Flipped classroom revolutionizes traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online, allowing students to learn at their own pace outside of class. This approach enhances in-class engagement through interactive activities and personalized support. Discover how implementing a flipped classroom can transform Your learning experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
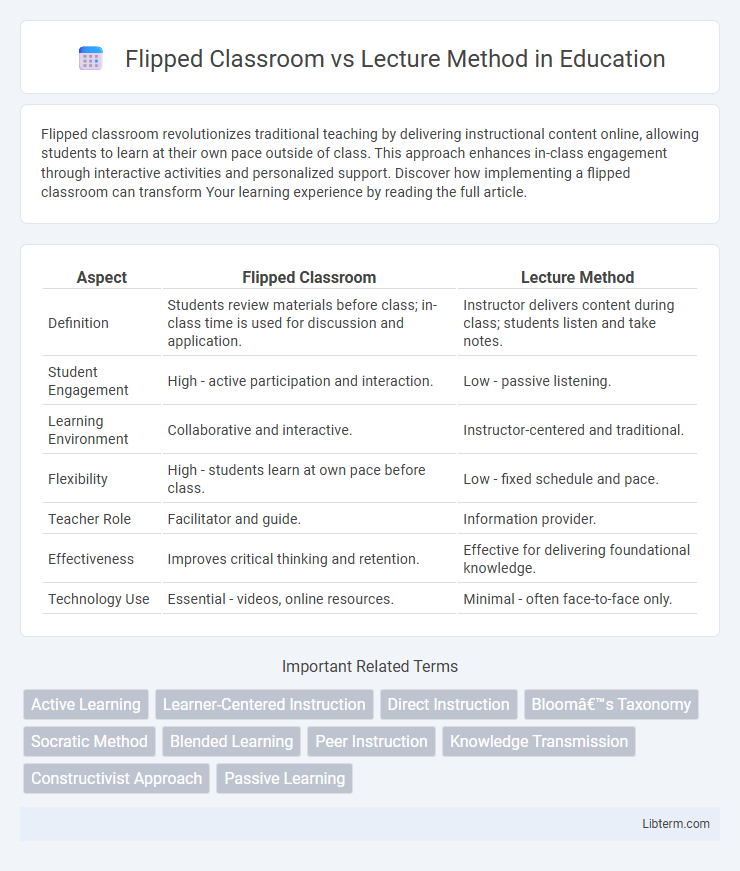
| Aspect | Flipped Classroom | Lecture Method |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students review materials before class; in-class time is used for discussion and application. | Instructor delivers content during class; students listen and take notes. |
| Student Engagement | High - active participation and interaction. | Low - passive listening. |
| Learning Environment | Collaborative and interactive. | Instructor-centered and traditional. |
| Flexibility | High - students learn at own pace before class. | Low - fixed schedule and pace. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and guide. | Information provider. |
| Effectiveness | Improves critical thinking and retention. | Effective for delivering foundational knowledge. |
| Technology Use | Essential - videos, online resources. | Minimal - often face-to-face only. |
Introduction to Flipped Classroom and Lecture Method
The flipped classroom approach reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content online outside of class, allowing interactive, hands-on activities during in-person sessions. In contrast, the lecture method primarily involves direct instruction where teachers present information verbally while students passively receive knowledge. Flipped classrooms promote active learning and student engagement, whereas lectures emphasize information transmission and note-taking.
Historical Overview of Teaching Methods
The lecture method, rooted in ancient Greek and Roman education, dominated traditional teaching for centuries with instructors delivering knowledge directly to passive students. In contrast, the flipped classroom model emerged in the early 21st century, leveraging digital technology to invert traditional pedagogy by assigning instructional content outside class and dedicating in-class time to interactive learning. This shift reflects a broader historical trend toward student-centered approaches that emphasize active participation and critical thinking over rote memorization.
Key Principles of the Lecture Method
The Lecture Method centers on direct instruction where the teacher delivers content verbally to a passive audience, emphasizing one-way communication and standardized delivery. It prioritizes the clear presentation of organized information, relying on repetition and note-taking to reinforce learning. This method often limits student interaction and immediate feedback, focusing instead on transmitting expert knowledge efficiently.
Core Concepts of the Flipped Classroom
The flipped classroom model emphasizes active learning by delivering instructional content outside of traditional class time, often through video lectures or digital resources, allowing in-class sessions to focus on collaborative activities and problem-solving. This approach promotes student engagement, deeper understanding, and personalized feedback, contrasting with the lecture method where passive listening predominates. Core concepts include pre-class preparation, interactive classroom experiences, and continuous formative assessment to enhance mastery and retention.
Student Engagement: Flipped Classroom vs Lecture
The Flipped Classroom model significantly enhances student engagement by promoting active learning through pre-class video lectures and interactive in-class activities. In contrast, the traditional Lecture Method often results in passive listening, reducing opportunities for student participation and immediate feedback. Research shows that flipped classrooms increase motivation and comprehension by encouraging collaboration and critical thinking during class time.
Impact on Learning Outcomes
The flipped classroom approach significantly enhances learning outcomes by promoting active student engagement and improving critical thinking skills through pre-class preparation and in-class collaborative activities. In contrast, the traditional lecture method often results in passive learning, leading to lower retention rates and reduced student motivation. Studies indicate that students in flipped classrooms achieve higher test scores and demonstrate deeper conceptual understanding compared to those in conventional lecture-based settings.
Teacher’s Role in Both Methods
In the flipped classroom model, the teacher acts as a facilitator who guides students through interactive discussions and personalized support, enhancing active learning and critical thinking. In contrast, the lecture method positions the teacher as the primary knowledge dispenser, focusing on delivering content directly to students with limited student engagement. Effective teaching in the flipped classroom requires adaptability and continuous assessment, while the lecture method emphasizes clear presentation and content coverage.
Challenges and Limitations
The flipped classroom faces challenges such as requiring students to have self-discipline and access to reliable technology, while teachers must invest significant time in creating pre-class materials. The traditional lecture method often limits student engagement and interaction, leading to passive learning and decreased retention. Both approaches struggle with addressing diverse learning styles and ensuring consistent student participation, impacting overall educational effectiveness.
Technological Requirements and Accessibility
The Flipped Classroom demands reliable internet access and digital devices to stream or download lecture materials, ensuring students can engage with content anytime. In contrast, the Lecture Method primarily relies on physical classroom presence and minimal technology, such as projectors or audio systems, making it accessible in low-tech environments. While the Flipped Classroom leverages adaptive learning platforms for personalized education, its effectiveness is limited by technological disparities among students.
Which Method is Best: Conclusion and Recommendations
The flipped classroom method enhances student engagement and improves knowledge retention compared to the traditional lecture method by promoting active learning and critical thinking. Research shows that students in flipped classrooms achieve higher academic performance and demonstrate better problem-solving skills. It is recommended to adopt the flipped classroom approach in diverse educational settings to foster deeper learning and adapt to varied learning styles.
Flipped Classroom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com