Rote learning involves memorizing information through repetition without understanding the underlying meaning. This method can be effective for retaining basic facts or formulas but often limits deep comprehension and critical thinking skills. Explore the rest of the article to discover when rote learning can be beneficial and how to balance it with more meaningful study techniques.
Table of Comparison
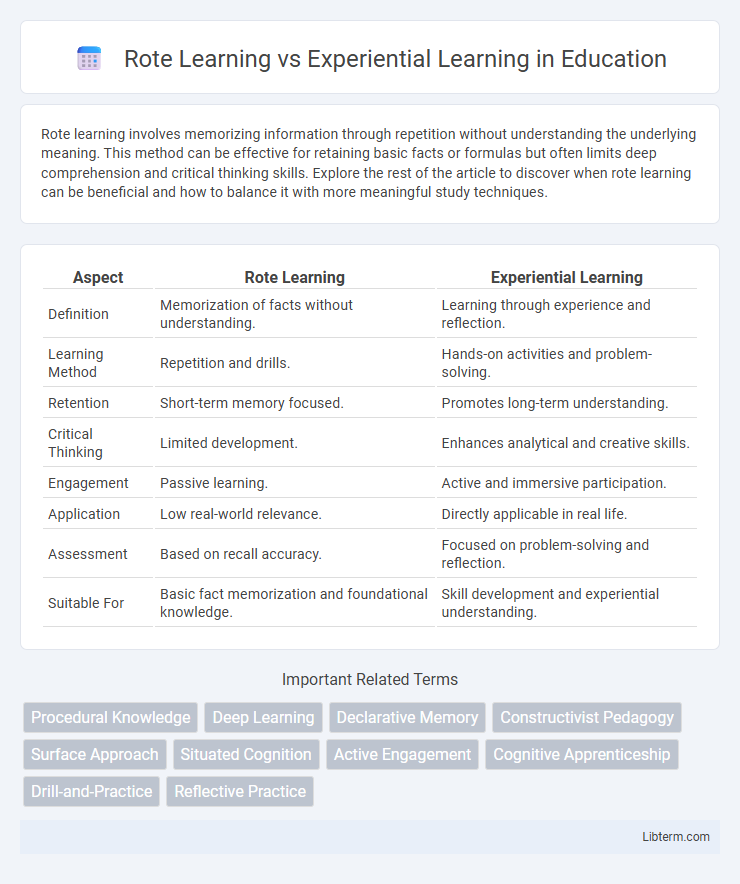
| Aspect | Rote Learning | Experiential Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Memorization of facts without understanding. | Learning through experience and reflection. |
| Learning Method | Repetition and drills. | Hands-on activities and problem-solving. |
| Retention | Short-term memory focused. | Promotes long-term understanding. |
| Critical Thinking | Limited development. | Enhances analytical and creative skills. |
| Engagement | Passive learning. | Active and immersive participation. |
| Application | Low real-world relevance. | Directly applicable in real life. |
| Assessment | Based on recall accuracy. | Focused on problem-solving and reflection. |
| Suitable For | Basic fact memorization and foundational knowledge. | Skill development and experiential understanding. |
Introduction to Rote Learning and Experiential Learning
Rote learning involves memorizing information through repetition without necessarily understanding the underlying meaning, making it effective for quickly acquiring facts like multiplication tables or vocabulary. Experiential learning emphasizes active engagement and reflection, allowing learners to develop deeper comprehension by connecting experiences with theoretical concepts. Both methods serve distinct educational purposes, with rote learning aiding quick recall and experiential learning fostering critical thinking and practical application.
Defining Rote Learning: Key Characteristics
Rote learning involves memorization through repetition without understanding underlying concepts, emphasizing quick recall of facts and data. It relies heavily on drills and practice to embed information into long-term memory, often neglecting critical thinking and application skills. This method contrasts with experiential learning by prioritizing retention over comprehension and real-world experience.
Understanding Experiential Learning: Core Principles
Experiential learning centers on active engagement and reflection, emphasizing learning through direct experience rather than memorization. Core principles include concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation, forming a continuous learning cycle. This approach enhances deep understanding, critical thinking, and practical application of knowledge compared to rote learning's emphasis on repetition and recall.
Historical Evolution of Learning Methods
Rote learning, rooted in ancient education systems like the Gurukul and classical Greek methods, emphasized memorization and repetition as primary tools for knowledge retention. Experiential learning emerged prominently in the 20th century, influenced by educational theorists such as John Dewey and David Kolb, who advocated learning through direct experience and reflective practice. The shift from rote to experiential learning marks a historical evolution prioritizing critical thinking, problem-solving, and real-world application over mere memorization.
Cognitive Outcomes: Retention and Application
Rote learning emphasizes memorization, which often leads to short-term retention but limited ability to apply knowledge in novel contexts. Experiential learning enhances deep cognitive processing, resulting in better long-term retention and improved application of concepts through hands-on experiences. Studies show experiential methods engage multiple neural pathways, fostering critical thinking and adaptive problem-solving skills.
Advantages of Rote Learning
Rote learning enhances memory retention by enabling quick recall of foundational facts and formulas essential in fields like mathematics, languages, and sciences. This method provides a structured approach that supports standardized testing and early knowledge acquisition, ensuring learners build a solid base for advanced concepts. Its repetitive nature aids in reinforcing neural pathways, making information retrieval faster and more reliable during exams or practical applications.
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging learners in real-world scenarios, fostering deeper understanding and retention compared to rote memorization. It promotes active participation, adaptability, and collaboration, which are essential for practical application and lifelong learning. Research shows experiential methods improve motivation and meaningful comprehension, leading to better academic and professional outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Approaches
Rote learning faces challenges such as limited critical thinking development and difficulty in applying knowledge to real-world contexts, often resulting in superficial understanding. Experiential learning may encounter limitations including resource intensity, time consumption, and variability in learning outcomes due to reliance on individual engagement and reflection quality. Both approaches can struggle with balancing knowledge retention and practical application, highlighting the need for integrated educational strategies.
Real-World Examples: Classroom and Workplace Scenarios
Rote learning in classrooms often involves memorizing definitions or formulas, which helps students recall information quickly but may limit deep understanding or application. Experiential learning in the workplace, such as hands-on training or project-based tasks, fosters critical thinking and problem-solving by engaging employees directly with real-world challenges. For instance, medical students memorize anatomy through rote learning but refine skills and decision-making during clinical rotations, illustrating the complementary roles of both methods.
Choosing the Right Approach: Recommendations and Best Practices
Choosing the right learning approach depends on the goals and context of education; rote learning is effective for memorizing foundational facts such as multiplication tables or vocabulary, while experiential learning enhances deep understanding through hands-on activities, problem-solving, and real-world application. Best practices recommend integrating both methods by using rote techniques for basic knowledge acquisition and experiential strategies to develop critical thinking, creativity, and practical skills. Tailoring the approach to learner needs, subject complexity, and desired outcomes maximizes retention and engagement, supporting a balanced and effective educational experience.
Rote Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com