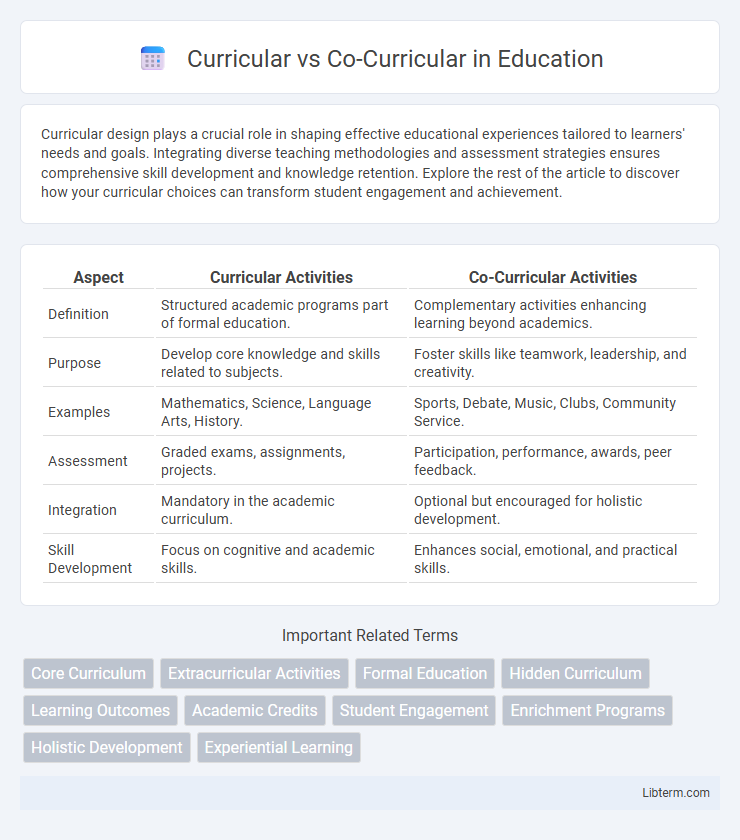
| Aspect | Curricular Activities | Co-Curricular Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured academic programs part of formal education. | Complementary activities enhancing learning beyond academics. |
| Purpose | Develop core knowledge and skills related to subjects. | Foster skills like teamwork, leadership, and creativity. |
| Examples | Mathematics, Science, Language Arts, History. | Sports, Debate, Music, Clubs, Community Service. |
| Assessment | Graded exams, assignments, projects. | Participation, performance, awards, peer feedback. |
| Integration | Mandatory in the academic curriculum. | Optional but encouraged for holistic development. |
| Skill Development | Focus on cognitive and academic skills. | Enhances social, emotional, and practical skills. |
Introduction to Curricular and Co-Curricular Activities
Curricular activities encompass structured academic tasks such as lessons, examinations, and assignments directly tied to a formal syllabus. Co-curricular activities include extracurricular engagements like sports, clubs, and cultural events that complement academic learning and foster personal development. Both curricular and co-curricular activities are integral in shaping well-rounded students by promoting cognitive, social, and emotional growth.
Defining Curricular Activities
Curricular activities are structured, formal educational experiences directly linked to the academic syllabus, including lessons, exams, and projects that align with institutional learning objectives. These activities are designed to develop core knowledge and skills as outlined in official educational frameworks and standards. By engaging in curricular activities, students systematically acquire subject-specific competencies essential for academic progression and certification.
Understanding Co-Curricular Activities
Co-curricular activities complement the academic curriculum by enhancing students' skills, interests, and social development outside traditional classroom settings. These activities, such as sports, music, debate clubs, and community service, provide experiential learning that fosters teamwork, leadership, and time management. Integrating co-curricular activities with curricular goals promotes holistic education and better prepares students for real-world challenges.
Key Differences Between Curricular and Co-Curricular Activities
Curricular activities are structured educational experiences directly linked to the academic syllabus, such as lectures, exams, and classroom projects, which assess students' knowledge and skills. Co-curricular activities complement the curriculum by promoting holistic development through sports, clubs, and arts, enhancing social, leadership, and interpersonal skills. The key difference lies in curricular activities being mandatory and graded, while co-curricular activities are often optional and focus on experiential learning outside traditional academics.
Importance of Curricular Activities in Academic Development
Curricular activities form the core of academic development by providing structured learning experiences aligned with educational standards and objectives. These activities enhance cognitive skills, subject comprehension, and critical thinking, directly contributing to students' academic performance and knowledge retention. Emphasizing curricular engagement ensures a solid foundation for intellectual growth and future educational success.
Benefits of Co-Curricular Involvement
Co-curricular involvement enhances student learning by providing practical experiences that complement academic curriculum, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Participation in clubs, sports, and community service promotes social interaction, teamwork, and leadership development, contributing to well-rounded personal growth. These experiences also improve time management and self-discipline, preparing students for future professional and life challenges.
Impact on Student Skill Development
Curricular activities directly enhance core academic skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and subject-specific knowledge, forming the foundation of student learning. Co-curricular activities complement this by fostering interpersonal skills, leadership qualities, and emotional intelligence, contributing to holistic development. The integration of both approaches results in a balanced skill set that prepares students for real-world challenges and professional environments.
Role in Personality and Leadership Building
Curricular activities contribute significantly to foundational knowledge and cognitive skills, shaping a student's discipline and time management, which are essential for personality development. Co-curricular activities enhance interpersonal skills, emotional intelligence, and practical leadership abilities by providing real-world experiences and collaborative environments. Together, these activities foster a balanced personality and nurture effective leadership qualities through theory and practice integration.
Integration and Balance in Education Systems
Effective education systems emphasize the integration and balance between curricular and co-curricular activities to foster holistic student development. Curricular activities, centered on academic knowledge and skills, are complemented by co-curricular experiences that enhance social, emotional, and practical abilities. Strategic alignment of both components promotes critical thinking, teamwork, and real-world application, ultimately enriching student learning outcomes and personal growth.
Conclusion: Maximizing Educational Outcomes
Maximizing educational outcomes requires a balanced integration of both curricular and co-curricular activities, as curricular programs provide essential academic knowledge while co-curricular experiences enhance soft skills, creativity, and real-world application. Effective education strategies leverage the synergy between structured coursework and extracurricular participation to foster holistic student development, critical thinking, and lifelong learning. Emphasizing this dual approach ensures students are well-prepared for both academic success and practical challenges beyond the classroom.
Curricular Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com