Sequencing is a crucial process in genetic research that determines the exact order of nucleotides within a DNA molecule, enabling scientists to decode biological information. High-throughput sequencing technologies have revolutionized genomics, making data analysis faster and more accurate for applications such as personalized medicine and evolutionary studies. Explore the full article to understand how sequencing impacts various scientific fields and how it can benefit your research.
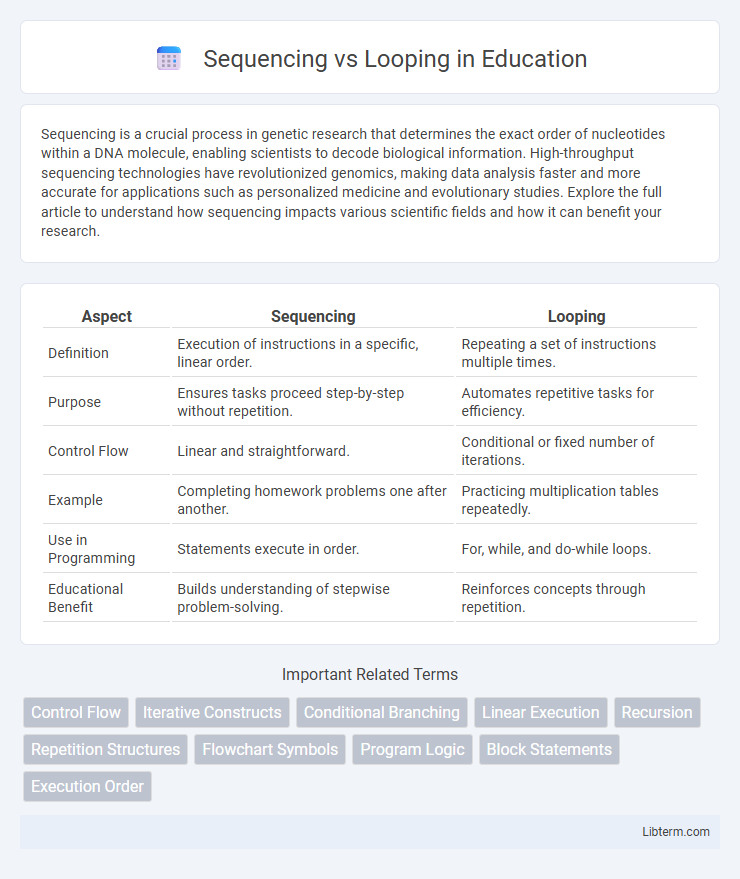
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sequencing | Looping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Execution of instructions in a specific, linear order. | Repeating a set of instructions multiple times. |
| Purpose | Ensures tasks proceed step-by-step without repetition. | Automates repetitive tasks for efficiency. |
| Control Flow | Linear and straightforward. | Conditional or fixed number of iterations. |
| Example | Completing homework problems one after another. | Practicing multiplication tables repeatedly. |
| Use in Programming | Statements execute in order. | For, while, and do-while loops. |
| Educational Benefit | Builds understanding of stepwise problem-solving. | Reinforces concepts through repetition. |
Introduction to Sequencing and Looping
Sequencing and looping are fundamental concepts in programming that control the order of execution in a program. Sequencing executes statements one after another in a linear fashion, ensuring each step is completed before moving to the next. Looping enables repetition of a block of code multiple times based on specified conditions, increasing efficiency in tasks like iterations and data processing.
Defining Sequencing in Programming
Sequencing in programming refers to the execution of instructions in a linear, step-by-step order, where each statement runs one after the other. This control structure ensures that commands are processed sequentially without any repetition or branching, forming the foundation of program flow. Understanding sequencing is critical for mastering more complex structures like looping and conditional statements.
What is Looping?
Looping is a programming technique that executes a set of instructions repeatedly based on a specified condition, enabling automation of repetitive tasks. Common loop structures include for, while, and do-while loops, which control iteration by evaluating logical expressions. Looping enhances code efficiency by reducing redundancy and allowing dynamic processing of data collections and sequences.
Key Differences Between Sequencing and Looping
Sequencing executes instructions in a linear order, one after another, without repetition, ensuring each step follows the previous one exactly once. Looping involves repeating a set of instructions multiple times based on a condition, allowing processes to be automated and repeated efficiently. Key differences include execution flow--sequential versus repetitive--and condition dependency, with looping relying on conditions to continue or terminate cycles.
Use Cases for Sequencing
Sequencing is ideal for scenarios requiring precise order execution, such as automated manufacturing processes, executing complex algorithms step-by-step, and running data pipelines where each stage depends on the completion of the previous one. It ensures tasks follow a strict linear progression, essential for workflow automation in industries like automotive assembly and software build processes. Sequencing also supports error handling by isolating failures at specific steps, making debugging more efficient in sequential task flows.
Use Cases for Looping
Looping is essential for tasks requiring repetitive execution, such as processing batch data in machine learning, automating repetitive system administration jobs, or iterating through elements in data structures like arrays and lists. It enables efficient handling of large-scale data transformations, real-time sensor data monitoring, and executing repeated database operations in software development. Use cases include data analytics pipelines, game development for repeated actions, and web scraping to collect data from multiple pages.
Benefits of Proper Control Flow
Proper control flow in programming enhances code readability and maintainability by ensuring clear sequencing and efficient looping structures. Effective sequencing enables logical execution of statements, reducing errors and simplifying debugging. Optimized looping conserves system resources by preventing infinite loops and minimizing redundant computations, leading to improved performance and scalability.
Common Mistakes in Sequencing and Looping
Common mistakes in sequencing include incorrect order of steps, causing logical errors or unexpected outcomes, and neglecting dependencies between tasks. Looping errors often arise from infinite loops, off-by-one errors, or improper loop termination conditions that lead to premature exits or endless iterations. Understanding the control flow and carefully defining loop boundaries are essential to avoid these frequent sequencing and looping pitfalls.
Sequencing and Looping in Popular Programming Languages
Sequencing and looping are fundamental control structures in popular programming languages like Python, Java, and JavaScript, where sequencing executes statements line-by-line, ensuring a specific order of operations crucial for tasks such as data processing and function calls. Looping, available through constructs like for, while, and do-while loops, enables repeated execution of code blocks, optimizing tasks such as iteration over arrays or repetitive calculations. Understanding the performance and readability differences between sequencing and looping in languages like C++ and Ruby is essential for writing efficient, maintainable code in software development.
Best Practices for Control Structures
Best practices for control structures emphasize choosing sequencing when tasks require a linear, step-by-step execution for clarity and predictability in code flow. Looping is optimal for repeated operations, enhancing efficiency and reducing redundancy by automating repetition based on conditions or counters. Effective use of control structures improves code readability, maintainability, and performance in software development.
Sequencing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com