Experiential learning immerses you in hands-on activities that bridge theory and real-world practice, enhancing retention and skill development. This approach fosters critical thinking, adaptability, and deeper understanding by engaging multiple senses in the learning process. Discover the transformative benefits and practical applications of experiential learning in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
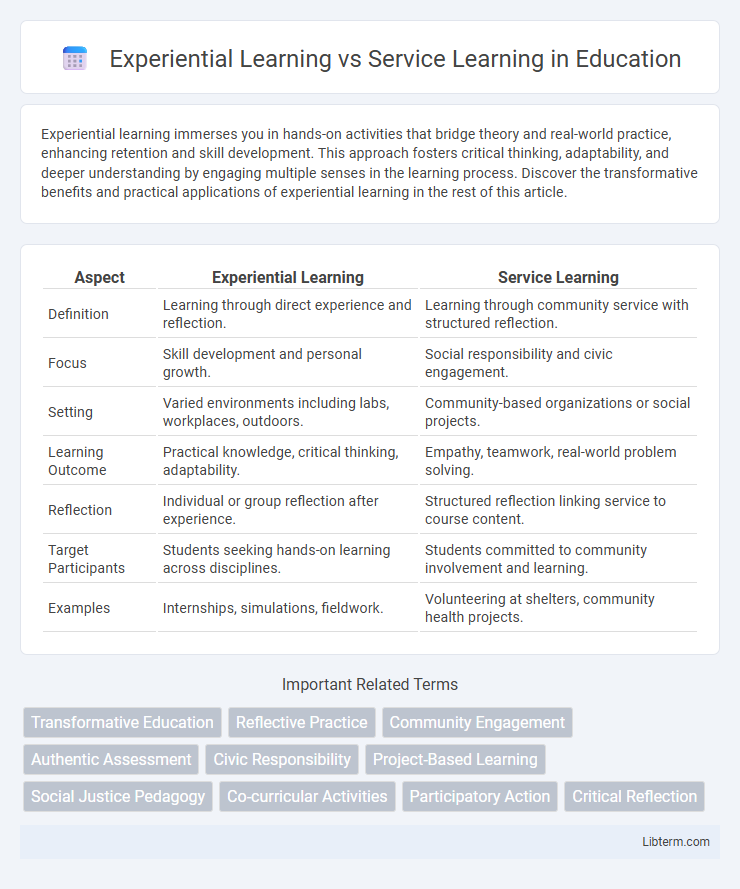
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Service Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection. | Learning through community service with structured reflection. |
| Focus | Skill development and personal growth. | Social responsibility and civic engagement. |
| Setting | Varied environments including labs, workplaces, outdoors. | Community-based organizations or social projects. |
| Learning Outcome | Practical knowledge, critical thinking, adaptability. | Empathy, teamwork, real-world problem solving. |
| Reflection | Individual or group reflection after experience. | Structured reflection linking service to course content. |
| Target Participants | Students seeking hands-on learning across disciplines. | Students committed to community involvement and learning. |
| Examples | Internships, simulations, fieldwork. | Volunteering at shelters, community health projects. |
Understanding Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes active engagement where learners acquire knowledge through direct experience and reflection, fostering deeper understanding and skill development. It integrates concrete experiences, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation in a cyclical process. This method enhances critical thinking and adaptability by encouraging learners to connect theory with real-world applications.
Defining Service Learning
Service learning integrates community service with structured reflection, enabling students to apply academic knowledge to real-world challenges while fostering civic responsibility. It differs from experiential learning by emphasizing reciprocal partnerships where both students and communities benefit. This pedagogical approach combines meaningful service tasks with critical thinking to deepen learning outcomes and social engagement.
Core Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning centers on active engagement, reflection, and the application of knowledge in real-world contexts, emphasizing concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation as core principles. Service learning integrates community service with academic instruction, promoting civic responsibility and reciprocal learning opportunities. Key to experiential learning is the cyclical process that deepens understanding through direct experience and critical reflection, fostering skills development and personal growth.
Core Principles of Service Learning
Service learning integrates meaningful community service with instruction and reflection to enrich the learning experience, emphasizing reciprocity, reflection, and social responsibility as core principles. The approach encourages students to apply academic skills to real-world challenges while fostering civic engagement and ethical development. Unlike experiential learning, which broadly focuses on learning through experience, service learning specifically centers on community impact and developing a sense of social justice.
Key Differences Between Experiential and Service Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, reflective experiences to enhance personal and professional growth, often within diverse settings, while service learning integrates community service with structured reflection to foster civic responsibility and social awareness. Experiential learning is broad, encompassing internships, simulations, and fieldwork, whereas service learning specifically aligns academic objectives with meaningful community engagement. The key difference lies in service learning's dual focus on academic goals and community impact, contrasting with experiential learning's primary focus on individual skill development through experience.
Educational Objectives Compared
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on activities that promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and personal reflection to deepen understanding of theoretical concepts. Service learning integrates community service with curriculum goals, fostering civic responsibility, social awareness, and practical application of academic knowledge. Both approaches aim to enhance student engagement and retention but differ in their focus on individual skill development versus community impact.
Impact on Student Engagement
Experiential learning and service learning both significantly enhance student engagement by providing hands-on, real-world experiences that deepen understanding and retention. Experiential learning emphasizes active participation and reflection in practical tasks, which boosts motivation and critical thinking skills. Service learning integrates community service with academic study, fostering a sense of social responsibility and increasing intrinsic engagement through meaningful, context-driven activities.
Academic and Community Outcomes
Experiential learning fosters academic success by immersing students in hands-on activities that enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills, leading to improved retention and application of knowledge. Service learning integrates community service with curriculum, promoting civic responsibility and real-world impact while reinforcing academic content through meaningful engagement. Both approaches strengthen student development and community benefits, but service learning places a unique emphasis on social awareness and community collaboration alongside academic growth.
Real-World Examples of Each Approach
Experiential learning involves hands-on activities such as internships at tech companies like Google, where students apply theoretical knowledge to solve actual business problems. Service learning integrates community service projects, exemplified by students partnering with local nonprofits to develop sustainable urban gardens, enhancing both civic responsibility and practical skills. Both approaches foster critical thinking and real-world problem-solving by immersing learners in authentic contexts related to their academic disciplines.
Choosing the Right Learning Strategy
Choosing the right learning strategy depends on the educational goals and context; experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, immersive activities that foster critical thinking and problem-solving skills, while service learning integrates community service with academic objectives to enhance social responsibility and real-world impact. Experiential learning is ideal for skill development and personal growth through active participation, whereas service learning is effective for cultivating civic engagement and empathy by addressing community needs. Evaluating the desired outcomes and learner engagement levels is essential for selecting between these complementary approaches.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com