A spiral curriculum revisits key concepts repeatedly over time, deepening understanding and reinforcing learning through successive layers of complexity. This approach aligns with how your brain naturally builds knowledge, allowing for better retention and application of skills. Explore the rest of the article to discover how a spiral curriculum can transform your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
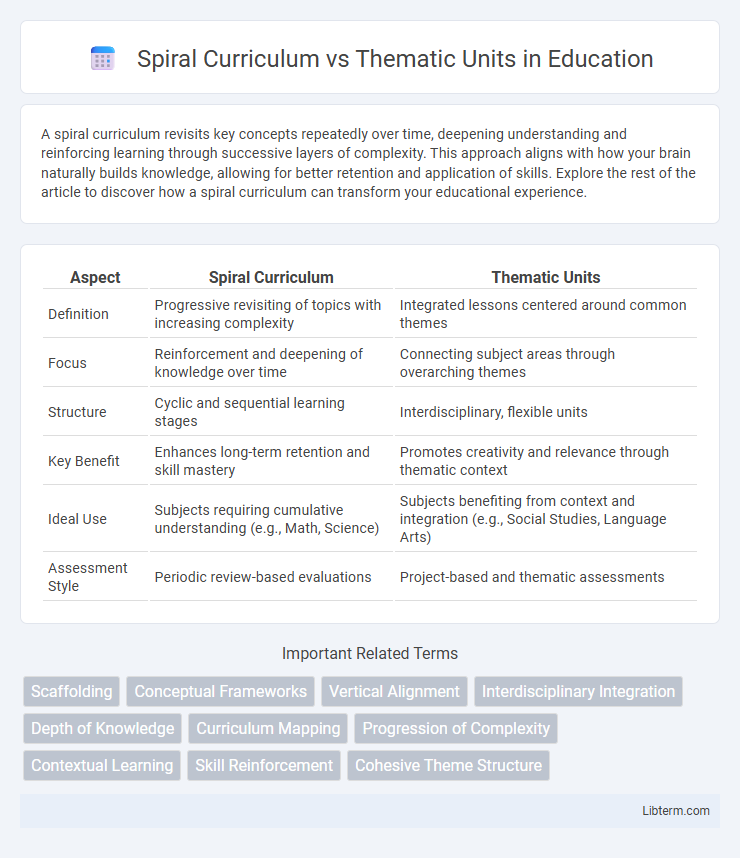
| Aspect | Spiral Curriculum | Thematic Units |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Progressive revisiting of topics with increasing complexity | Integrated lessons centered around common themes |
| Focus | Reinforcement and deepening of knowledge over time | Connecting subject areas through overarching themes |
| Structure | Cyclic and sequential learning stages | Interdisciplinary, flexible units |
| Key Benefit | Enhances long-term retention and skill mastery | Promotes creativity and relevance through thematic context |
| Ideal Use | Subjects requiring cumulative understanding (e.g., Math, Science) | Subjects benefiting from context and integration (e.g., Social Studies, Language Arts) |
| Assessment Style | Periodic review-based evaluations | Project-based and thematic assessments |
Introduction to Spiral Curriculum and Thematic Units
Spiral Curriculum is an educational approach where key concepts are revisited and expanded upon at increasing levels of complexity throughout the learning process, enhancing long-term retention and deeper understanding. Thematic Units organize curriculum content around central themes, integrating multiple subject areas to create cohesive, interdisciplinary learning experiences that promote student engagement and real-world application. Both methods aim to improve knowledge acquisition, with Spiral Curriculum emphasizing progressive mastery and Thematic Units focusing on contextual relevance and connected learning.
Defining the Spiral Curriculum Approach
The Spiral Curriculum approach structures learning by revisiting key concepts repeatedly over time, each encounter increasing in complexity and reinforcing prior knowledge. This method aligns with cognitive development theories, emphasizing gradual mastery through spaced repetition and deepening understanding. Unlike Thematic Units, which focus on integrating content around specific themes in a single period, the Spiral Curriculum ensures long-term retention and skill-building across multiple subject areas.
Understanding Thematic Units in Education
Thematic units in education integrate multiple subjects around a central topic, promoting deeper understanding and making learning more relevant by connecting concepts across disciplines such as science, literacy, and social studies. This approach encourages critical thinking and creativity, as students explore themes through diverse activities and assessments tailored to different learning styles. By emphasizing real-world applications, thematic units enhance student engagement and facilitate retention of knowledge through meaningful, context-based learning experiences.
Core Principles of Spiral Curriculum
The Spiral Curriculum is grounded in the core principle of revisiting key concepts repeatedly, with increasing complexity and depth, to reinforce understanding and retention over time. This approach contrasts with Thematic Units, which organize learning around comprehensive themes but may focus on topics in isolation. Emphasizing continuous reinforcement and progressive mastery, the Spiral Curriculum supports long-term cognitive development through systematic revisiting of fundamental knowledge.
Key Features of Thematic Unit Design
Thematic unit design centers on integrating multiple subjects around a central theme to create cohesive and meaningful learning experiences. It emphasizes real-world connections, student engagement, and interdisciplinary approaches that foster deeper understanding. Key features include utilizing thematic content to enhance critical thinking, promoting collaborative learning, and aligning activities with curriculum standards to ensure comprehensive skill development.
Benefits of the Spiral Curriculum Model
The Spiral Curriculum model enhances long-term retention by revisiting core concepts at increasing levels of complexity, enabling deeper understanding and mastery over time. It supports differentiated learning through continuous reinforcement, allowing students to build on prior knowledge and adapt to their evolving cognitive abilities. This approach fosters stronger concept connections and promotes cumulative skill development compared to Thematic Units, which often compartmentalize learning into isolated topics.
Advantages of Thematic Teaching Methods
Thematic teaching methods enhance student engagement by connecting learning content across multiple subject areas through relevant themes, fostering deeper understanding and retention. This approach promotes critical thinking and creativity by encouraging students to explore real-world issues within integrated contexts. Thematic units also support differentiated instruction, allowing teachers to tailor activities to diverse learning styles and needs within the classroom.
Comparing Spiral Curriculum and Thematic Units
Spiral Curriculum revisits key concepts repeatedly over time, reinforcing and expanding student knowledge through incremental complexity, while Thematic Units integrate multiple subjects around a central theme, promoting interdisciplinary connections and contextual learning. Spiral Curriculum excels in mastery of foundational skills by revisiting topics in varying contexts, whereas Thematic Units enhance engagement and motivation through real-world relevance. Both approaches support differentiated instruction but differ in structure: Spiral Curriculum emphasizes cyclical review, and Thematic Units emphasize comprehensive exploration within a unified topic.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Spiral Curriculum faces challenges in ensuring students revisit concepts with increasing complexity without redundancy, which can lead to gaps in depth or confusion if not well-coordinated. Thematic Units often struggle with integrating subject matter cohesively across disciplines, risking superficial coverage and difficulty in meeting standardized testing requirements. Both approaches require careful planning to balance breadth and depth while maintaining student engagement and curriculum coherence.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Selecting between a spiral curriculum and thematic units depends on your classroom goals and student needs. Spiral curriculum revisits key concepts over time, promoting deeper understanding and long-term retention, which suits subjects requiring cumulative learning like math and science. Thematic units integrate multiple subjects around a central theme, fostering critical thinking and creativity, ideal for interdisciplinary and project-based learning environments.
Spiral Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com