Experiential learning immerses you in hands-on activities that enhance understanding through direct experience rather than passive observation. This approach fosters critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and deeper retention of knowledge by engaging multiple senses and emotional responses. Explore the following article to discover effective strategies for incorporating experiential learning into your educational journey.
Table of Comparison
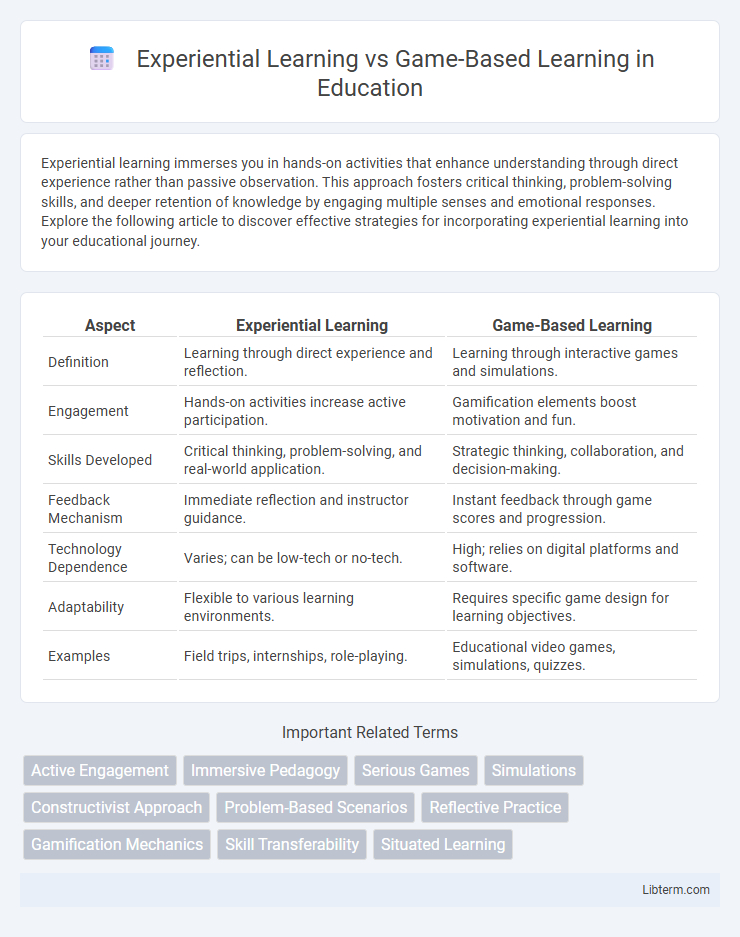
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Game-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection. | Learning through interactive games and simulations. |
| Engagement | Hands-on activities increase active participation. | Gamification elements boost motivation and fun. |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, problem-solving, and real-world application. | Strategic thinking, collaboration, and decision-making. |
| Feedback Mechanism | Immediate reflection and instructor guidance. | Instant feedback through game scores and progression. |
| Technology Dependence | Varies; can be low-tech or no-tech. | High; relies on digital platforms and software. |
| Adaptability | Flexible to various learning environments. | Requires specific game design for learning objectives. |
| Examples | Field trips, internships, role-playing. | Educational video games, simulations, quizzes. |
Understanding Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is a hands-on educational approach that emphasizes learning through direct experience, reflection, and application, fostering deep comprehension and skill development. Unlike game-based learning, which incorporates interactive play elements to engage learners, experiential learning relies on real-world activities such as internships, simulations, and project-based tasks. This method promotes critical thinking and adaptability by allowing learners to connect theory with practice in authentic contexts.
What Is Game-Based Learning?
Game-Based Learning leverages interactive games to enhance knowledge acquisition, engagement, and skill development by immersing learners in problem-solving scenarios embedded within entertaining gameplay. This educational approach integrates cognitive challenges and adaptive feedback to reinforce concepts, making complex subjects more accessible and retention more effective. By simulating real-world contexts through virtual environments, Game-Based Learning fosters experiential understanding while maintaining motivation and participation.
Core Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning centers on immersive, hands-on experiences that foster deep understanding through active participation and reflection, emphasizing Kolb's Learning Cycle: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. This approach cultivates critical thinking, problem-solving, and real-world application by engaging learners in meaningful tasks that mirror authentic challenges. Unlike game-based learning, experiential learning prioritizes direct interaction with environments or materials to build knowledge organically rather than through structured game mechanics or rewards.
Key Elements of Game-Based Learning
Game-based learning centers on interactive gameplay, immediate feedback, and goal-oriented challenges to enhance engagement and retention. Key elements include clear rules, meaningful rewards, adaptive difficulty, and immersive storylines that motivate learners. This approach leverages competition and collaboration, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills through simulated real-world scenarios.
Similarities Between Experiential and Game-Based Learning
Experiential learning and game-based learning both emphasize active participation and hands-on experience to deepen understanding and retention of knowledge. Both approaches foster critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and real-world application by engaging learners in immersive scenarios that simulate authentic challenges. They prioritize learner motivation and engagement through interactive, dynamic environments that promote exploration and feedback.
Differentiating Experiential Learning from Game-Based Learning
Experiential learning involves direct, hands-on experiences that facilitate learning through reflection and real-world application, emphasizing personal engagement and critical thinking skills development. Game-based learning integrates game elements such as rules, goals, and feedback into educational contexts to boost motivation and interactive problem-solving within a structured, often competitive environment. Differentiating them, experiential learning centers on authentic activities tied to real-life scenarios, while game-based learning uses simulated game mechanics to create immersive and engaging learning experiences.
Benefits of Experiential Learning in Education
Experiential learning enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by immersing students in real-world scenarios that foster deeper understanding and retention. It promotes active engagement and personal reflection, allowing learners to connect theory with practice effectively. This approach also supports the development of soft skills such as collaboration, adaptability, and decision-making, which are essential for academic and professional success.
Advantages of Game-Based Learning for Engagement
Game-based learning enhances engagement by offering interactive and immersive experiences that motivate learners through challenge and competition. It leverages instant feedback and reward systems, which boost motivation and reinforce concepts effectively. This approach promotes active participation and sustained attention, leading to higher retention rates compared to traditional experiential learning methods.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Approaches
Experiential learning faces challenges such as resource intensity, requiring significant time, space, and skilled facilitation to create meaningful hands-on experiences. Game-based learning often struggles with balancing educational content and engagement, where poorly designed games may prioritize entertainment over learning outcomes or fail to address diverse learner needs. Both approaches can encounter limitations in scalability, assessment complexity, and ensuring consistent transfer of skills to real-world contexts.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Learning Goals
Experiential learning immerses learners in real-world scenarios to develop practical skills and critical thinking, ideal for goals emphasizing hands-on experience and reflection. Game-based learning leverages interactive gameplay and challenges to boost engagement and motivation, making it effective for reinforcing knowledge and fostering problem-solving in a dynamic environment. Selecting the right method depends on whether your learning objectives prioritize applied practice or interactive skill-building within a structured framework.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com